Who cares about running DOOM on a pregnancy test?
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
Your PC could soon play old Xbox and Xbox 360 games officially
Microsoft may soon allow PC players to enjoy original Xbox and Xbox 360 games thanks to an official emulator for Windows. While the talk of the town is the upcoming Project Helix, a new report suggests that we might get the classic Xbox experience before the next-gen Xbox platform.
It seems like the company is exploring emulation as a way to improve backwards compatibility across platforms, especially as the company continues to blur the lines between Xbox consoles and Windows PCs.
Over the last decade or so, Microsoft has been slowly pushing toward a unified gaming ecosystem that spans Windows PCs, handhelds, and Xbox consoles. And it seems that emulation could be a new part of this strategy, particularly for games that aren’t easily accessible on modern platforms.
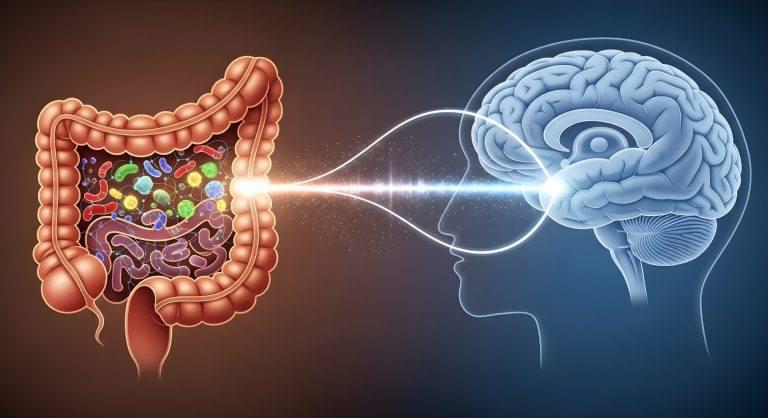
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
The sight of a delectable plate of lasagna or the aroma of a holiday ham are sure to get hungry bellies rumbling in anticipation of a feast to come. But although we’ve all experienced the sensation of “eating” with our eyes and noses before food meets mouth, much less is known about the information superhighway, known as the vagus nerve, that sends signals in the opposite direction — from your gut straight to your brain.
These signals relay more than just what you’ve eaten and when you are full. A new study in mice from researchers at Stanford Medicine and the Palo Alto, California-based Arc Institute has identified a critical link between the bacteria that live in your gut and the cognitive decline that often occurs with aging.
“Although memory loss is common with age, it affects people differently and at different ages,” said Christoph Thaiss, PhD, assistant professor of pathology. “We wanted to understand why some very old people remain cognitively sharp while other people see significant declines beginning in their 50s or 60s. What we learned is that the timeline of memory decline is not hardwired; it’s actively modulated in the body, and the gastrointestinal tract is a critical regulator of this process.”
Aging causes changes in gut bacteria in mice, which hampers communication between the intestines and the brain. Restoring this connection helped old mice form memories as well as young animals.

