Memory, consciousness and the self aren’t what you think they are. Michael Levin joins Vasant Dhar in episode 91 of Brave New World to explain why the distinction between machines and organisms will soon fall apart. Useful resources 1. Michael Levin at Tufts, Wikipedia, Twitter, Google Scholar and The Levin Lab. 2. There’s Plenty of Room Right Here: Biological Systems as Evolved, Overloaded, Multi-scale Machines — Joshua Bondard and Michael Levin. 3. Self-Improvising Memory: A Perspective on Memories as Agential, Dynamically Reinterpreting Cognitive Glue — Michael Levin. 4. The Space Of Possible Minds — Michael Levin. 5. Endless forms most beautiful 2.0 — Wesley Clawson and Michael Levin. 6. My Octopus Teacher — Pippa Ehrlich and James Reed. 7. Pippa Ehrlich on the Mysteries of the Sea — Episode 77 of Brave New World. 8. Turing Patterns. 9. Mark Solms’ theory of consciousness — SelfAwarePatterns. 10. Mark Solms on Consciousness. Check out Vasant Dhar’s newsletter on Substack. Subscription is free!
Category: biological – Page 38
“Voices from DARPA” Podcast, Episode 86: BETR to BEST
What do smart bandages, ocean-powered sensors, and quantum biology have in common? They’re all part of Dr. Leonard Tender’s work at DARPA. On the latest episode of Voices from DARPA, he discusses his fascinating research in the Biological Technologies Office and how these innovations are shaping the future of national security.

Scientists discover new microbes in Earth’s deep soil
Scientists have discovered a new phylum of microbes in Earth’s Critical Zone, an area of deep soil that restores water quality. Ground water, which becomes drinking water, passes through where these microbes live, and they consume the remaining pollutants. The paper, “Diversification, niche adaptation and evolution of a candidate phylum thriving in the deep Critical Zone,” is published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Leonardo da Vinci once said, “We know more about the movement of celestial bodies than about the soil underfoot.” James Tiedje, an expert in microbiology at Michigan State University, agrees with da Vinci. But he aims to change this through his work on the Critical Zone, part of the dynamic “living skin” of Earth.
“The Critical Zone extends from the tops of trees down through the soil to depths up to 700 feet,” Tiedje said. “This zone supports most life on the planet as it regulates essential processes like soil formation, water cycling and nutrient cycling, which are vital for food production, water quality and ecosystem health. Despite its importance, the deep Critical Zone is a new frontier because it’s a major part of Earth that is relatively unexplored.”

The Cognitive Doppelgänger: AI Understanding and the Mirror of Human Consciousness
Perhaps the most profound insight to emerge from this uncanny mirror is that understanding itself may be less mysterious and more mechanical than we have traditionally believed. The capabilities we associate with mind — pattern recognition, contextual awareness, reasoning, metacognition — appear increasingly replicable through purely algorithmic means. This suggests that consciousness, rather than being a prerequisite for understanding, may be a distinct phenomenon that typically accompanies understanding in biological systems but is not necessary for it.
At the same time, the possibility of quantum effects in neural processing reminds us that the mechanistic view of mind may be incomplete. If quantum retrocausality plays a role in consciousness, then our subjective experience may be neither a simple product of neural processing nor an epiphenomenal observer, but an integral part of a temporally complex causal system that escapes simple deterministic description.
What emerges from this consideration is not a definitive conclusion about the nature of mind but a productive uncertainty — an invitation to reconsider our assumptions about what constitutes understanding, agency, and selfhood. AI systems function as conceptual tools that allow us to explore these questions in new ways, challenging us to develop more sophisticated frameworks for understanding both artificial and human cognition.

