CRISPR gene editing has created chickens that resist a common virus. It may be possible to use the same technique to make poultry resistant to bird flu too.


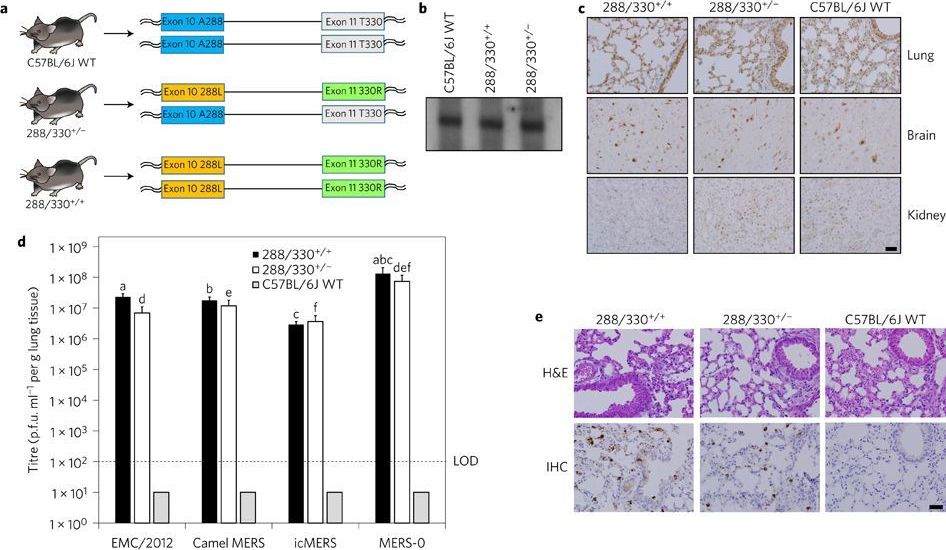
A, C57BL/6J mice were genetically engineered using CRISPR–Cas9 genomic editing to encode 288L and 330R in mDPP4 on one chromosome (heterozygous, 288/330+/−) or on both chromosomes (homozygous, 288/330+/+). b, Northern blot of mDPP4 mRNA expression. c, Immunohistochemistry (IHC) of mDPP4 protein in the lungs, brain and kidneys of individual C57BL/6J wild-type (WT), 288/330+/− and 288/330+/+ mice. d, Viral titres for MERS-CoV at 3 days post-infection from C57BL/6J WT, 288/330+/− and 288/330+/+ (all n = 4) mice infected with 5 × 105 plaque-forming units (p.f.u.) of the indicated viruses. Bar graphs show means + s.d.

If you look up ‘scientific overachiever’ in the dictionary, you’re likely to find a two-word definition: George Church.
The American geneticist, molecular engineer, and chemist splits his time between roles as Professor of Genetics at Harvard Medical School and Professor of Health Sciences and Technology at Harvard and MIT. He’s also a member of the National Academy of Sciences, acts as an advisor to a plethora of cutting edge companies, and heads up synthetic biology at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, of which he’s a founding member.
Oh, and George is author to hundreds of published papers, 60 patents and a popular science book (also, theoretically, George Church may live in an alternate reality where there are more than 24 hours in a day).

Tooth loss is a concern that most people will face at some point in their life. According to studies, by the age of 74, 26 percent of adults will have lost all of their permanent teeth. Dentures are sufficient, but they’re uncomfortable and dental implants can fail and have no ability to “remodel” as the surrounding jaw bone changes with age.
All of these are reasons why some people have placed their hope in stem cell research. While there are controversy surrounds the new medical method such as the use and destruction of human embryos, not all research involves human tissue and has the potential to change a lot of lives.
A new technique being tested in the Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine Laboratory of Dr. Jeremy Mao, Edward V. Zegarelli prof of odontology, and a professor of biomedical engineering at Columbia University, could make “tooth loss” a thing of the past. The cluster believes they need to find some ways to own the body’s stem cells, migrate it to a three-dimensional scaffold manufactured from natural material and insert it to a patient’s mouth.
