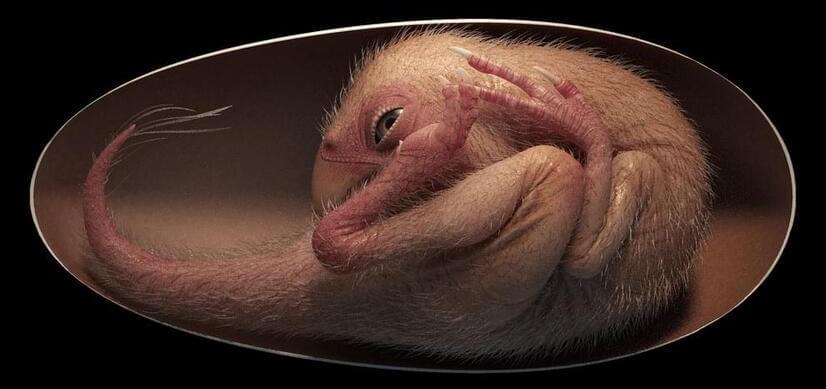
An incredibly rare, fully articulated dinosaur embryo has been found inside a fossilized egg that had been collecting dust for over a decade in the storage room of a museum in China. Thought to be between 66 and 72 million years old, the unborn specimen reveals an incredible link between dinosaurs and modern birds.
Belonging to a group of feathered, toothless theropods known as oviraptorosaurs, the unhatched creature is estimated to be about 27 centimeters (10.6 inches) long, and marks the first discovery of a dinosaur embryo displaying a posture that is typical of present-day bird embryos. Shortly before hatching, modern birds engage in a series of maneuvers known as tucking, which involves curving the body and bringing the head down under the wing, yet the evolutionary origins of this behavior had until now remained unknown.
Reporting their discovery in a 2021 paper, the study authors explain that their specimen – nicknamed Baby Yingliang – was found with its head “ventral to the body, with the feet on either side, and the back curled along the blunt pole of the egg.” Such a posture, they say, is “previously unrecognized in a non-avian dinosaur, but reminiscent of a late-stage modern bird embryo.”