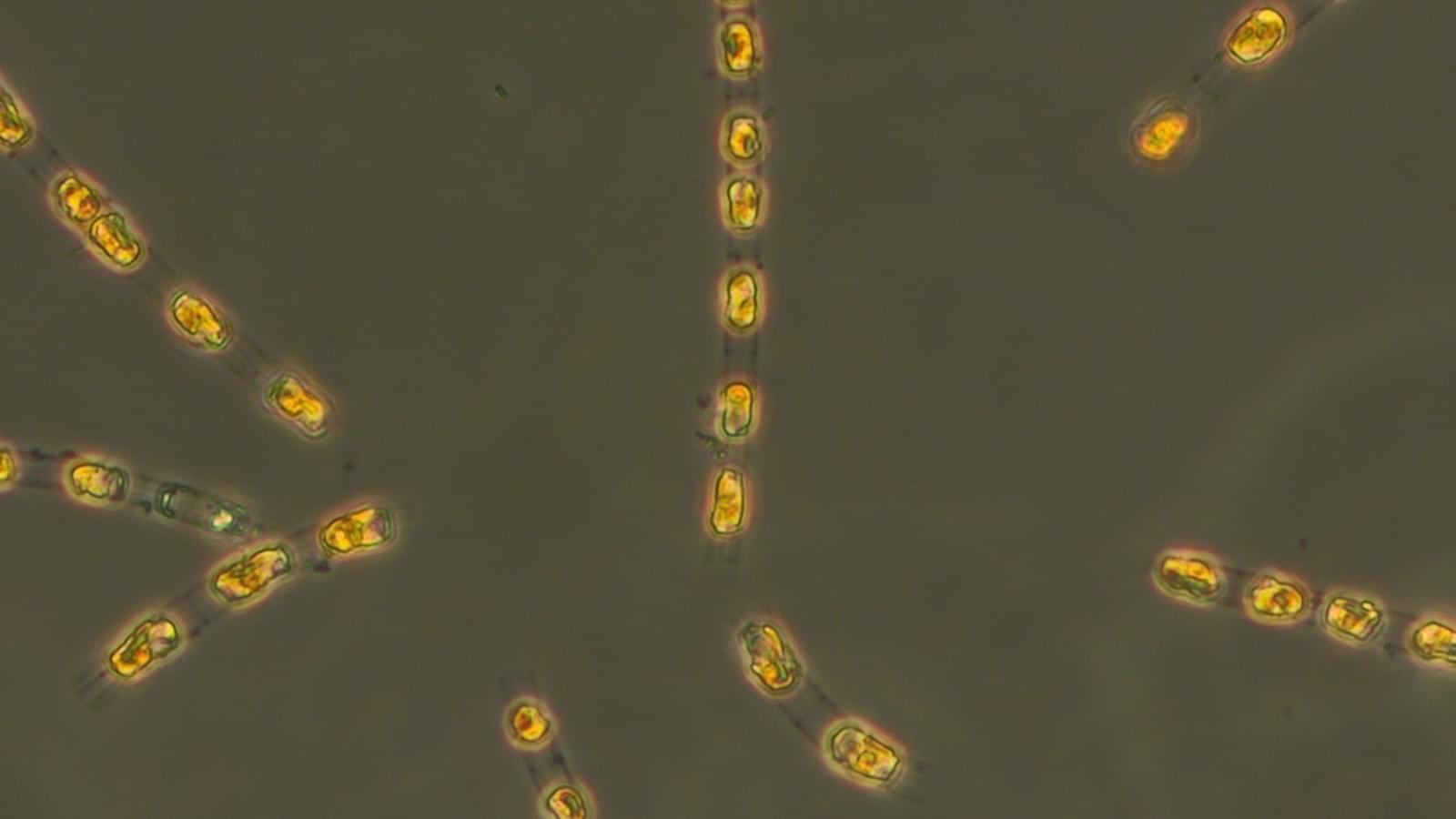

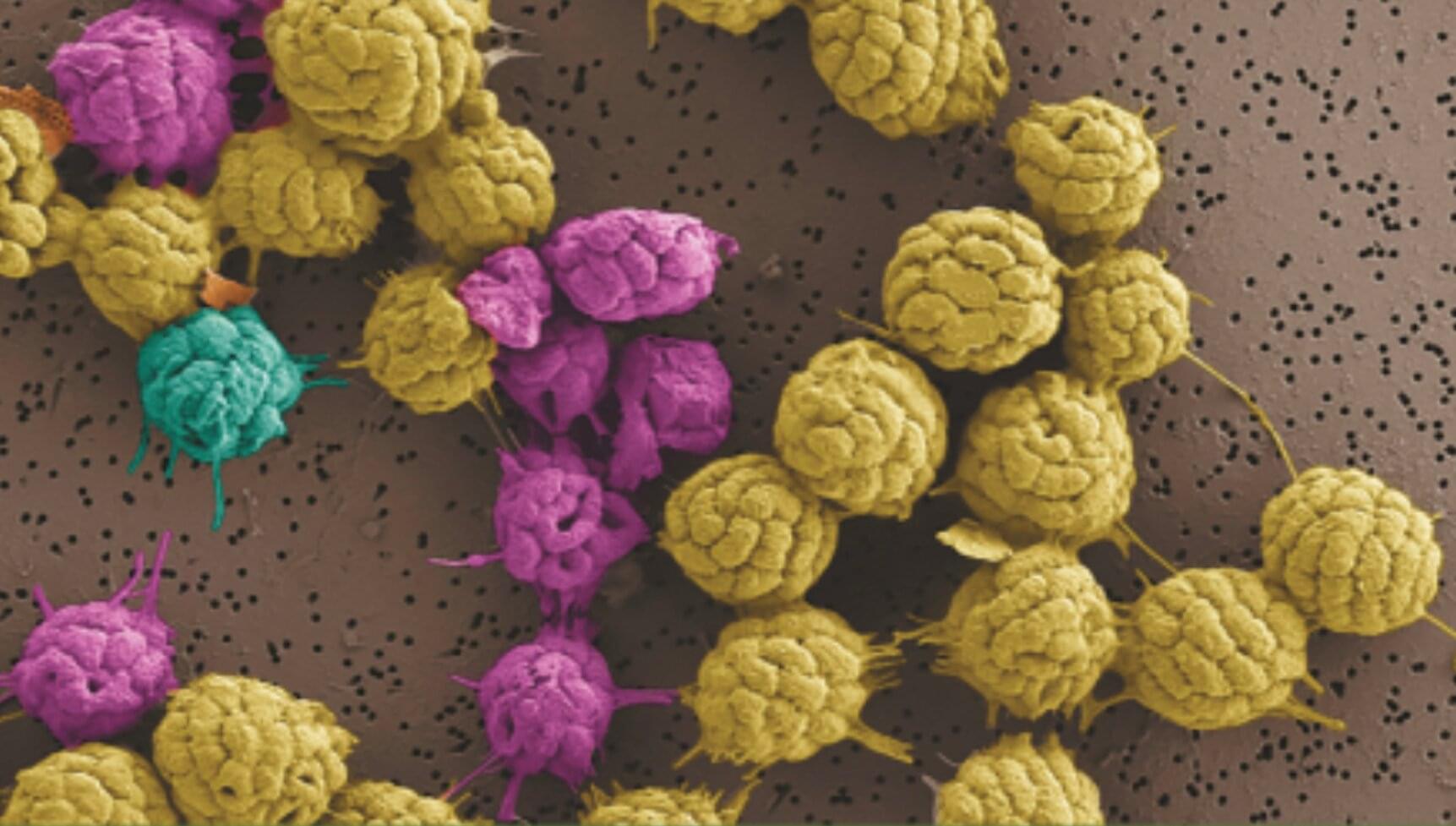
Unique bacteria that survive by employing multicellular behavior offer clues to life’s evolution
In a recent study, researchers gained new insight into the lives of bacteria that survive by grouping together as if they were a multicellular organism. The organisms in the study are the only bacteria known to do this in this way, and studying them could help astrobiologists explain important steps in the evolution of life on Earth.
The work is published in the journal PLOS Biology.
The organisms in the study are known as multicellular magnetotactic bacteria (MMB). Being magnetotactic means that MMB are part of a select group of bacteria that orient their movement based on Earth’s magnetic field using tiny “compass needles” in their cells. As if that weren’t special enough, MMB also live bunched up in collections of cells that are considered by some scientists to exhibit “obligate” multicellularity, the trait on which the new study is focused.
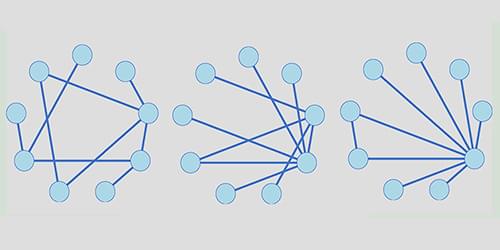
The Reconstructability of Networks
Network models provide a flexible way of representing objects and their multifaceted relationships. Deriving a network entails mapping hidden structures in inevitably noisy data—a critical task known as reconstruction. Now Gang Yan and Jia-Jie Qin of Tongji University in China have provided a mathematical proof showing what makes some networks easier to reconstruct than others [1].
Complex systems in biology, physics, and social sciences tend to involve a vast number of interacting entities. In a network model, these entities are represented by nodes, linked by connections weighted to describe the strength of each interaction. Yan and Qin took an empirical dataset and used a statistical inference method to calculate the likelihood that any pair of nodes is directly linked. Then, based on the true positive and false positive rates of these inferred connections, they analyzed the fidelity of the reconstructed networks. They found that the most faithful reconstructions are obtained with systems for which the number of connections per node varies most widely across the network. Yan and Qin saw the same tendency when they tested their model on synthetic and real networks, including metabolic networks, plant-pollinator webs, and power grids.
With the rapid increase in available data across research areas, network reconstruction has become an important tool for studying complex systems. Yan and Qin say their new result both solves the problem of what complex systems can be easily mapped into a network and provides a solid foundation for developing methods of doing so.