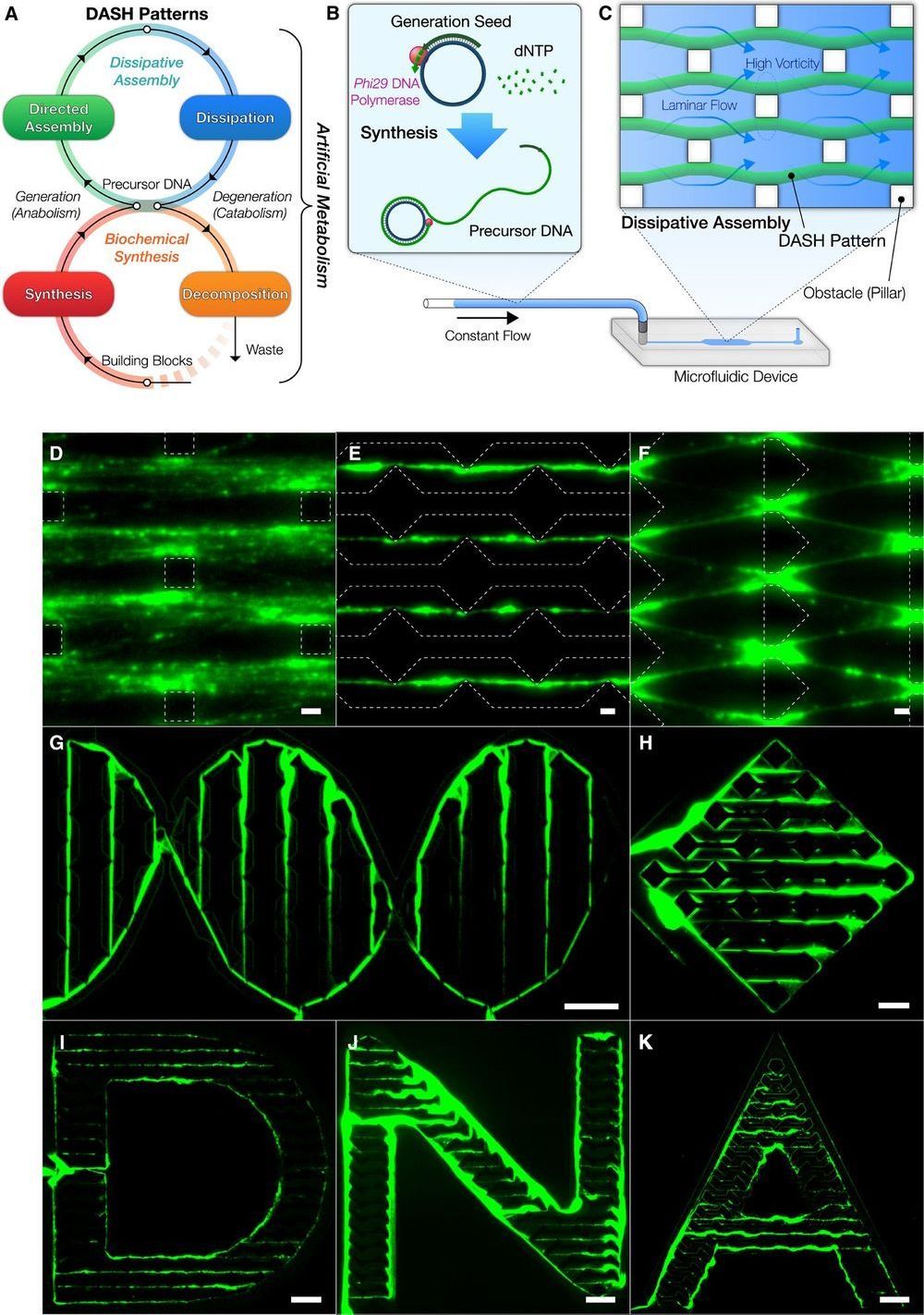
Interesting research paper on a new nanobot technology. I’m watching for ways in which suitable substrates for mind uploading can be constructed, and DNA self-guided assembly has potential.
