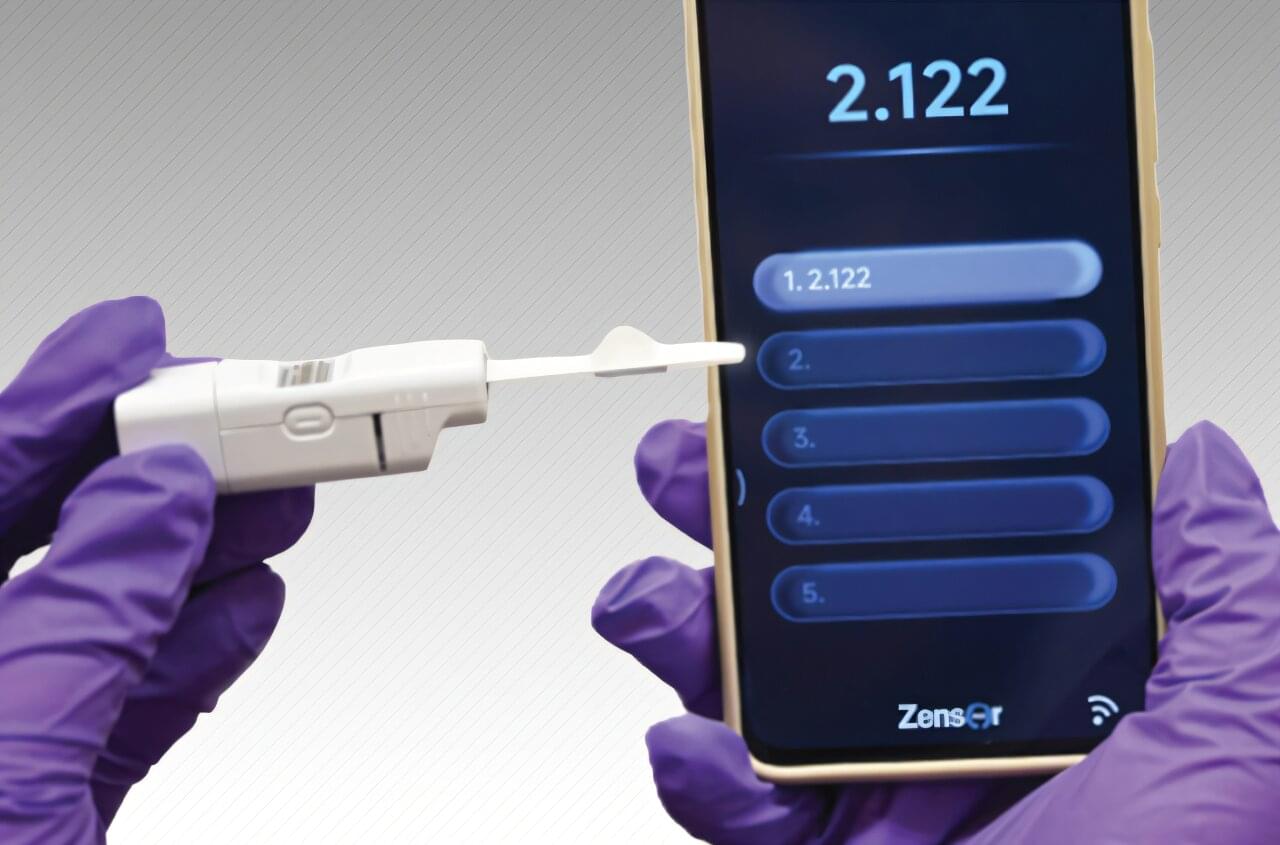
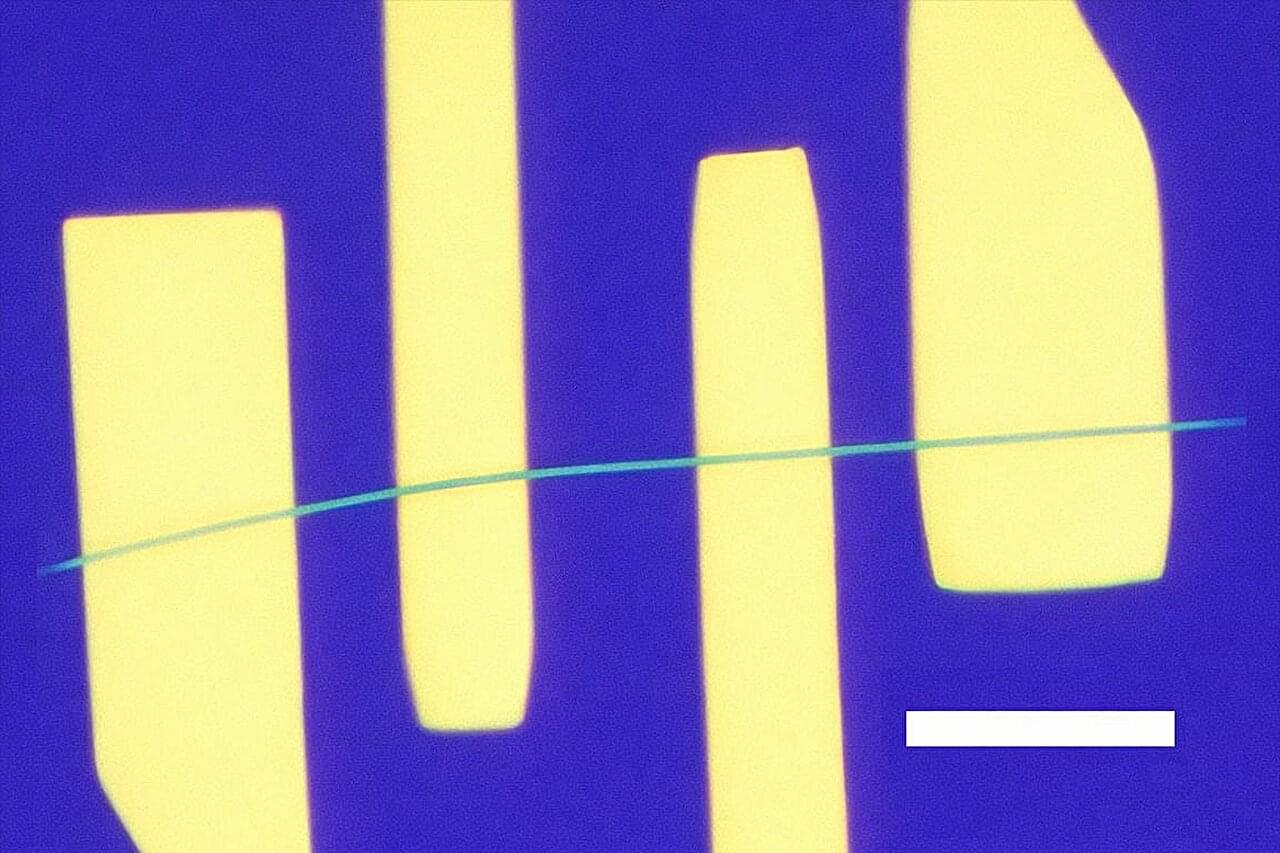A wearable biosensor developed by Washington State University researchers could improve wireless glucose monitoring for people with diabetes, making it more cost-effective, accurate, and less invasive than current models. The WSU researchers have developed a wearable and user-friendly sensor that uses microneedles and sensors to measure sugar in the fluid around cells, providing an alternative to continuous glucose monitoring systems. Reporting in the journal The Analyst, the researchers were able to accurately detect sugar levels and wirelessly transmit the information to a smartphone in real time.
“We were able to amplify the signal through our new single-atom catalyst and make sensors that are smaller, smarter, and more sensitive,” said Annie Du, research professor in WSU’s College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences and co-corresponding author on the work. “This is the future and provides a foundation for being able to detect other disease biomarkers in the body.”
Measuring glucose levels is important for diabetes, helping to keep patients healthy and preventing complications. Continuous glucose monitors on the market require the use of small needles to insert the monitor, and people can get skin irritation or rashes from the chemical processes that are done under the skin. Furthermore, they’re not always sensitive enough.