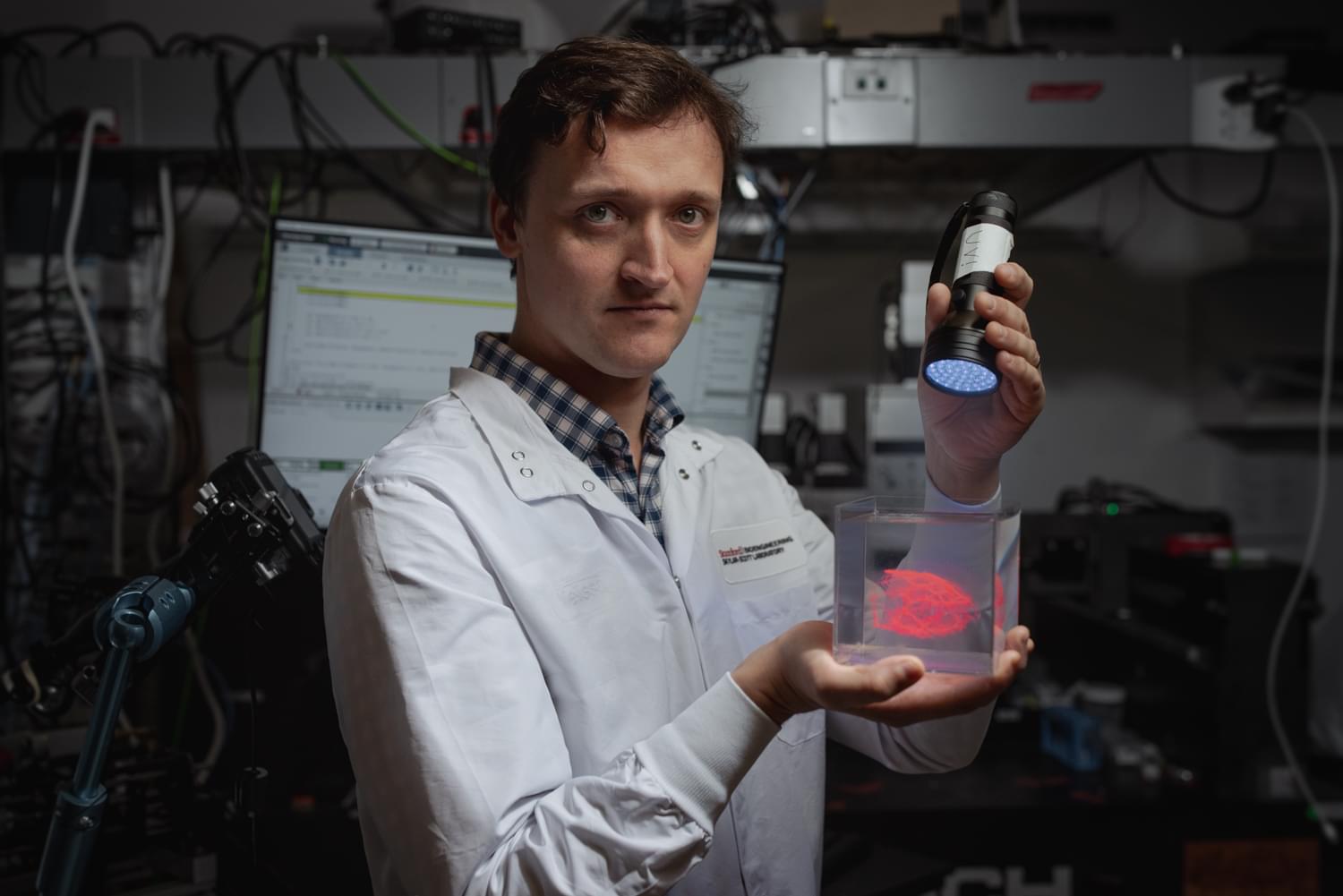
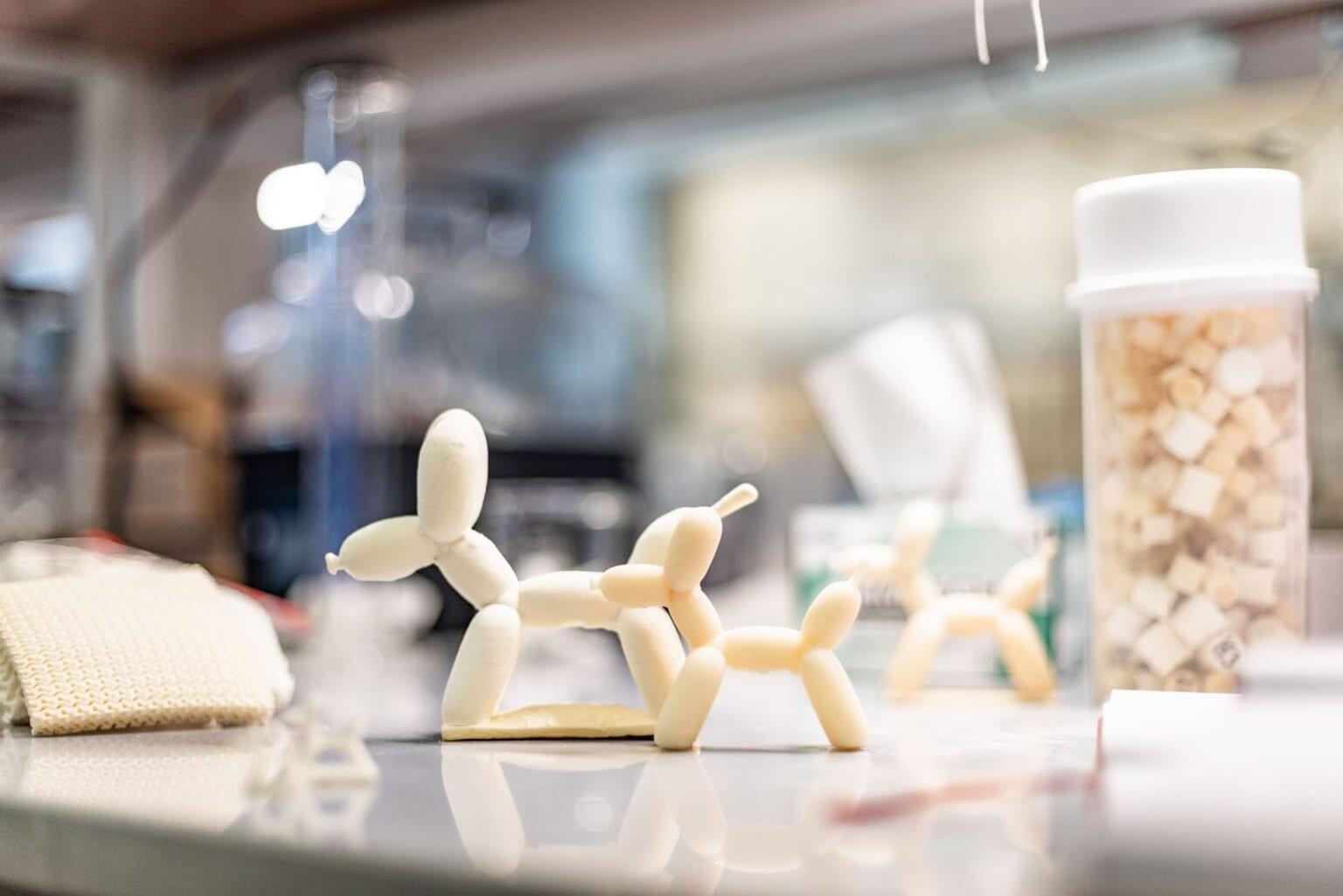
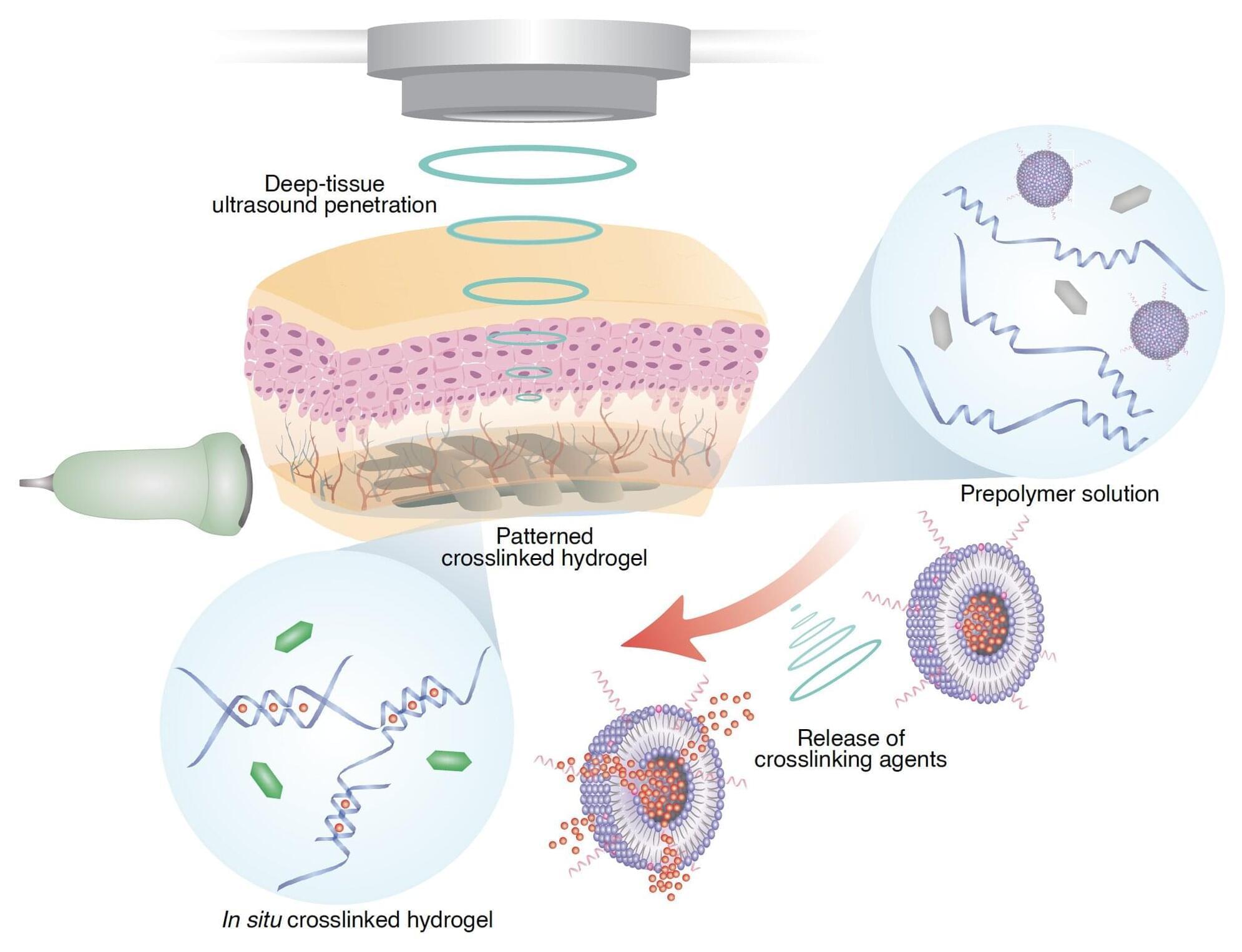
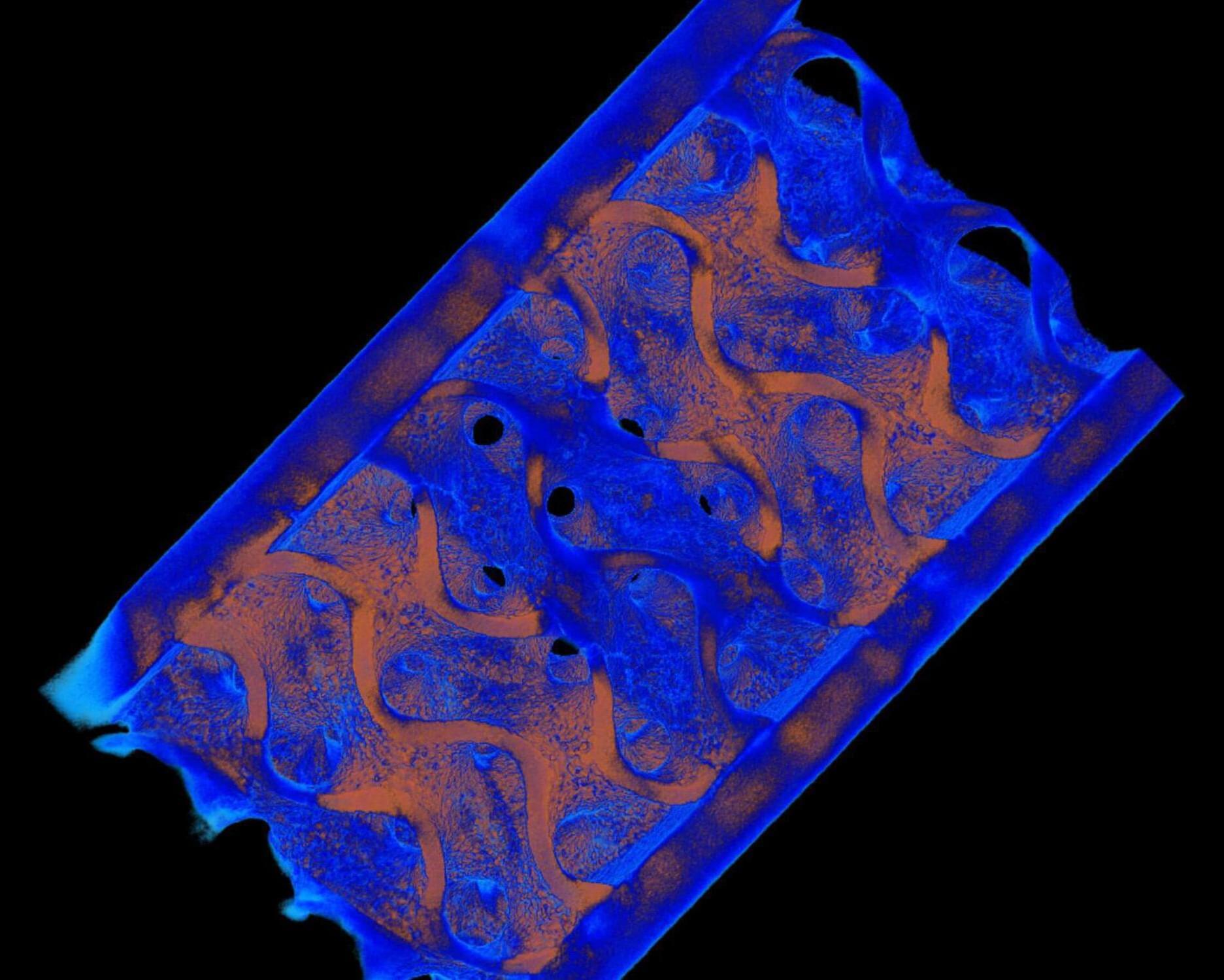
Researchers headed by a team at the California Institute of Technology developed an ultrasound-guided 3D printing technique that could make it possible to fabricate medical implants in vivo and deliver tailored therapies to tissues deep inside the body—all without invasive surgery. The researchers say the imaging-guided deep tissue in vivo sound printing (DISP) platform utilizes low-temperature–sensitive liposomes (LTSLs) as carriers for cross-linking agents, enabling precise, controlled in situ fabrication of biomaterials within deep tissues.
Reporting on their development in Science “Imaging-guided deep tissue in vivo sound printing”, first author Elham Davoodi, PhD, and senior, corresponding author Wei Gao, PhD, described proof of concept studies demonstrating in vivo printing within the bladders and muscles of mice, and rabbits, respectively. Gas vesicle (GV)–based ultrasound imaging integrated into the printing platform enabled real-time monitoring of the printing process and precise positioning. In their paper, the authors concluded, “DISP’s ability to print conductive, drug-loaded, cell-laden, and bioadhesive biomaterials demonstrates its versatility for diverse biomedical applications.”
Three-dimensional (3D) bioprinting technologies offer significant promise to modern medicine by enabling the creation of customized implants, intricate medical devices, and engineered tissues, tailored to individual patients, the authors wrote. “However, the implantation of these constructs often requires invasive surgeries, limiting their utility for minimally invasive treatments.”