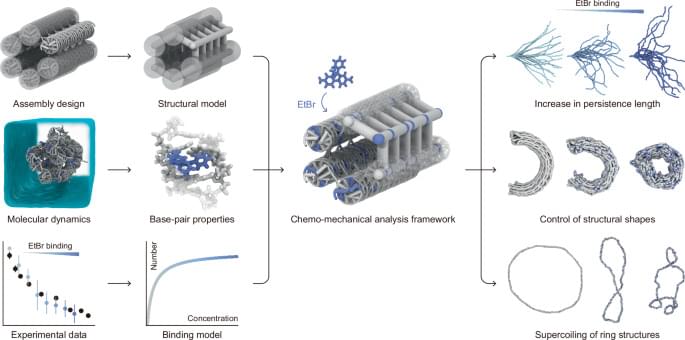
Chemo-mechanical deformation of structured DNA assemblies driven by DNA-binding ligands is promising for biological and therapeutic applications, but it is elusive how to effectively model and predict their effects on the deformation and mechanical properties of DNA structures. Here, the authors present a computational framework for simulating chemo-mechanical change of structured DNA assemblies, using ethidium bromide intercalation as an example.