Harvest-now-decrypt-later threats push organizations toward hybrid cryptography and ML-KEM as quantum risks grow. Learn strategies in a webinar.


Bitwarden announced support for logging into Windows 11 devices using passkeys stored in the manager’s vault, enabling phishing-resistant authentication.
The new feature is available for all plans, including the free tier, and allows logging into Windows by selecting the security key option and scanning a QR code with a mobile device to confirm access to the passkey stored in the Bitwarden encrypted vault.
Bitwarden is an open-source password and secrets manager that can store account passwords, passkeys, API keys, credit card details, identity data, and private notes.

By Chuck Brooks and Bill Bowers.
Every time you send a text, pay for groceries with your phone, or use your health site, you are relying on encryption. It’s an invisible shield that protects your data from prying eyes. Encryption is more than just a technological protection; it is the basis for digital trust.
Encryption is more than just safeguarding data; it is also about protecting people. It helps ensure privacy by protecting persons from spying and exploitation. And it is widely adopted to help ensure digital transaction security. For National Security it serves to protect key infrastructure and government communications. And it has a human rights function by providing citizens with peace of mind by ensuring the safety of their personal information. In places where surveillance is widespread, encryption can even defend free expression and opposition. It is a human right in this digital age.
In my book Inside Cyber: How AI, 5G, IoT, and Quantum Computing Will Transform Privacy and Security, I referred to encryption as the “linchpin of privacy and commerce in a connected society.” Without it, the digital economy would crumble under the strain of criminality, fraud, and spying.
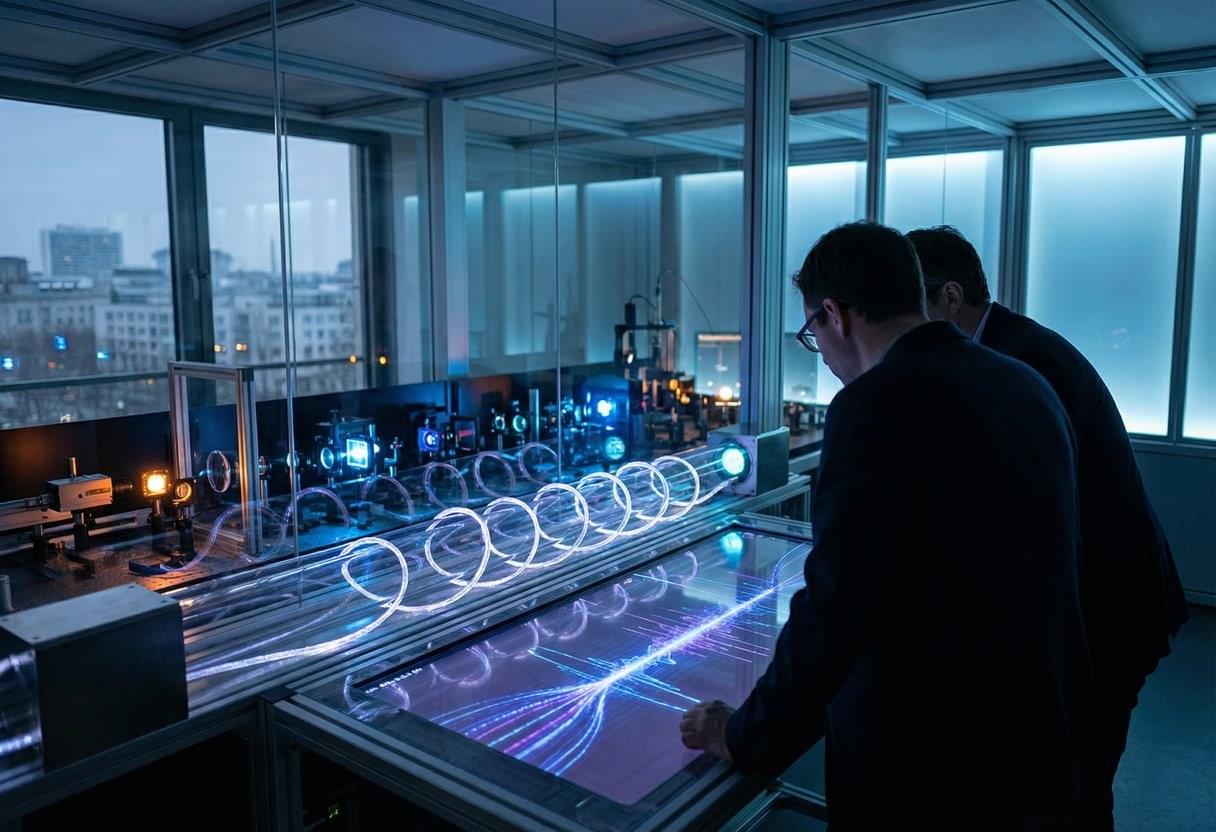

