Posted on Big Think.




Is this true?
The Perseverance rover has been on Mars for two weeks and has now spun its wheels and began its maiden trek over the red planet’s surface. According to new images transmitted to Earth by the one-ton robot on Friday, the voyage was a quick one.
Engineers have worked tirelessly to get the vehicle and its numerous equipment up and operating, including instruments and a robotic arm. Perseverance’s mission is to look for indications of alien life in the Jezero crater, which is located near the equator. This will take roughly 15 kilometers throughout the following Martian year (approximately two Earth years).
Scientists want to gain access to a series of rock formations in the crater that might provide traces of ancient biological activity. According to satellite images, one of them appears to be a delta, a structure consisting of silt and sand pushed up by a river as it reaches a larger body of water. In Jezero’s case, this greater mass was most likely a crater-wide lake that existed billions of years ago. However, Perseverance must first undertake an experiment before they can begin.
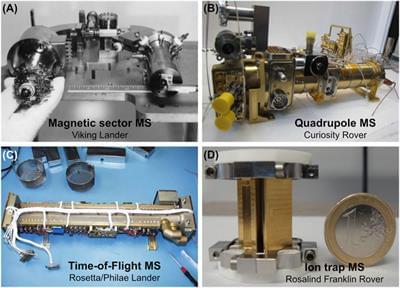
For the past fifty years of space exploration, mass spectrometry has provided unique chemical and physical insights on the characteristics of other planetary bodies in the Solar System. A variety of mass spectrometer types, including magnetic sector, quadrupole, time-of-flight, and ion trap, have and will continue to deepen our understanding of the formation and evolution of exploration targets like the surfaces and atmospheres of planets and their moons. An important impetus for the continuing exploration of Mars, Europa, Enceladus, Titan, and Venus involves assessing the habitability of solar system bodies and, ultimately, the search for life—a monumental effort that can be advanced by mass spectrometry. Modern flight-capable mass spectrometers, in combination with various sample processing, separation, and ionization techniques enable sensitive detection of chemical biosignatures.
Circa 2021
For the past fifty years of space exploration, mass spectrometry has provided unique chemical and physical insights on the characteristics of other planetary bodies in the Solar System. A variety of mass spectrometer types, including magnetic sector, quadrupole, time-of-flight, and ion trap, have and will continue to deepen our understanding of the formation and evolution of exploration targets like the surfaces and atmospheres of planets and their moons. An important impetus for the continuing exploration of Mars, Europa, Enceladus, Titan, and Venus involves assessing the habitability of solar system bodies and, ultimately, the search for life—a monumental effort that can be advanced by mass spectrometry. Modern flight-capable mass spectrometers, in combination with various sample processing, separation, and ionization techniques enable sensitive detection of chemical biosignatures. While our canonical knowledge of biosignatures is rooted in Terran-based examples, agnostic approaches in astrobiology can cast a wider net, to search for signs of life that may not be based on Terran-like biochemistry. Here, we delve into the search for extraterrestrial chemical and morphological biosignatures and examine several possible approaches to agnostic life detection using mass spectrometry. We discuss how future missions can help ensure that our search strategies are inclusive of unfamiliar life forms.
Biosignatures are the tantalizing chemical and physical imprints associated with life, and the possibility that life exists elsewhere beyond Earth drives us to search for these biosignatures on other planets and moons. The enterprise of space exploration, galvanized by the question of “Are we alone in the Universe?”, demands a stronger understanding of the diversity of biosignatures that life could express, thereby driving payload instruments on board astrobiology missions to offer broader and more advanced detection capabilities. In tandem with cutting-edge instrument platforms, research in data processing and data analysis on Earth-based (Terran) astrobiology analogs and on extraterrestrial materials also serves to increase the breadth of interpretations possible with mission data.
The Festival will take place, from 7 to 9 July 2022, at the Archenhold Observatory in Berlin (Germany).
You are welcome to join the Festival in presence, sizing an excellent opportunity to visit the historic Archenhold Observatory and the beautiful city of Berlin. However, the Festival will be an hybrid conference, therefore virtual attendees are welcome as well.
Register here for free: https://spacerenaissance.space/register-to-the-space-renaiss…rlin-2022/
A detailed programme, and all the information — including logistics and hotels accommodations — are ** available on this page:**
**The agenda, in brief:** * The first day, 7 of July, focuses on ** Space Philosophy & Policy**, with a Panel on Civilian Space Development — How to accelerate it? How to support new space industry to achieve the goal of kicking off civilian space development within 2030? What should space agencies do, and what should the space activist organizations do? * The 8 of July, ** Astronauts and Civilians, Science & Tech Day**, will see two panels: on Space Habitats and Analog Training; Space Night, after dinner: Night Observation at the giant telescope * The 9 of July, the ** Space Art Day**, with two art panels, in German and English language.
The programme includes several keynote speakers, e.g. Seth Shostak (SETI), Giuseppe Reibaldi and John Mankins (Moon Village Association), Michelle Hanlon (NSS President), Bob Zubrin (Mars Society Founder), Jan Wörner (former ESA Director General), Bernard Foing (SRI President, chair of ITACCUS and EuroMoonMars). Many experts will tell us what’s going on on the edge of space settlement, science, art and exploration.
Several space artists will present their artworks, including: Priscilla Thomas, Mary Kuiper, Barbara King, and many members of the MoonMars art group.
The Festival will host the GALIX Congress 2022.
Visit https://brilliant.org/isaacarthur/ to get started learning STEM for free, and the first 200 people will get 20% off their annual premium subscription.
One day humanity might journey to new worlds and settle them, or discover life already on them, but first we’ll have to find those exoplanets under aliens suns.
International Space Development Conference Registration: https://isdc2022.nss.org.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Support us on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/IsaacArthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-arthur.
Facebook Group: https://www.facebook.com/groups/1583992725237264/
Reddit: https://www.reddit.com/r/IsaacArthur/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Isaac_A_Arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: https://discord.gg/53GAShE
Listen or Download the audio of this episode from Soundcloud: Episode’s Audio-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/surveying-for-…ar-systems.
Episode’s Narration-only version: https://soundcloud.com/isaac-arthur-148927746/surveying-for-…ation-only.
Credits:
Surveying for Habitable Interstellar Star Systems.
Science & Futurism with Isaac Arthur.
Episode 343, May 19, 2022
Written, Produced & Narrated by Isaac Arthur.
Editors:
Andrew Nelson.
Curt Hartung.
David McFarlane.
Cover Art:


Can humanity last another 400,000 years? We might have to if we want to talk to another technological civilization.
If there are so many galaxies, stars, and planets, where are all the aliens, and why haven’t we heard from them? Those are the simple questions at the heart of the Fermi Paradox. In a new paper, a pair of researchers ask the next obvious question: how long will we have to survive to hear from another alien civilization?
Their answer? 400,000 years.
