Things are only impossible until they’re not.


During that uncomfortable period between puberty and adulthood, the brain undergoes carefully orchestrated changes in gene expression and epigenetic modification. Alcohol, unfortunately, interferes with this biological architecture. Consequently, mistakes are made, and gene expression and modification do not go as planned, leaving the person vulnerable to a lifetime of psychiatric challenges, such as anxiety and alcoholism.
A team of researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago recently found they could reverse these changes in rats via gene editing. If their findings carry through to human studies, gene editing may be a potential treatment for anxiety and alcohol-use disorder in adults who were exposed to binge drinking in their adolescence.

In a few months, a daring clinical trial may fundamentally lower heart attack risk in the most vulnerable people. If all goes well, it will just take one shot.
It’s no ordinary shot. The trial, led by Verve Therapeutics, a biotechnology company based in Massachusetts, will be one of the first to test genetic base editors directly inside the human body. A variant of the gene editing tool CRISPR-Cas9, base editors soared to stardom when first introduced for their efficiency at replacing single genetic letters without breaking delicate DNA strands. Because it’s safer than the classic version of CRISPR, the new tool ignited hope that it could be used for treating genetic diseases.
Verve’s CEO, Dr. Sekar Kathiresan, took note. A cardiologist at Harvard University, Kathiresan wondered if base editing could help solve one of the main killers of our time: heart attacks. It seemed the perfect test case. We know one major cause of heart attacks—high cholesterol levels, particularly a version called LDL-C (Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol). We also know several major genes that control its level. And—most importantly—we know the DNA letter swap that can, in theory, drastically lower LDL-C and in turn throttle the risk of heart attacks.
An international team which includes University of Manchester scientists has for the first time demonstrated that nerve signals are exchanged between clogged up arteries and the brain.
The discovery of the previously unknown electrical circuit is a breakthrough in our understanding of atherosclerosis, a potentially deadly disease where plaques form on the innermost layer of arteries.
The study of mice found that new nerve bundles are formed on the outer layer of where the artery is diseased, so the brain can detect where the damage is and communicate with it.
Gene editing reverses brain genetic reprogramming caused by adolescent binge drinking.
Gene editing may be a potential treatment for anxiety and alcohol use disorder in adults who were exposed to binge drinking in their adolescence, according to the findings of an animal study published on May 4, 2022, in the journal Science Advances.
The study was issued by researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago (UIC) who have been studying the effects of early-life binge drinking on health later in life.

Circa 2017
Schizophrenia is a genetically related mental illness, in which the majority of genetic alterations occur in the non-coding regions of the human genome. In the past decade, a growing number of regulatory non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) including microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been identified to be strongly associated with schizophrenia. However, the studies of these ncRNAs in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia and the reverting of their genetic defects in restoration of the normal phenotype have been hampered by insufficient technology to manipulate these ncRNA genes effectively as well as a lack of appropriate animal models. Most recently, a revolutionary gene editing technology known as Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated nuclease 9 (Cas9; CRISPR/Cas9) has been developed that enable researchers to overcome these challenges. In this review article, we mainly focus on the schizophrenia-related ncRNAs and the use of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated editing on the non-coding regions of the genomic DNA in proving causal relationship between the genetic defects and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. We subsequently discuss the potential of translating this advanced technology into a clinical therapy for schizophrenia, although the CRISPR/Cas9 technology is currently still in its infancy and immature to put into use in the treatment of diseases. Furthermore, we suggest strategies to accelerate the pace from the bench to the bedside. This review describes the application of the powerful and feasible CRISPR/Cas9 technology to manipulate schizophrenia-associated ncRNA genes. This technology could help researchers tackle this complex health problem and perhaps other genetically related mental disorders due to the overlapping genetic alterations of schizophrenia with other mental illnesses.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; gene editing; lncRNAs; miRNAs; non-coding RNAs; schizophrenia.
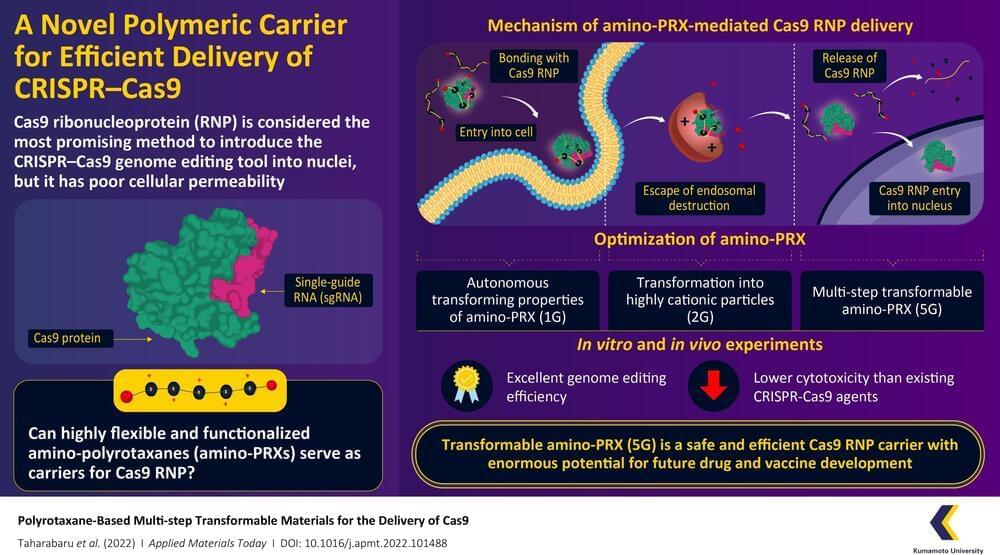
CRISPR-Cas9 is considered a revolutionary gene editing tool, but its applications are limited by a lack of methods by which it can be safely and efficiently delivered into cells. Recently, a research team from Kumamoto University, Japan, have constructed a highly flexible CRISPR-Cas9 carrier using aminated polyrotaxane (PRX) that can not only bind with the unusual structure of Cas9 and carry it into cells, but can also protect it from intracellular degradation by endosomes.
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) and their accompanying protein, CRISPR-associated protein 9 (Cas9), made international headlines a few years ago as a game-changing genome editing system. Consisting of Cas9 and strand of genetic material known as a single-guide RNA (sgRNA), the system can target specific regions of DNA and function as “molecular scissors” to make precise edits. The direct delivery of Cas9–sgRNA complexes, i.e. Cas9 ribonucleoproteins (RNPs), into the nucleus of the cell is considered the safest and most efficient way to achieve genome editing. However, the Cas9 RNP has poor cellular permeability, and thus requires a carrier molecule to transport it past the first hurdle of the cell membrane before it can get to the cell nucleus. These carriers need to bind with Cas9 RNP, carry it into the cell, prevent its degradation by intracellular organelles called “endosomes,” and finally release it without causing any changes to its structure.
In a recent paper published in the June 2022, Volume 27 of Applied Materials Today, a research team from Kumamoto University has developed a transformable polyrotaxane (PRX) carrier that can facilitate genome editing using Cas9RNP with high efficiency and usability. “While there have been some PRX-based drug carriers for nucleic acids and proteins reported before, this is the first report on PRX-based Cas9 RNP carrier. Moreover, our findings describe how to precisely control intracellular dynamics across multiple steps. This will prove invaluable for future research in this direction,” says Professor Keiichi Motoyama, a corresponding author of the paper.