Something once thought too delicate for real cities just survived them. A quiet test in Germany hints that the next internet may be both unbreakable and already under our feet.
On a 30-kilometer loop of commercial fiber in Berlin, researchers just teleported data while ordinary internet traffic flowed on the same line without a hiccup. The feat, executed by T-Labs with Qunnect’s Carina platform, kept delicate quantum states steady against city vibrations and temperature swings, hitting 95 percent fidelity in real time. It shows that today’s networks can carry tomorrow’s quantum links, with stakes that range from unbreakable cryptography to connected quantum computers. For Deutsche Telekom’s Abdu Mudesir, it also signals a path to European technological sovereignty as the system scales to longer distances and more nodes.
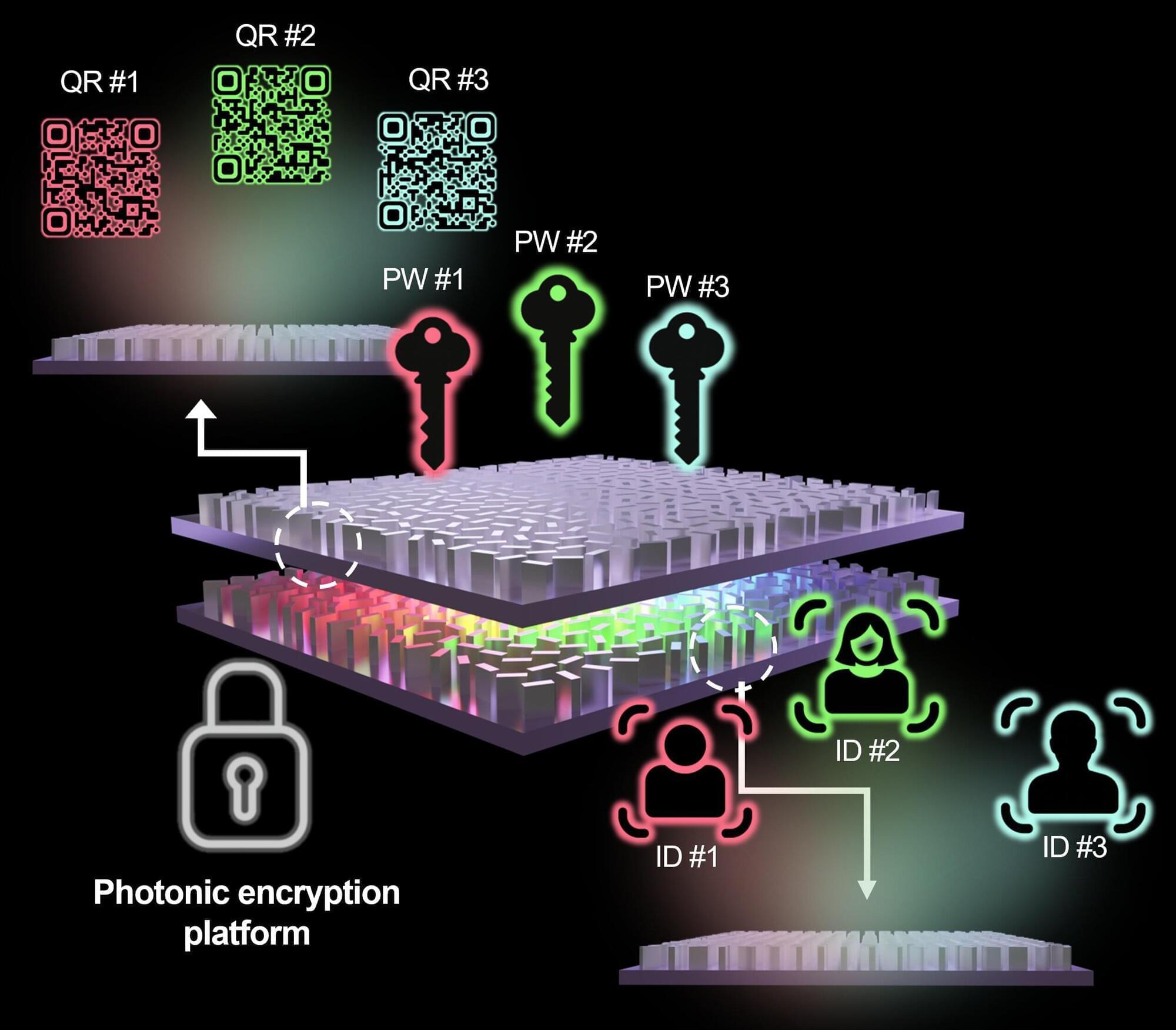
A research team led by Professor Junsuk Rho at POSTECH (Pohang University of Science and Technology) has developed a secure hologram platform that operates solely based on the wavelength of light and the spacing between metasurface layers. The technology makes hacking and counterfeiting virtually impossible, and is expected to be widely adopted for security cards, anticounterfeiting, and military communications. The paper is published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
With a growing number of hacking incidents and data breaches, the limitations of digital security are becoming increasingly evident. No matter how sophisticated an encryption scheme is, as long as it exists as code, it is difficult to completely eliminate the risk of intrusion. Motivated by this challenge, the team proposed a new approach that uses the physical conditions of light itself as a security key.
At the core of this innovation is the “metasurface,” an ultrathin optical device that arranges microscopic structures to control light. By illuminating a metasurface, a holographic image can be reconstructed in free space. However, conventional holograms have typically been limited in that a single device could store only one piece of information.


