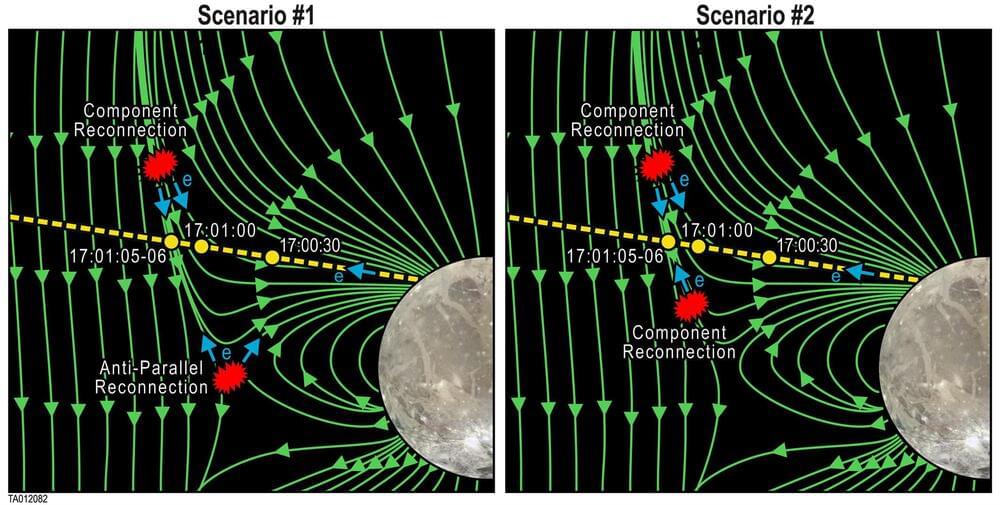
In June 2021, NASA’s Juno spacecraft flew close to Ganymede, Jupiter’s largest moon, observing evidence of magnetic reconnection. A team led by Southwest Research Institute used Juno data to examine the electron and ion particles and magnetic fields as the magnetic field lines of Jupiter and Ganymede merged, snapped and reoriented, heating and accelerating the charged particles in the region.
“Ganymede is the only moon in our solar system with its own magnetic field,” said Juno Principal Investigator Dr. Scott Bolton of SwRI. “The snapping and reconnecting of Ganymede’s magnetic field lines with Jupiter’s creates the magnetospheric fireworks.”
Magnetic reconnection is an explosive physical process that converts stored magnetic energy into kinetic energy and heat. Ganymede’s mini-magnetosphere interacts with Jupiter’s massive magnetosphere, in the magnetopause, the boundary between the two regions.