Bioengineer Keenan Pinto designed an application that helps hydroponic farmers “talk” to their plants.


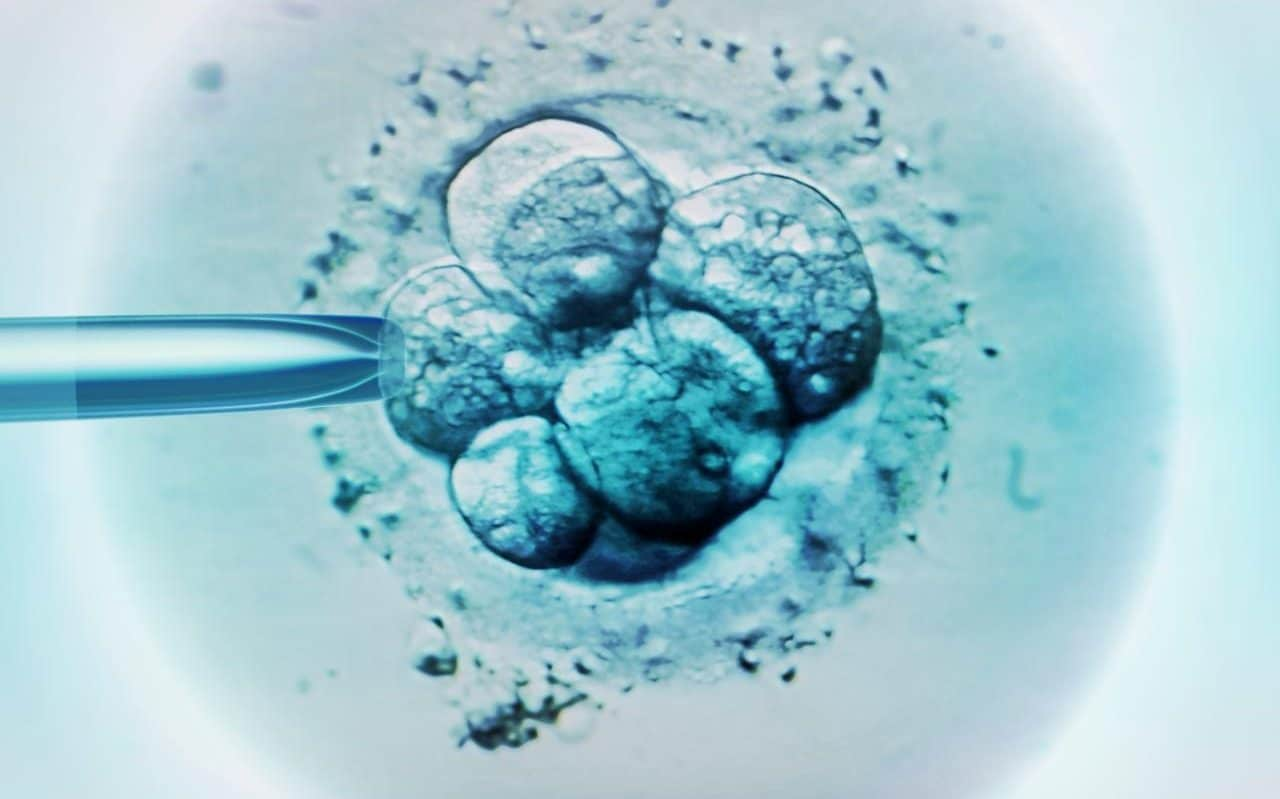
S cientists have edited human embryos for the first time in the UK to discover a “master gene” that underpins successful pregnancies. The “game-changing” research promises improved IVF outcomes and a breakthrough in understanding why so many pregnancies fail.
The Government-funded investigation, undertaken by the Francis Crick Institute, is the first to prove that gene editing can be used to study the genetic behaviour of human embryos in their first few days of life.