Here are some excerpts and a weblink to the paper:
“…Chemical approaches have opened synthetic routes to build dynamic materials from scratch using chemical reactions, ultimately allowing flexibility in design…”
… As a realization of this concept, we engineered a mechanism termed DASH—DNA-based Assembly and Synthesis of Hierarchical materials—providing a mesoscale approach to create dynamic materials from biomolecular building blocks using artificial metabolism. DASH was developed on the basis of nanotechnology that uses DNA as a generic material ranging from nanostructures to hydrogels, for enzymatic substrates, and as linkers between nanoparticles…”
“…Next, to illustrate the potential uses of self-generated materials, we created various hybrid functional materials from the DASH patterns. The DASH patterns served as a versatile mesoscale scaffold for a diverse range of functional nanomaterials beyond DNA, ranging from proteins to inorganic nanoparticles, such as avidin, quantum dots, and DNA-conjugated gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) (Fig. 4D, figs. S37 and S38, and Supplementary Text). The generated patterns were also rendered functional with catalytic activity when conjugated with enzymes (figs. S39 and S40 and Supplementary Text). We also showed that the DNA molecules within the DASH patterns retained the DNA’s genetic properties and that, in a cell-free fashion, the materials themselves successfully produced green fluorescent proteins (GFPs) by incorporating a reporter gene for sfGFP (Fig. 4E and figs. S9 and S41) (40). The protein production capability of the materials established the foundation for future cell-free production of proteins, including enzymes, in a spatiotemporally controlled manner.
…” Our implementation of the concept, DASH, successfully demonstrated various applications of the material. We succeeded in constructing machines from this novel dynamic biomaterial with emergent regeneration, locomotion, and racing behaviors by programming them as a series of FSAs. Bottom-up design based on bioengineering foundations without restrictions of life fundamentally allowed these active and programmable behaviors. It is not difficult to envision that the material could be integrated as a locomotive ele-ment in biomolecular machines and robots. The DASH patterns could be easily recognized by naked eyes or smartphones, which may lead to better detection technologies that are more feasible in point-of-care settings. DASH may also be used as a template for other materials, for example, to create dynamic waves of protein expression or nanoparticle assemblies. In addition, we envision that further expansion of artificial metabolism may be used for self-sustaining structural components and self-adapting substrates for chemical production pathways. Ultimately, our material may allow the construction of self-reproducing machines through the production of enzymes from generated materials that, in turn, reproduce the material. Our biomaterial powered by artificial metabolism is an important step toward the creation of “artificial” biological systems with dynamic, life-like capabilities.”…

The insulin pumps diabetics currently rely on do a great job of delivering the hormone as needed, but need regular replacing due to what are known as fibrils. These form over a day or two as insulin compounds accumulate into clumps and create the risk of blockages, but scientists in Australia have engineered what they say is a safer alternative, with egg yolks serving as their starting point.
The formation of fibrils means that diabetics need to replace their insulin pumps every 24 to 72 hours to avoid the risk of dangerous blockages, which bring with them a risk of life-threatening under-dosing. Beyond the dangers to the patient’s well-being, the need to regularly replace the pump increases the workload needed to manage their disease and means that portions of the medicine often go to waste.
So, there is considerable interest in developing synthetic insulin that doesn’t behave in this way. Researchers at Melbourne’s Florey Institute of Neuroscience and Mental Health approached this problem through a new technique it developed with scientists in Japan, whereby the insulin is engineered from egg yolks to allow for greater freedom over the final design.
A newly published study has described the successful results in mice of a novel vaccine designed to prevent neurodegeneration associated with Alzheimer’s disease. The researchers suggest this “dementia vaccine” is now ready for human trials, and if successful could become the “breakthrough of the next decade.”
The new study, led by the Institute for Molecular Medicine and University of California, Irvine, describes the effect of a vaccine designed to generate antibodies that both prevent, and remove, the aggregation of amyloid and tau proteins in the brain. The accumulation of these two proteins is thought to be the primary pathological cause of neurodegeneration associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
The research revealed the vaccine led to significant decreases in both tau and amyloid accumulation in the brains of bigenic mice engineered to exhibit aggregations of these toxic proteins. Many prior failed Alzheimer’s treatments over the past few years have focused individually on either amyloid or tau protein reductions, but growing evidence suggests a synergistic relationship between the two toxic proteins may be driving neurodegeneration. Hence the hypothesis a combination therapy may be the most effective way to prevent this kind of dementia.
