This study demonstrated that APOE genotype significantly affects Parkinson disease clinical, biological, and neurophysiologic profiles since disease onset.
Background and Objectives.

Imaging technology has transformed how we observe the universe—from mapping distant galaxies with radio telescope arrays to unlocking microscopic details inside living cells. Yet despite decades of innovation, a fundamental barrier has persisted: capturing high-resolution, wide-field images at optical wavelengths without cumbersome lenses or strict alignment constraints.
A new study by Guoan Zheng, a biomedical engineering professor and the director of the UConn Center for Biomedical and Bioengineering Innovation (CBBI), and his research team at the UConn College of Engineering, was published in Nature Communications, introducing a breakthrough solution that could redefine optical imaging across science, medicine, and industry.
“At the heart of this breakthrough is a longstanding technical problem,” said Zheng. “Synthetic aperture imaging—the method that allowed the Event Horizon Telescope to image a black hole—works by coherently combining measurements from multiple separated sensors to simulate a much larger imaging aperture.”
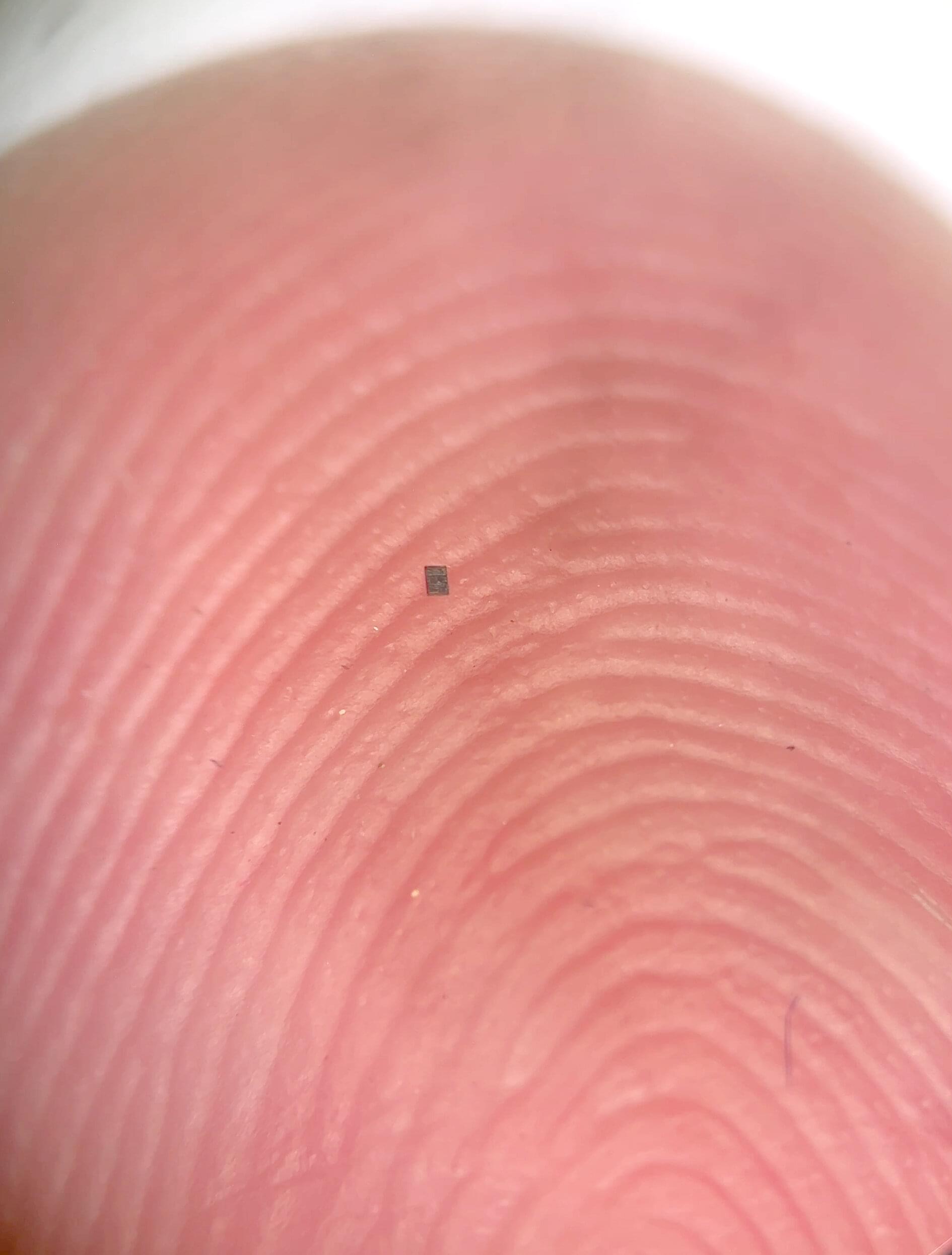

Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania and University of Michigan have created the world’s smallest fully programmable, autonomous robots: microscopic swimming machines that can independently sense and respond to their surroundings, operate for months and cost just a penny each.
