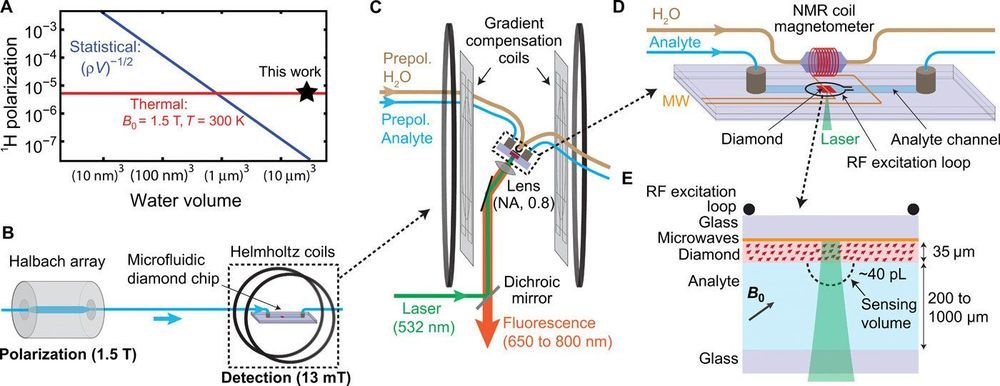
Quantum sensors based on nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers in diamond are a promising detection mode for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy due to their micron-scale detection volume and noninductive-based sample detection requirements. A challenge that exists is to sufficiently realize high spectral resolution coupled with concentration sensitivity for multidimensional NMR analysis of picolitre sample volumes. In a new report now on Science Advances, Janis Smits and an interdisciplinary research team in the departments of High Technology Materials, Physics and Astronomy in the U.S. and Latvia addressed the challenge by spatially separating the polarization and detection phases of the experiment in a microfluidic platform.
They realized a spectral resolution of 0.65±0.05 Hz, an order-of-magnitude improvement compared with previous diamond NMR studies. Using the platform, they performed 2-D correlation spectroscopy of liquid analytes with an effective detection volume of ~40 picoliters. The research team used diamond quantum sensors as in-line microfluidic NMR detectors in a major step forward for applications in mass-limited chemical analysis and single-cell biology.
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a powerful and well-established technique for compositional, structural and functional analysis in a variety of scientific disciplines. In conventional NMR spectrometry the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is strongly dependent on the external field strength (B0). As the spectral resolution increased, the B0 increased as well, motivating the development of increasingly large and expensive superconducting magnets for improved resolution and SNR, resulting in a two-fold increase in field strength within the past 25 years.