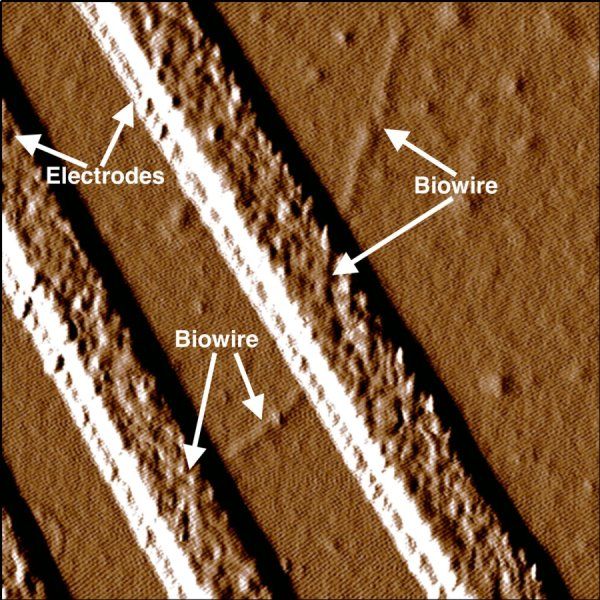
Biowire.
Researchers led by microbiologist Derek Lovely say the wires, which rival the thinnest wires known to man, are produced from renewable, inexpensive feedstocks and avoid the harsh chemical processes typically used to produce nanoelectronic materials.
Lovley says, “New sources of electronic materials are needed to meet the increasing demand for making smaller, more powerful electronic devices in a sustainable way.” The ability to mass-produce such thin conductive wires with this sustainable technology has many potential applications in electronic devices, functioning not only as wires, but also transistors and capacitors. Proposed applications include biocompatible sensors, computing devices, and as components of solar panels.
This advance began a decade ago, when Lovley and colleagues discovered that Geobacter, a common soil microorganism, could produce “microbial nanowires,” electrically conductive protein filaments that help the microbe grow on the iron minerals abundant in soil. These microbial nanowires were conductive enough to meet the bacterium’s needs, but their conductivity was well below the conductivities of organic wires that chemists could synthesize.