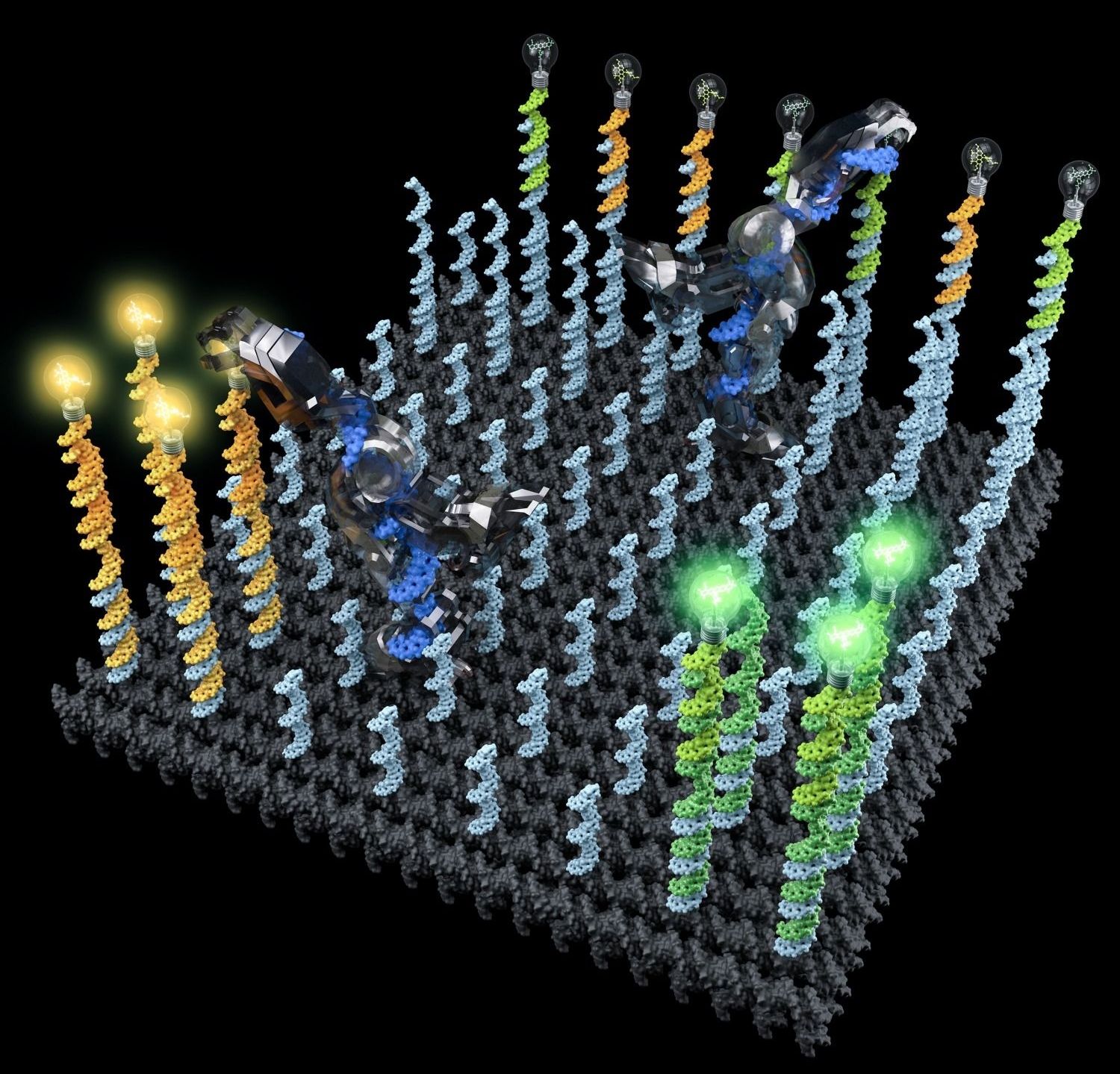
Imagine a robot that could help you tidy your home: roving about, sorting stray socks into the laundry and dirty dishes into the dishwasher. While such a practical helper may still be the stuff of science fiction, Caltech scientists have developed an autonomous molecular machine that can perform similar tasks—at the nanoscale. This “robot,” made of a single strand of DNA, can autonomously “walk” around a surface, pick up certain molecules and drop them off in designated locations.
The work was done in the laboratory of Lulu Qian, assistant professor of bioengineering. It appears in a paper in the September 15 issue of Science.
Why Nanobots?

