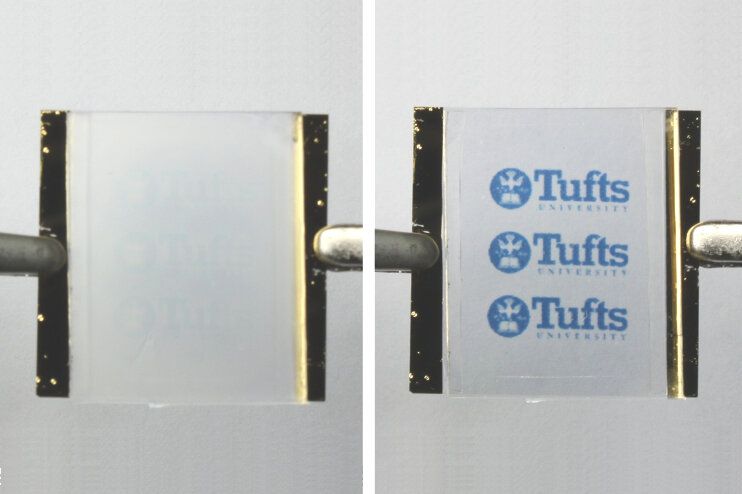
Researchers at Tufts University School of Engineering have developed silk materials that can wrinkle into highly detailed patterns—including words, textures and images as intricate as a QR code or a fingerprint. The patterns take about one second to form, are stable, but can be erased by flooding the surface of the silk with vapor, allowing the researchers to “reverse” the printing and start again. In an article published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the researchers demonstrate examples of the silk wrinkle patterns, and envision a wide range of potential applications for optical electronic devices.
The smart textile takes advantage of the natural ability of silk fiber proteins—fibroin—to undergo a change of conformation in response to external conditions, including exposure to water vapor, methanol vapor and UV radiation. Water and methanol vapor, for example, can soak into the fibers and interfere with hydrogen bond cross links in the silk fibroin, causing it to partially ‘unravel’ and release tension in the fiber. Taking advantage of this property, the researchers fabricated a silk surface from dissolved fibroin by depositing it onto a thin plastic membrane (PDMS). After a cycle of heating and cooling, the silk surface of the silk/PDMS bilayer folds into nanotextured wrinkles due to the different mechanical properties of the layers.
Exposing any part of that wrinkled surface to water or methanol vapor causes the fibers to relax and the wrinkles to flatten. The smooth surface transmits more than 80% of light, while the wrinkled surface only allows 20% or less through, creating a visible contrast and the perception of a printed pattern. The surface can be selectively exposed to vapor using a patterned mask, resulting in a matched pattern in the textured silk. Patterns may also be created by depositing water using inkjet printing. The resolution of this printing method is determined by the resolution of the mask itself, or the nozzle diameter of the inkjet printer.