#Quantum #CyberSecurity
Quantum computing is not merely a frontier of innovation; it is a countdown. Q-Day is the pivotal moment when scalable quantum computers undermine the cryptographic underpinnings of our digital realm. It is approaching more rapidly than many comprehend.
For corporations and governmental entities reliant on outdated encryption methods, Q-Day will not herald a smooth transition; it may signify a digital catastrophe.
Comprehending Q-Day: The Quantum Reckoning
Q-Day arrives when quantum machines using Shor’s algorithm can dismantle public-key encryption within minutes—a task that classical supercomputers would require billions of years to accomplish.
Elon Musk Announces MAJOR Company Changes as XAI/SpaceX ## Elon Musk is announcing significant changes and advancements across his companies, primarily focused on developing and integrating artificial intelligence (AI) to drive innovation, productivity, and growth ## ## Questions to inspire discussion.
Product Development & Market Position.
🚀 Q: How fast did xAI achieve market leadership compared to competitors?
A: xAI reached number one in voice, image, video generation, and forecasting with the Grok 4.20 model in just 2.5 years, outpacing competitors who are 5–20 years old with larger teams and more resources.
📱 Q: What scale did xAI’s everything app reach in one year?
A: In one year, xAI went from nothing to 2M Teslas using Grok, deployed a Grok voice agent API, and built an everything app handling legal questions, slide decks, and puzzles.

A Chinese research team has reported a pair of advances that could remove two of the biggest technical barriers to building large-scale quantum communication networks, including the generation of ultra-secure encryption keys over 11 kilometers of optical fiber and the validation of the approach at distances up to 100 kilometers, according to China Daily, a state-associated news service.
Researchers from the University of Science and Technology of China said they have demonstrated, for the first time, a scalable core component of a quantum repeater — a long-sought technology needed to extend quantum communication across long distances — while also setting new records for ultra-secure quantum key distribution over fiber networks.
The findings were published in Nature and Science, underscoring their significance within the international research community. Noted Chinese physicist Pan Jianwei led the work.