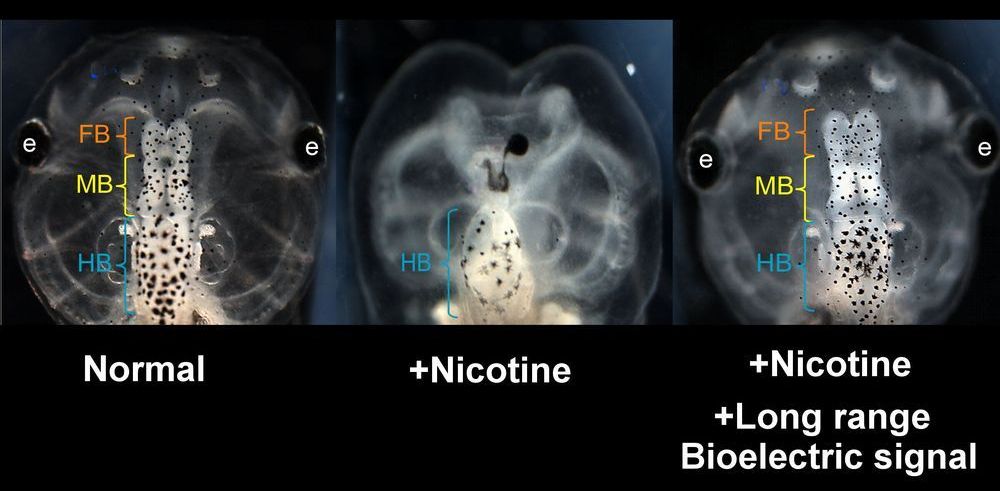
Researchers led by biologists at Tufts University have discovered that the brains of developing frog embryos damaged by nicotine exposure can be repaired by treatment with certain drugs called “ionoceuticals” that drive the recovery of bioelectric patterns in the embryo, followed by repair of normal anatomy, gene expression and brain function in the growing tadpole. The research, published today in Frontiers in Neuroscience, introduces intervention strategies based on restoring the bioelectric “blueprint” for embryonic development, which the researchers suggest could provide a roadmap for the exploration of therapeutic drugs to help repair birth defects.