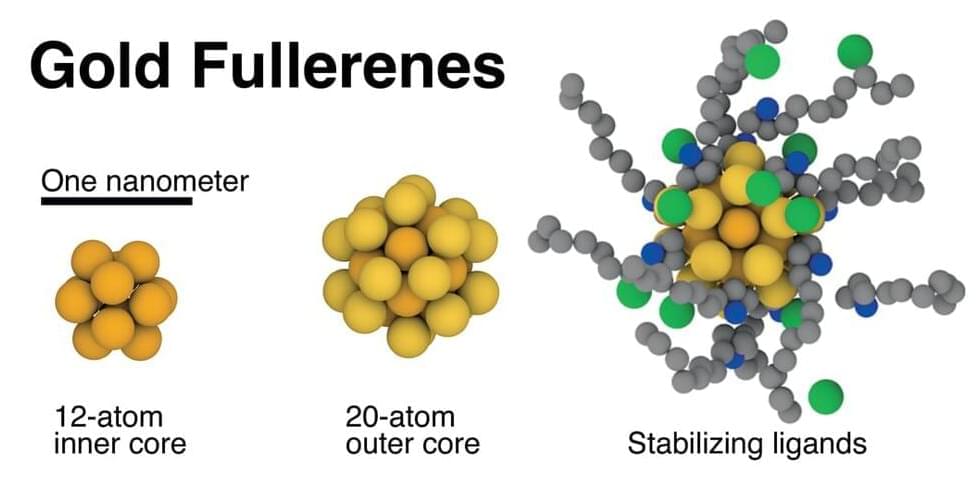
Rice University chemists have discovered that tiny gold “seed” particles, a key ingredient in one of the most common nanoparticle recipes, are one and the same as gold buckyballs, 32-atom spherical molecules that are cousins of the carbon buckyballs discovered at Rice in 1985.
Carbon buckyballs are hollow 60-atom molecules that were co-discovered and named by the late Rice chemist Richard Smalley. He dubbed them “buckminsterfullerenes” because their atomic structure reminded him of architect Buckminster Fuller’s geodesic domes, and the “fullerene” family has grown to include dozens of hollow molecules.
In 2019, Rice chemists Matthew Jones and Liang Qiao discovered that golden fullerenes are the gold “seed” particles chemists have long used to make gold nanoparticles. The find came just a few months after the first reported synthesis of gold buckyballs, and it revealed chemists had unknowingly been using the golden molecules for decades.