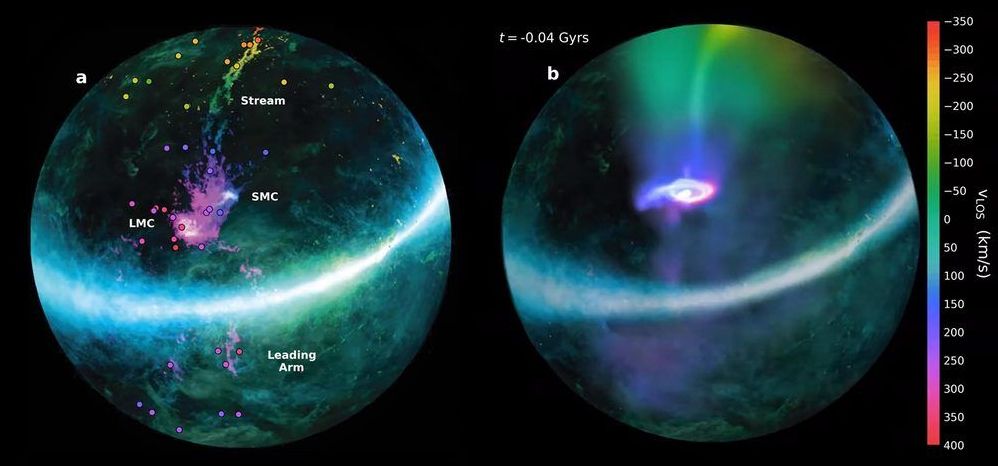
The Milky Way is not alone in its neighborhood. It has captured smaller galaxies in its orbit, and the two largest are known as the Small and Large Magellanic Clouds, visible as twin dusty smears in the Southern Hemisphere.
As the Magellanic Clouds began circling the Milky Way billions of years ago, an enormous stream of gas known as the Magellanic Stream was ripped from them. The stream now stretches across more than half of the night sky. But astronomers have been at a loss to explain how the stream became as massive at it is, over a billion times the mass of the sun.
Now, astronomers at the University of Wisconsin-Madison and their colleagues have discovered that a halo of warm gas surrounding the Magellanic Clouds likely acts as a protective cocoon, shielding the dwarf galaxies from the Milky Way’s own halo and contributing most of the Magellanic Stream’s mass. As the smaller galaxies entered the sphere of the Milky Way’s influence, parts of this halo were stretched and dispersed to form the Magellanic Stream. The researchers published their findings today (September 9, 2020) in the journal Nature.