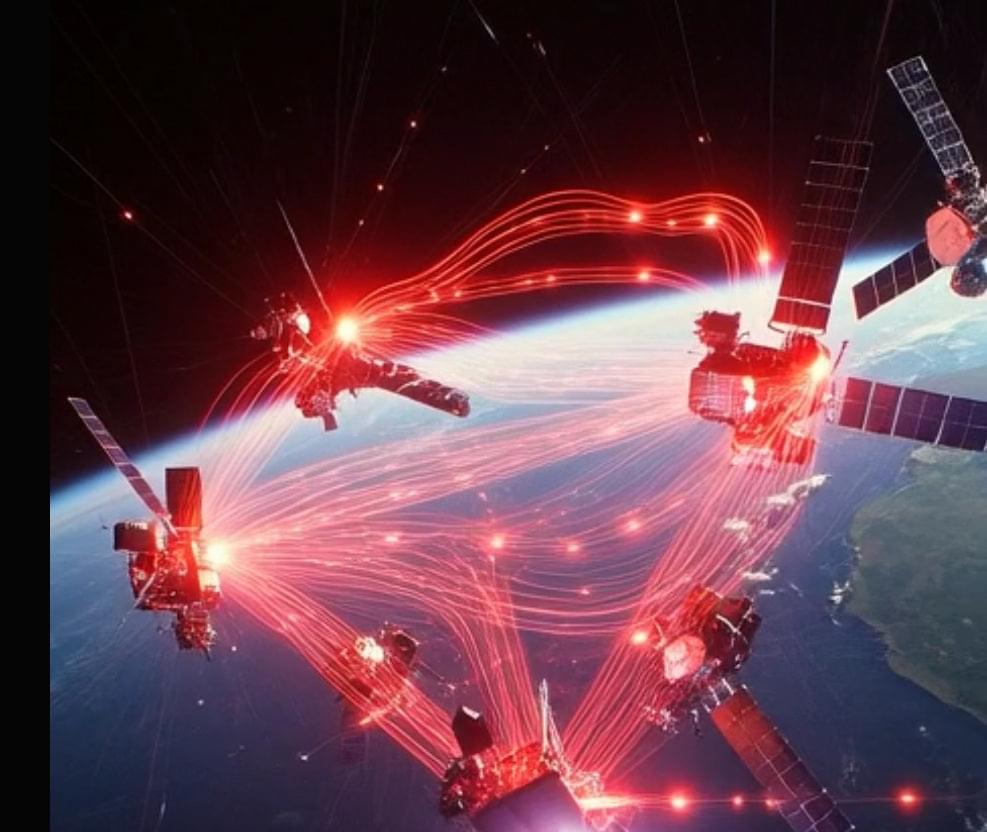
In a bold fusion of SpaceX’s satellite expertise and Tesla’s AI prowess, the Starthink Synthetic Brain emerges as a revolutionary orbital data center.
Proposed in Digital Habitats February 2026 document, this next-gen satellite leverages the Starlink V3 platform to create a distributed synthetic intelligence wrapping the planet.
Following SpaceX’s FCC filing for up to one million orbital data centers and its acquisition of xAI, Starthink signals humanity’s leap toward a Kardashev II civilization.
As Elon Musk noted in February 2026, ]
“In 36 months, but probably closer to 30, the most economically compelling place to put AI will be space.”
## The Biological Analogy.
Starthink draws from neuroscience: * Neural Cluster: A single Tesla AI5 chip, processing AI inference at ~250W, like a neuron group. * Synthetic Brain: One Starthink satellite, a 2.5-tonne self-contained node with 500 neural clusters, solar power, storage, and comms. * Planetary Neocortex: One million interconnected Brains forming a global mesh intelligence, linked by laser and microwave “synapses.”