Telecommunications have reshaped many aspects of our lives over the past few decades by providing incredibly convenient ways to share and access information. One of the most important enablers for this transformation has been the adoption and improvement of broadband technologies, which cram enormous amounts of data over wide frequency bands to achieve unprecedented transfer speeds. Today, most large cities have fiber optics-based networks that distribute high-speed internet directly to every home.
Unfortunately, it is not always feasible to deploy fiber optic links to remote locations and rural areas, due to the associated costs and civil engineering work required. Such places could benefit from a different approach to optical broadband communications: free-space optics. The main idea in free-space optical (FSO) communications is to set up aligned transmitter–receiver pairs where needed and use air as the medium to carry the signals.
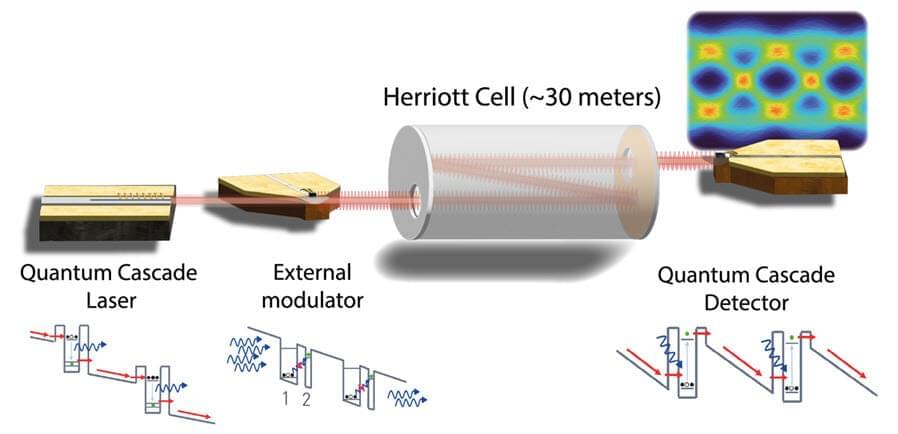
While there are still many challenges to address in FSO systems (such as low energy efficiency, impact of weather, and high background noise), scientists worldwide are continuously trying out new ways of solving these issues and achieving higher data rates.