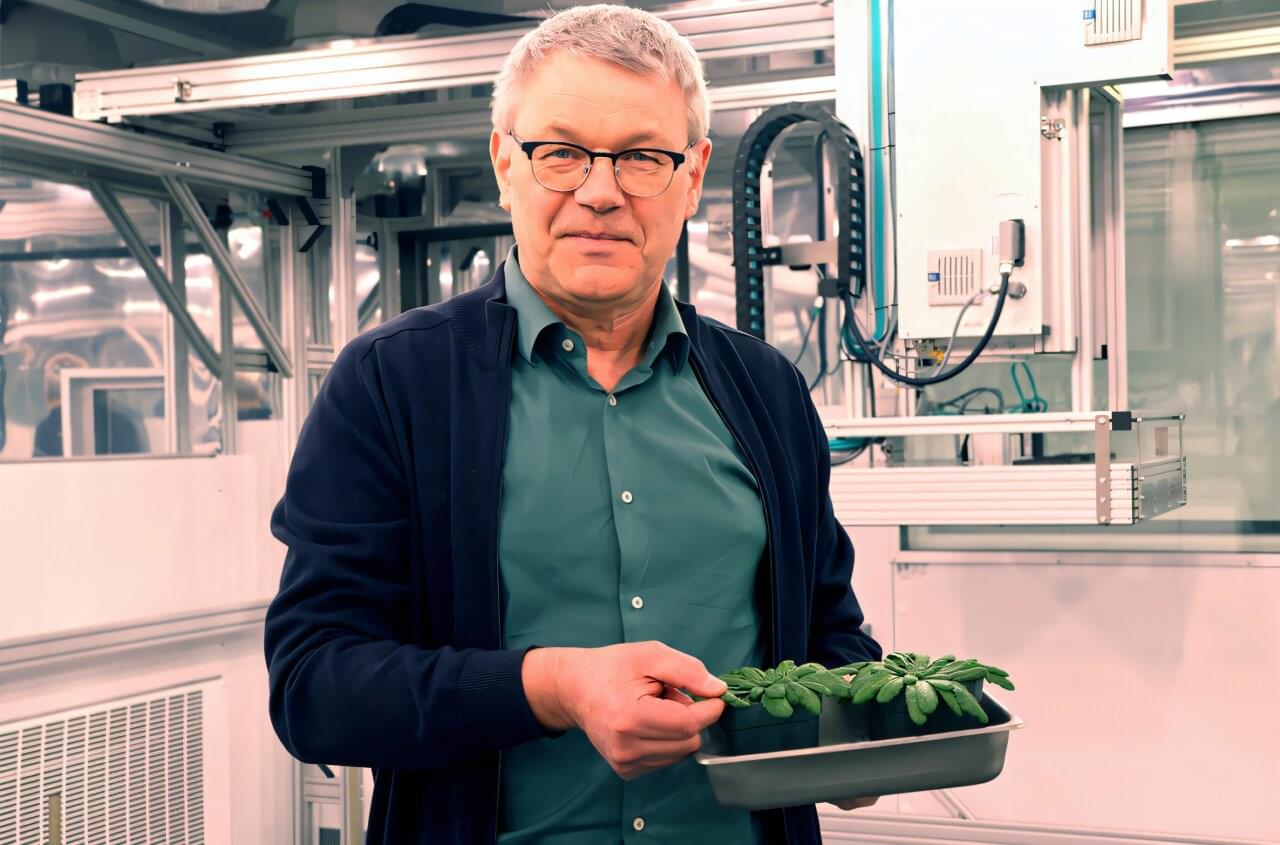
Dr. Sara Santos: “The research is about understanding the viability of growing crops on the moon. How do we transform this regolith into soil? What kinds of natural mechanisms can cause this conversion?” [ https://www.labroots.com/trending/space/30294/lunar-regolith…hickpeas-2](https://www.labroots.com/trending/space/30294/lunar-regolith…hickpeas-2)
How will astronauts grow food during long-term missions to the Moon? This is what a recent study published in Scientific Reports hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated the prospect of growing food on the Moon. This study has the potential to help scientists, mission planners, engineers, and astronauts develop new methods for growing food on the Moon, which could help advance such techniques when humans go to Mars.
For the study, the researchers grew chickpeas using simulated lunar regolith (often mistakenly called “soil”) and fungi, with the latter being used to test plant stress levels, decrease toxins, and enhance the mixture of regolith simulant and fungi. The team tested a variety of mixtures, including 25 to 100 percent regolith simulant and with and without the fungi. The goal of the study was to ascertain the plausibility of growing food on the Moon under climate-controlled conditions using lunar regolith and Earth-based products. In the end, the researchers found that the most promising mixture was 75 percent regolith simulant with fungi.