Barely visible to the naked eye, each robot measures about 200 by 300 by 50 micrometers, smaller than a grain of salt. Operating at the scale of many biological microorganisms, the robots could advance medicine by monitoring the health of individual cells and manufacturing by helping construct microscale devices.
Powered by light, the robots carry microscopic computers and can be programmed to move in complex patterns, sense local temperatures and adjust their paths accordingly.
For over a century, Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been considered irreversible. Consequently, research has focused on disease prevention or slowing, rather than recovery. Despite billions of dollars spent on decades of research, there has never been a clinical trial of a drug for AD with an outcome goal of reversing disease and recovering function.
Now, a research team from University Hospitals, Case Western Reserve University, and the Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center has challenged this long-held dogma in the field. They tested whether brains already badly afflicted with advanced AD could recover.
The study, led by Kalyani Chaubey, Ph.D., from the Pieper Laboratory, is published in Cell Reports Medicine.
Researchers have developed experimental drugs that encourage the mitochondria in our cells to work a little harder and burn more calories. The findings could open the door to new treatments for obesity and improve metabolic health.
Obesity is a global epidemic and a risk factor for many diseases, including diabetes and cancer. Current obesity drugs require injections and can cause side effects, so a safe way to boost weight loss could deliver significant public health benefits.
The study, led by Associate Professor Tristan Rawling from the University of Technology Sydney (UTS), has just been published in Chemical Science, where it was highlighted as “pick of the week.”
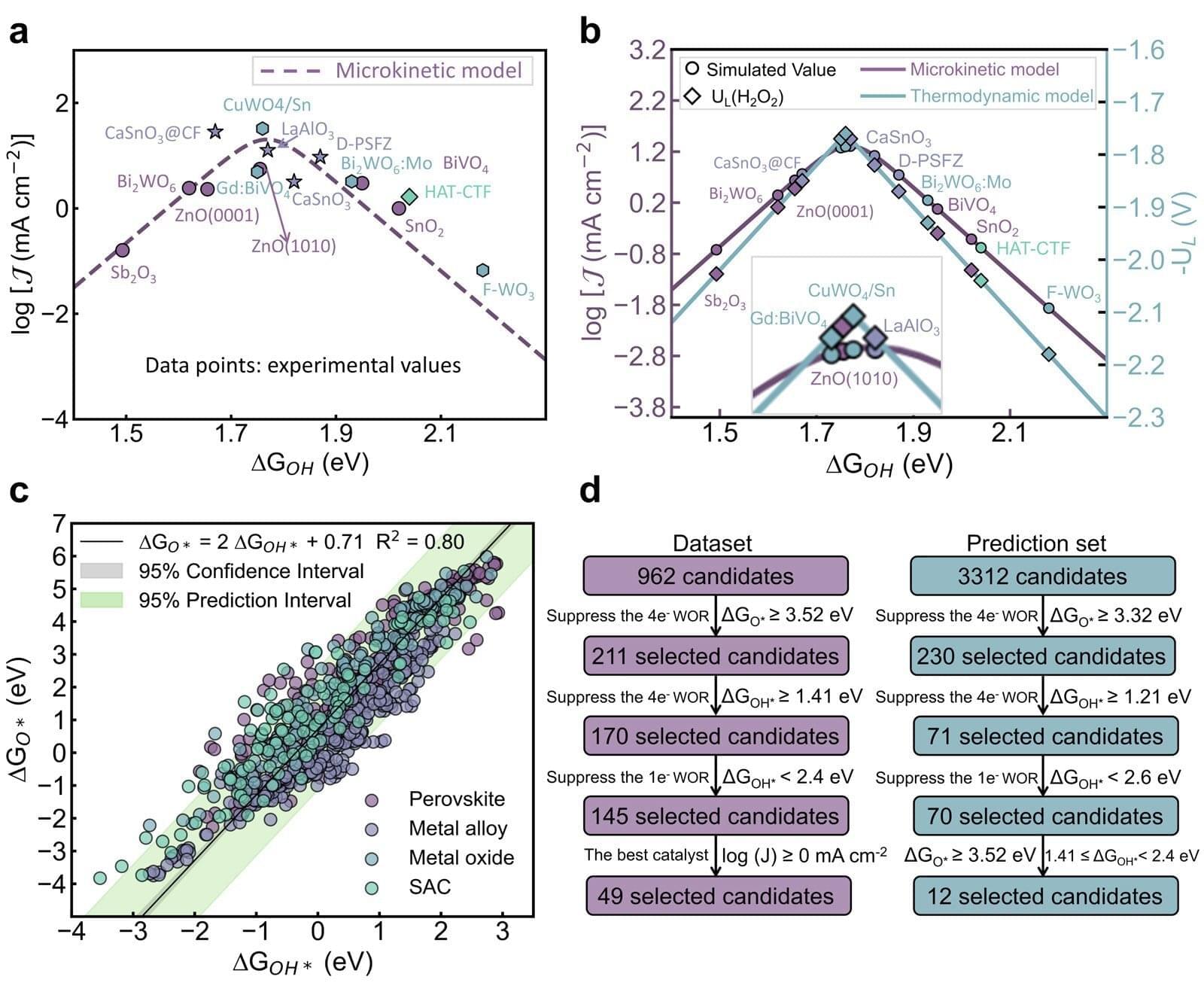
