Everyone has BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, but mutations in these genes—which can be inherited—increase the risk of breast and ovarian cancer.
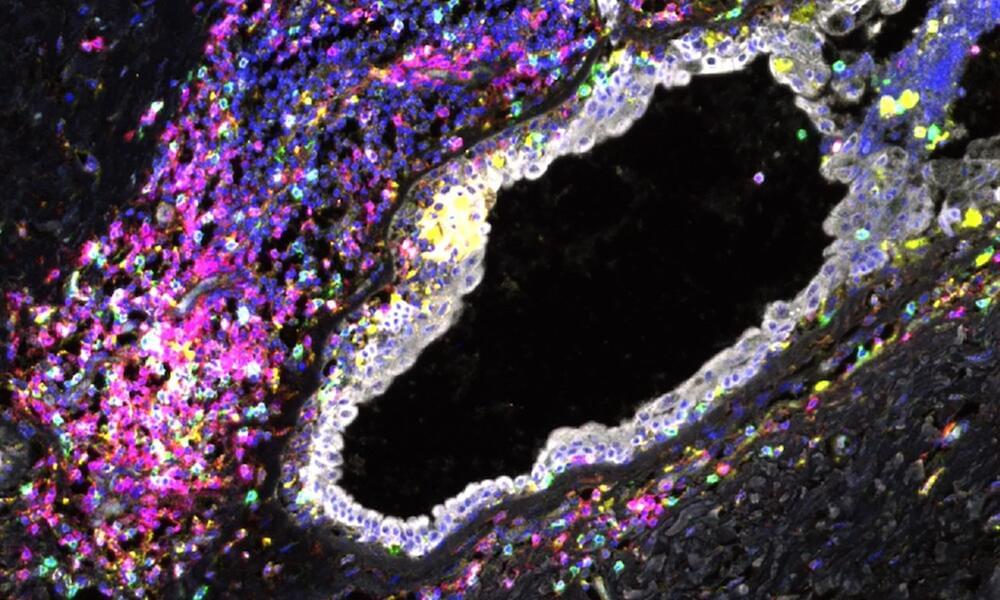
The study found that the immune cells in breast tissue of healthy women carrying BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations show signs of malfunction known as exhaustion. This suggests that the immune cells can’t clear out damaged breast cells, which can eventually develop into breast cancer.
This is the first time that exhausted immune cells have been reported in non-cancerous breast tissues at such scale—normally these cells are only found in late-stage tumors. The results raise the possibility of using existing immunotherapy drugs as early intervention to prevent breast cancer developing, in carriers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations.