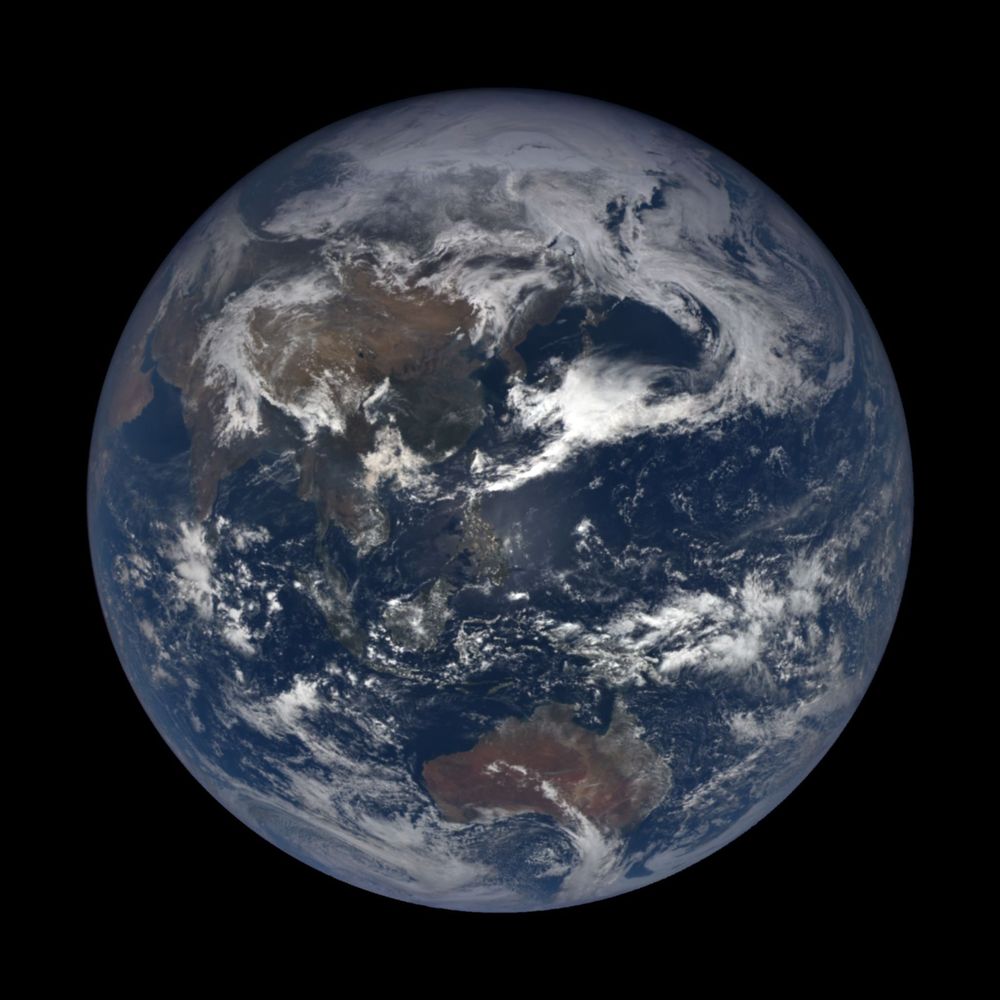
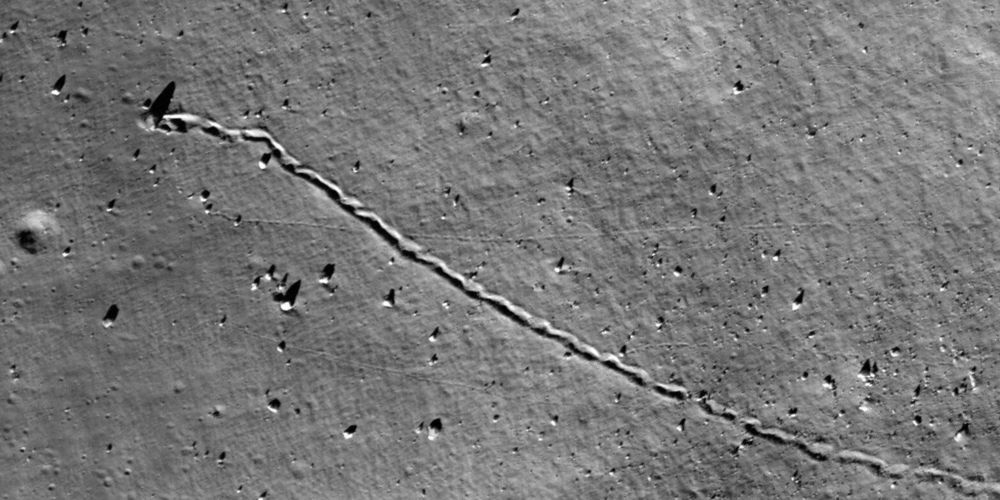
A research team from ETH Zurich and the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research in Göttingen counted over 136,000 rockfalls on the moon caused by asteroid impacts. Even billions of years old landscapes are still changing.
In October 2015, a spectacular rockfall occurred in the Swiss Alps: in the late morning hours, a large, snow-covered block with a volume of more than 1500 cubic meters suddenly detached from the summit of Mel de la Niva. It fell apart on its way downslope, but a number of boulders continued their journey into the valley. One of the large boulders came to a halt at the foot of the summit next to a mountain hut, after traveling more than 1.4 kilometers and cutting through woods and meadows.
On the moon, time and again boulders and blocks of rock travel downslope, leaving behind impressive tracks, a phenomenon that has been observed since the first unmanned flights to the moon in the 1960s. During the Apollo missions, astronauts examined a few such tracks on site and returned displaced rock block samples to Earth. However, until a few years ago, it remained difficult to gain an overview of how widespread such rock movements are and where exactly they occur.