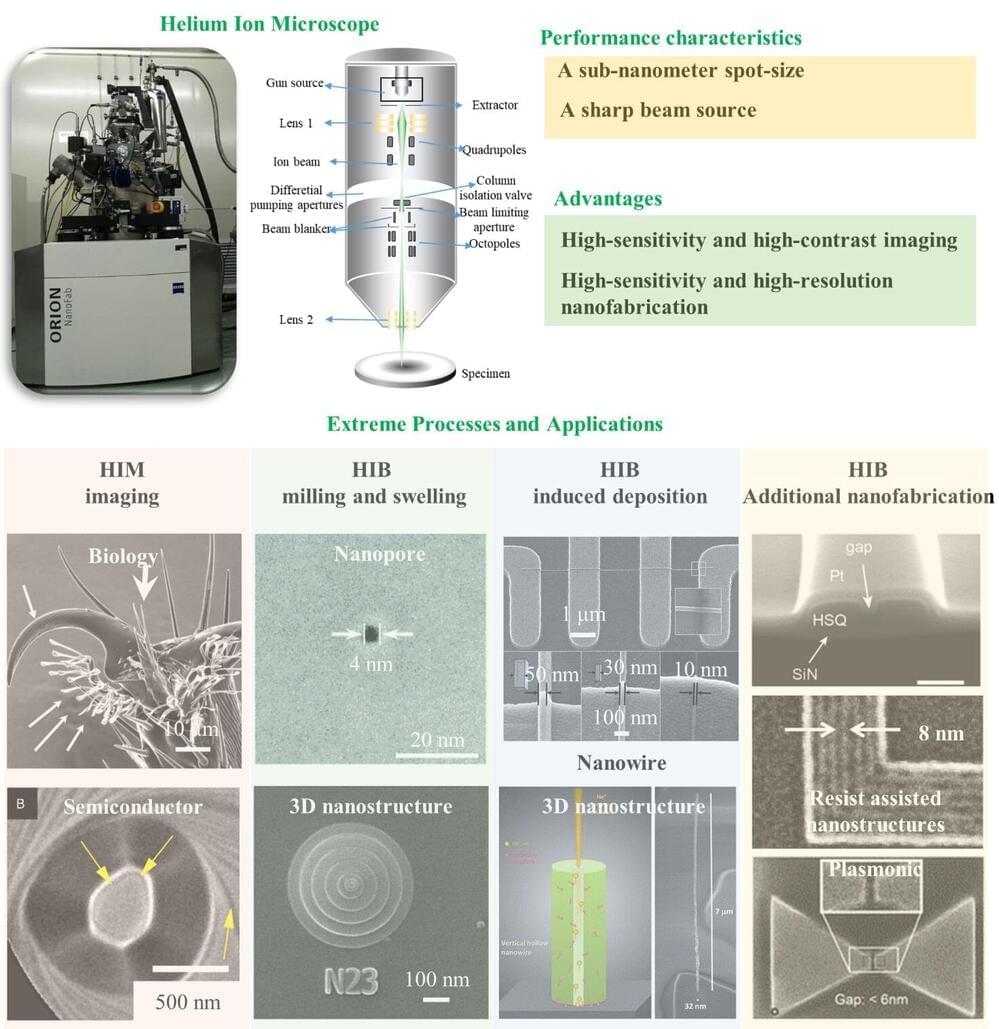
In recent years, material scientists have designed a wide range of innovative materials that could be used to create new technologies, including soft robots, controllers and smart textiles. These materials include artificial muscles, structures that resemble biological muscles in shape and that could improve the movements of robots or enable the creation of clothing that adapts to different environmental conditions.
As part of an ongoing project focused on textile-based soft actuators, a team of researchers at Jiangnan University in China recently developed new artificial muscles based on free-standing, single-helical woolen yarn. Their artificial muscles, introduced in a paper published in Smart Materials and Structures, could be used to easily and affordably produce twisted actuators that can detect and respond to humidity in their environment.
“We are trying to design flexible and versatile actuators by leveraging the hierarchical structure design of textiles, ranging from microscales (e.g., molecular chains and aggregation structures) to macroscales (e.g., fiber morphology and textile architectures),” Fengxin Sun, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Tech Xplore. “Realizing a yarn-based artificial muscle with free-standing and single-helical architecture via eco-friendly and easy-fabrication manufacturing process is still challenging.”