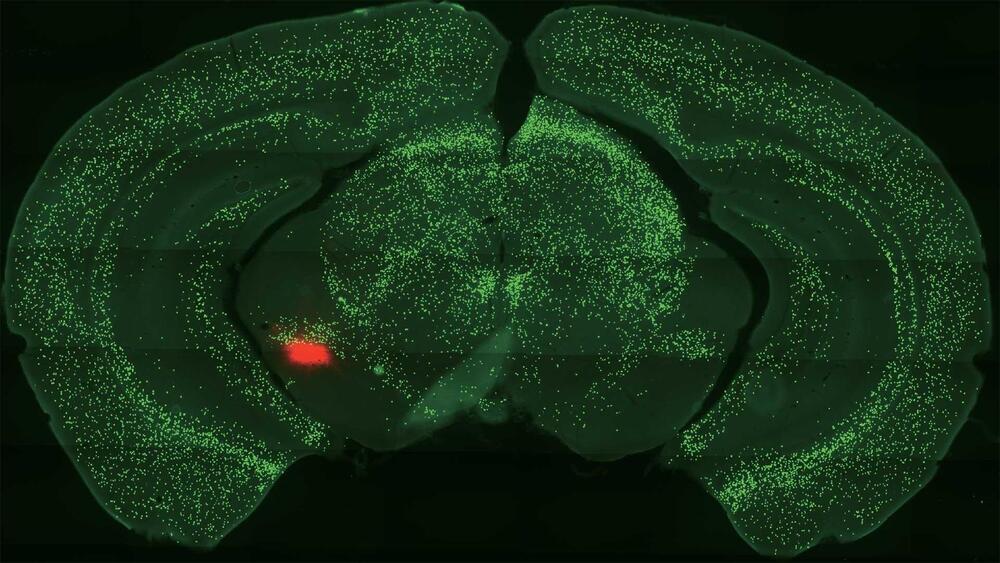
Deep within our brain’s temporal lobes, two almond-shaped cell masses help keep us alive. This tiny region, called the amygdala, assists with a variety of brain activities. It helps us learn and remember. It triggers our fight-or-flight response. It even promotes the release of a feel-good chemical called dopamine.
Scientists have learned all this by studying the amygdala over hundreds of years. But we still haven’t reached a full understanding of how these processes work.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory neuroscientist Bo Li has brought us several important steps closer. His lab recently made a series of discoveries that show how neurons called somatostatin-expressing (Sst+) central amygdala (CeA) neurons help us learn about threats and rewards. He also demonstrated how these neurons relate to dopamine. The discoveries could lead to future treatments for anxiety or drug addiction.