Circulating Markers of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps for Long‐Term Prognosis in Patients With Acute Chest Pain
Whole-brain cell mapping using AI
The researchers developed a highly multiplexed whole-mount staining technique, utilizing the repeated application of fluorescence in situ hybridization.
The technique called mFISH3D for multiplexed mRNA staining in whole mouse organs and human tissue.
The technique helps to visualize 10 types of mRNAs in an intact mouse brain.
This workflow provides a robust approach to studying selective cell vulnerability in disease. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission https://sciencemission.com/Artificial-intelligence-driven-wh…ll-mapping
Murakami et al. developed mFISH3D for multiplexed mRNA staining in whole-mouse organs and human tissue. Analysis of the stained mouse brains using the AI-driven ZenCell platform reveals unique cell populations activated by pharmacological perturbation. This workflow provides a robust approach to studying selective cell vulnerability in disease.
Pollen-replacing feed strengthens honey bee colonies, long-term study confirms
A man-made food source provided honey bees a nutritious diet at a commercial scale over the course of two winter seasons, according to a new study led by Washington State University researchers. The study, published in the journal Insects, looked at the new feed as used by five commercial beekeepers in California and Idaho from fall 2022 to spring 2024. This study is a follow-up to an initial paper describing the bee feed.
The nutritionally complete feed, which resembles an oversized, very thin granola bar, was developed by APIX Biosciences, a biotech company based in Belgium with a U.S. subsidiary. The company worked with WSU’s Honey Bee Program to test the nutritional supplement.
“The first paper was a trial during the spring and summer pollination season to make sure the feed worked in real-world field conditions,” said Brandon Hopkins, WSU’s P.F. Thurber Endowed Distinguished Professor of Pollinator Ecology and a corresponding author on the paper. “This study happened during the other half of the year when beekeepers tend to see the biggest losses and depend the most on supplemental feeding. It was also done on a significantly larger scale than our previous study.”
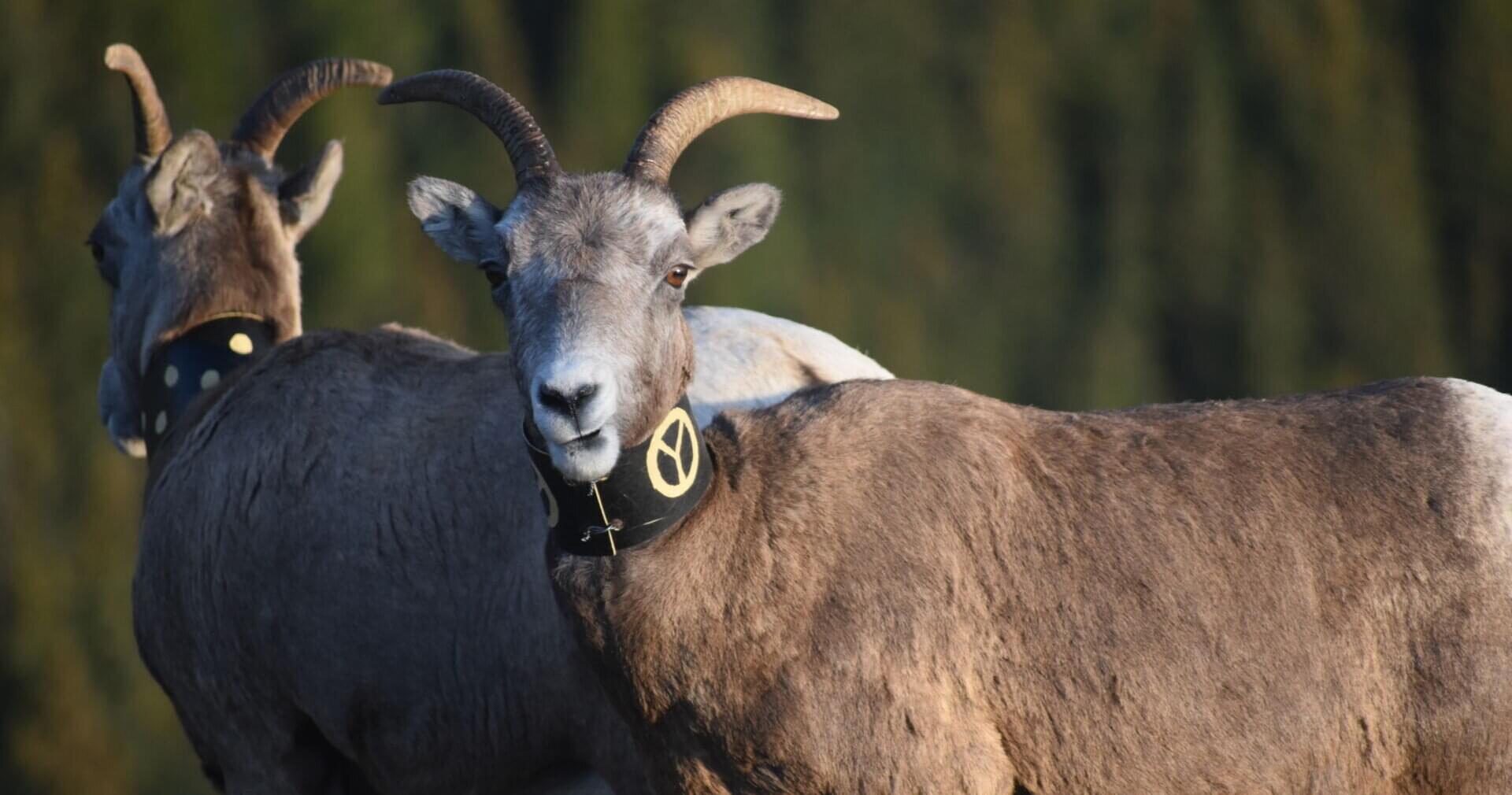



New DNA tools outperform traditional methods for detecting genetic risk in wildlife
Wildlife populations that become small and isolated, often due to habitat loss, inevitably experience inbreeding which can lead to the loss of fitness and eventual extinction. One solution is to perform a genetic rescue: a management intervention where new blood is brought in by introducing outsiders to a population to reduce inbreeding and restore diversity. But how do researchers know the inbreeding problem has been solved?
A new long-term study from Western, led by biology professor and chair David Coltman, shows DNA-based tools detected changes in inbreeding more accurately than traditional pedigree methods in a wild population of bighorn sheep that was recently genetically rescued. The study was published in the journal Evolutionary Applications.
Pedigree approaches estimate genetic health from family history, whereas genomic approaches directly analyze DNA.

A 100-solar-mass black hole merger ripples spacetime, and may flash in gamma rays
An international team from China and Italy has reported a possible cosmic encore to the landmark 2017 multi-messenger discovery. In November 2024, the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA observatories detected gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger, designated S241125n. Remarkably, just seconds later, satellites recorded a short gamma-ray burst (GRB) from the same region of the sky.
Typically, binary black hole mergers are not expected to produce electromagnetic counterparts. S241125n could be a very rare gravitational-wave event that has been linked to a GRB across multiple wavelengths, extending multi-messenger astronomy into a new regime. Although the association is not yet definitive and will require further follow-up, the probability of a chance coincidence appears low, making the result statistically intriguing while warranting caution.