My new policy article for the HuffPost on why more than ever we need to avoid war and armed conflict:
Some of the early years of my adult life were in conflict zones as a journalist—which included covering the Pakistan/Indian Kashmir conflict for the National Geographic Channel and The New York Times Syndicate. War zones are terrifying. One always is worried about bullying soldiers, speeding armed military vehicles, stray bullets, and whether there’s a roadside bomb on your path. Anyone that approaches you is suspect and could be carrying ready-to-detonate explosives.
One thing conflict zones teach you is that freedom is precious. The nearly 70-year Kashmir conflict has approximately a half million soldiers involved, so even if they’re supposedly on your side (depending on what country you’re in), you still feel under siege. My time in certain parts of Sudan, Israel, Palestine, Zimbabwe, Lebanon, Sri Lanka, Eritrea, Mali, and Yemen left me with the same feeling.
We face an unusual time with President Trump, whose bold behavior could prove dangerous to stable foreign policy. This situation has now become even more worrisome this month when Russia’s Vladimir Putin, according to RT, said publicly that whoever “leads in artificial intelligence will rule the world.” Some experts believe we will have an AI equivalent to human intelligence in less than 10 years time—which means in 15–20 years time, AI will far outdo human thinking and could be in control of all nuclear weaponry on the planet.
For this reason, nothing is more critical for nations and peoples to strive for peaceful times and to get along with one another. In any kind of modern conflict or 21st Century arms race—AI, genetic engineering, or nuclear arms—we likely will lose some of our freedoms and sense of security.
Short for Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats, CRISPR is a revolutionary gene editing technique that’s taken the scientific world by storm. Both ultra-precise and easy to access, CRISPR could be the next step towards wiping out genetically inherited diseases and even curing cancers. A host of exciting CRISPR concepts are currently undergoing clinical trials and proof-of-concept experiments, with one particularly controversial focus — human embryos.
A “cut and paste” concept
While there have been rumours coming out of China for years, US scientists have now confirmed that the first attempts to create genetically modified human embryos have been a success. Led by researchers at the Oregon Health and Science University in Portland, the study used CRISPR to change the DNA of multiple one-cell human embryos. Basically, this allowed them to “snip” out segments of a particular genome and switch them with customised replacements. As in previous cases, the embryos were terminated several days after creation to prevent them from developing into foetuses.

I was thinking about this the other day. How far off is using CRISPR for cosmetic changes? permanently changing of eye color, hair color, skin (although that one is gonna be a lightning rod), etc…
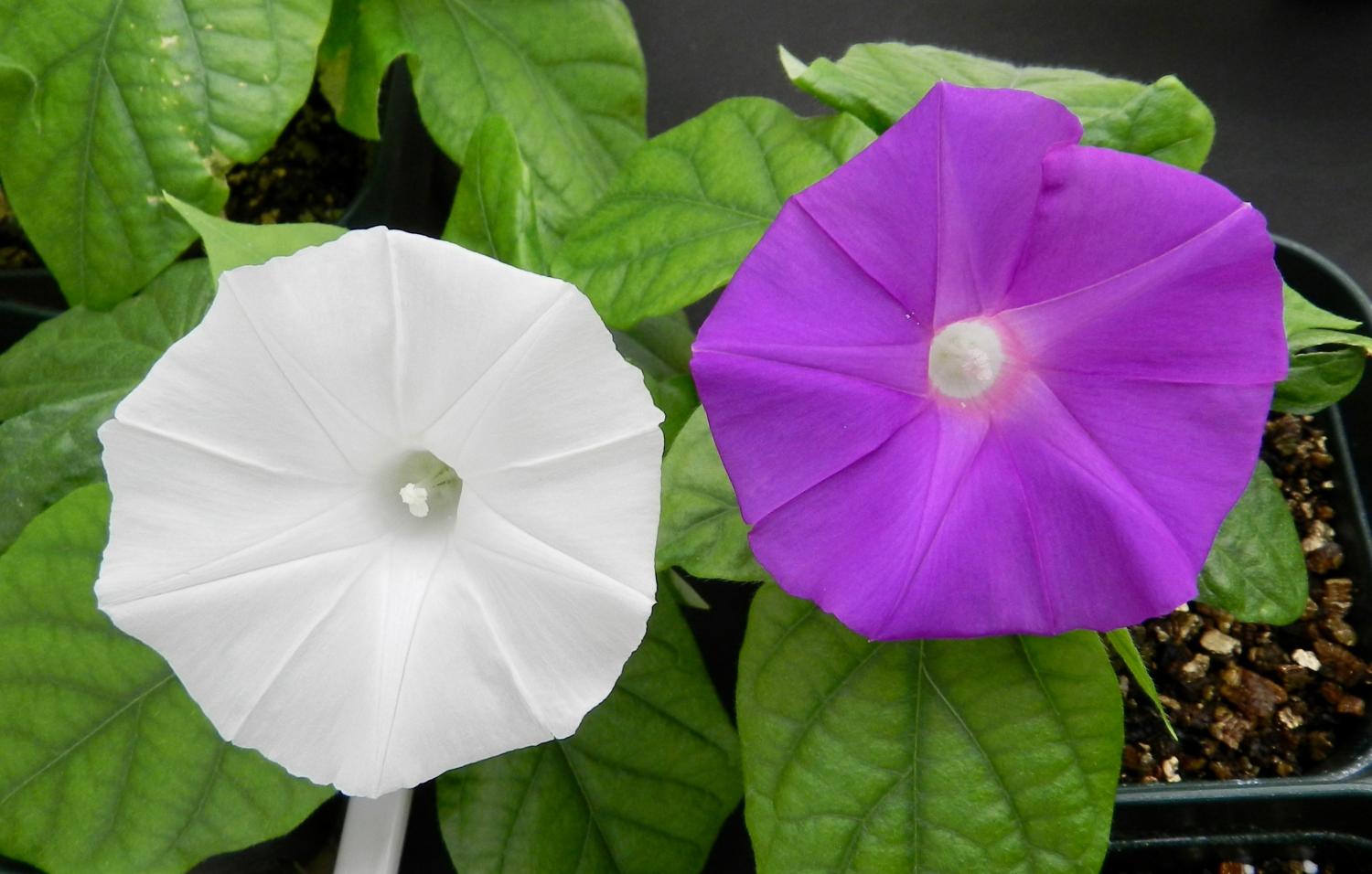
In a world-first, Japanese scientists have used the revolutionary CRISPR, or CRISPR/Cas9, genome- editing tool to change flower colour in an ornamental plant. Researchers from the University of Tsukuba, the National Agriculture and Food Research Organization (NARO) and Yokohama City University, Japan, altered the flower colour of the traditional Japanese garden plant, Japanese morning glory (Ipomoea nil or Pharbitis nil), from violet to white, by disrupting a single gene. This research highlights the huge potential of the CRISPR/Cas9 system to the study and manipulation of genes in horticultural plants.
Japanese morning glory, or Asagao, was chosen for this study as it is one of two traditional horticultural model plants in the National BioResource Project in Japan (NBRP). Extensive genetic studies of this plant have already been performed, its genome sequenced and DNA transfer methods established. In addition, as public concern with genetic technologies such as CRISPR/Cas9 is currently a social issue in Japan, studies using this popular and widely-grown plant may help to educate the public on this topic.
The research team targeted a single gene, dihydroflavonol-4-reductase-B (DFR-B), encoding an anthocyanin biosynthesis enzyme, that is responsible for the colour of the plant’s stems, leaves and flowers. Two other, very closely related genes (DFR-A and DRF-C) sit side-by-side, next to DFR-B. Therefore, the challenge was to specifically and accurately target the DFR-B gene without altering the other genes. The CRISPR/Cas9 system was used as it is currently the most precise method of gene editing.

