In modern electronics, a large amount of heat is produced as waste during usage—this is why devices such as laptops and mobile phones become warm during use, and require cooling solutions. In the last decade, the concept of managing this heat using electricity has been tested, leading to the development of electrochemical thermal transistors—devices that can be used to control heat flow with electrical signals.
Currently, liquid-state thermal transistors are in use, but have critical limitations: chiefly, any leakage causes the device to stop working.
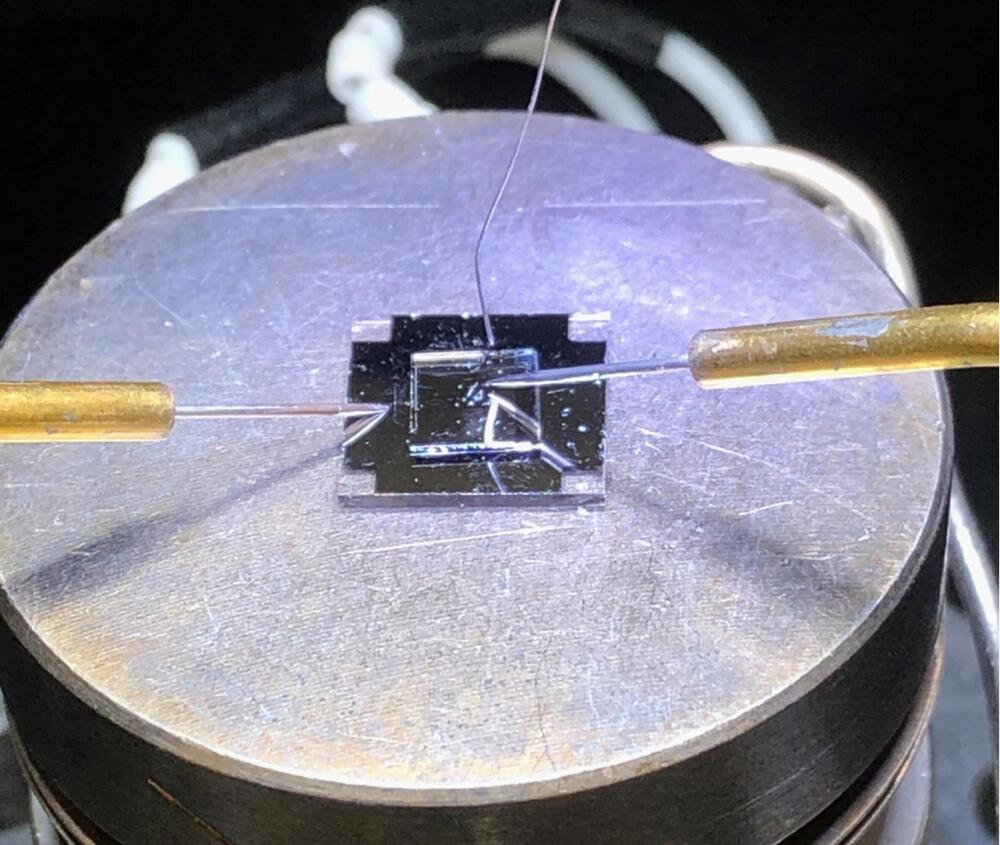
A research team at Hokkaido University lead by Professor Hiromichi Ohta at the Research Institute for Electronic science has developed the first solid-state electrochemical thermal transistor. Their invention, described in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, is much more stable than and just as effective as current liquid-state thermal transistors.