EPFL scientists have developed a digital model of the fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster, that realistically simulates the movements of the animal. The twin is a big step towards reverse engineering the neuromechanical control of animal behavior, and developing bioinspired robots.
“We used two kinds of data to build NeuroMechFly,” says Professor Pavan Ramdya at EPFL’s School of Life Sciences. “First, we took a real fly and performed a CT scan to build a morphologically realistic biomechanical model. The second source of data were the real limb movements of the fly, obtained using pose estimation software that we’ve developed in the last couple of years that allow us to precisely track the movements of the animal.”
Ramdya’s group, working with the group of Professor Auke Ijspeert at EPFL’s Biorobotics Laboratory, has published a paper in Nature Methods showcasing the first ever accurate “digital twin” of the fly Drosophila melanogaster, dubbed “NeuroMechFly”.
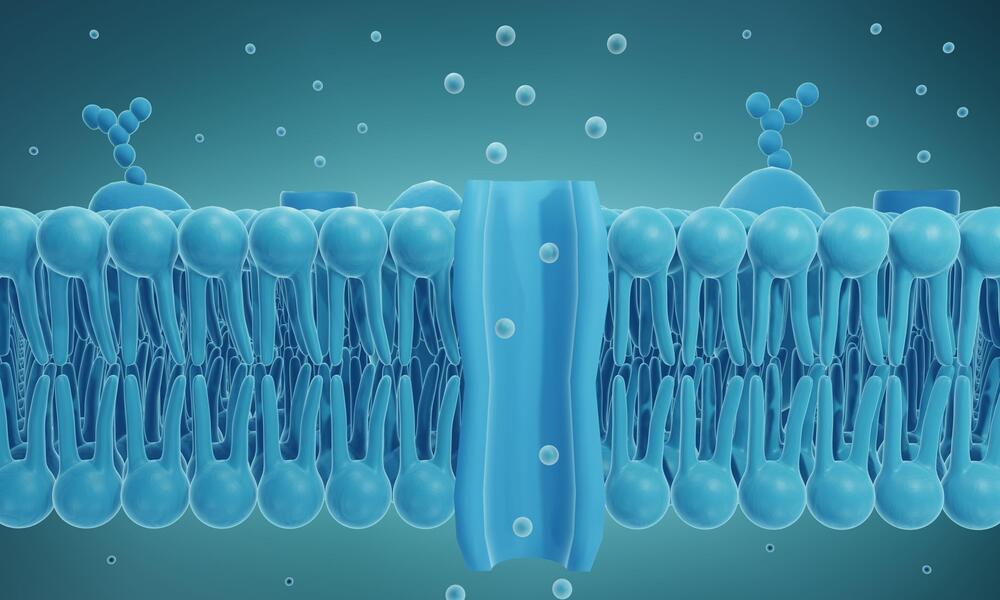
Just as countries import a vast array of consumer goods across national borders, so living cells are engaged in a lively import-export business. Their ports of entry are sophisticated transport channels embedded in a cell’s protective membrane. Regulating what kinds of cargo can pass through the borderlands formed by the cell’s two-layer membrane is essential for proper functioning and survival.
Award-winning author and futurist Amy Webb examines the world of synthetic biology in her book “The Genesis Machine.” She sits down with Hari Sreenivasan to discuss the potential and the concerns of redesigning our lives.
Originally aired on April 28, 2022.
For more from Amanpour and Company, including full episodes, click here: https://to.pbs.org/2NBFpjf.
Like Amanpour and Company on Facebook: https://bit.ly/2HNx3EF