‘In my lifetime, the singularity will happen,’ Alison Lowndes, head of AI developer relations at technology company Nvidia, tells Metro.co.uk at the AI Summit.
‘But why does everyone think they’d be hostile?
Robots ‘will reach human intelligence by 2029 and life as we know it will end in 2045’.
This isn’t the prediction of a conspiracy theorist, a blind dead woman or an octopus but of Google’s chief of engineering, Ray Kurzweil.

About two-thirds of Americans support the use of gene editing to treat diseases, according to a new survey. But opinions vary a lot based on people’s religious beliefs and how much they know about gene editing in general.
The research, published earlier this month in Science, shows that across the board, people want to be involved in a public discussion about editing the human genome. And that conversation with scientists and public officials needs to happen now, as the technology is still developing, says study co-author Dietram Scheufele, a science communication scholar at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. The results are based on a survey of 1,600 US adults conducted in December 2016 and January 2017.

Article out by Ron Bailey at Reason Magazine that discusses #transhumanism and #libertarianism:
Kai Weiss, a researcher at the Austrian Economics Center and Hayek Institute in Vienna, Austria, swiftly denounced the piece. “Transhumanism should be rejected by libertarians as an abomination of human evolution,” he wrote.
Clearly there is some disagreement.
Weiss is correct that Istvan doesn’t expend much intellectual effort linking transhumanism with libertarian thinking. Istvan largely assumes that people seeking to flourish should have the freedom to enhance their bodies and minds and those of their children without much government interference. So what abominable transhumanist technologies does Weiss denounce?
Weiss includes defeating death, robotic hearts, virtual reality sex, telepathy via mind-reading headsets, brain implants, ectogenesis, artificial intelligence, exoskeleton suits, designer babies, and gene editing tech. “At no point [does Istvan] wonder if we should even strive for these technologies,” Weiss thunders.