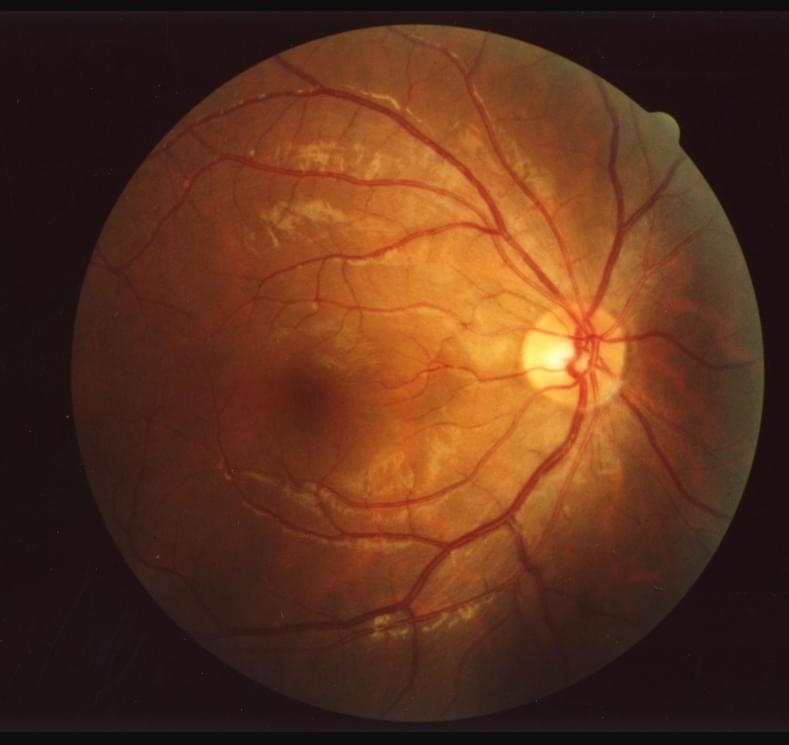
A team of biomedical researchers has developed a non-invasive, more accurate, and inexpensive “aging clock” for tracking and slowing human aging by examining retinal images and using trained deep-learning models of the eye’s fundus (the deepest area of the eye), using a new “eyeAge” system.
The researchers are affiliated with Buck Institute for Research on Aging, Google Research, Google Health, Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education, and Research (India), and University of California, San Francisco.
Tracking eye changes that accompany aging and age-related diseases: the eyeAge system.