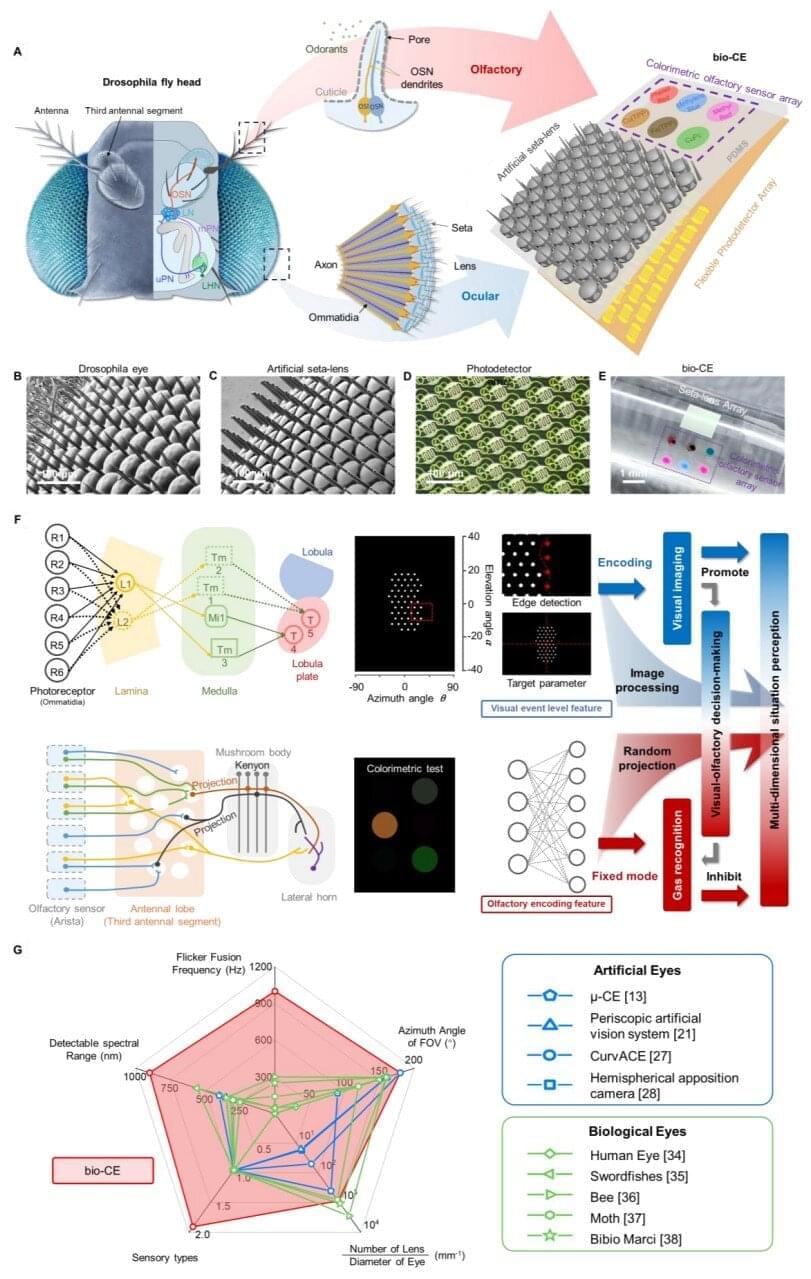
The compound eyes of the humble fruit fly are a marvel of nature. They are wide-angle and can process visual information several times faster than the human eye. Inspired by this biological masterpiece, researchers at the Chinese Academy of Sciences have developed an insect-scale compound eye that can both see and smell, potentially improving how drones and robots navigate complex environments and avoid obstacles.
Traditional cameras on robots and drones may excel at capturing high-definition photos, but struggle with a narrow field of view and limited peripheral vision. They also tend to be bulky and power-hungry.