Hydrogen peroxide is widely used in everyday life, from disinfectants and medical sterilization to environmental cleanup and manufacturing. Despite its importance, most hydrogen peroxide is still produced using large-scale industrial processes that require significant energy. Researchers are thus seeking cleaner alternatives.
A team of researchers has made a breakthrough in this regard, developing a new computational framework that helps identify effective catalysts for producing hydrogen peroxide directly from water and electricity.
The work focuses on the two-electron water oxidation reaction, an electrochemical process that can generate hydrogen peroxide in a more localized and potentially sustainable way.


New research suggests that specific personality traits may amplify the way childhood adversity shapes an individual’s approach to life. A study published in the journal Personality and Individual Differences provides evidence that subclinical psychopathy strengthens the link between childhood trauma and “fast” life history strategies. The findings indicate that for those who have experienced severe early difficulties, certain dark personality traits may function as adaptive mechanisms for survival.
Psychologists use a framework called Life History Theory to explain how people allocate their energy. This theory proposes that all living organisms must make trade-offs between investing in their own growth and investing in reproduction. These trade-offs create a spectrum of strategies that range from “fast” to “slow.”
A fast life history strategy typically emerges in environments that are harsh or unpredictable. Individuals with this orientation tend to prioritize immediate rewards and reproduction over long-term planning. They often engage in riskier behaviors and invest less effort in long-term relationships. This approach makes evolutionary sense when the future is uncertain.

Research from Mass General Brigham suggests that this increased risk is driven by stress-related brain activity, nervous system dysregulation, and chronic inflammation.
They also found that patients with both depression and anxiety were at even higher risk of cardiovascular disease than those diagnosed with just one condition.