The relevance of the gut microbiome, the community of microorganisms living in the digestive tract, to human health is a topic of intense interest. However, among the numerous benevolent bacteria living in the gut, there are some species that are harmful to humans.
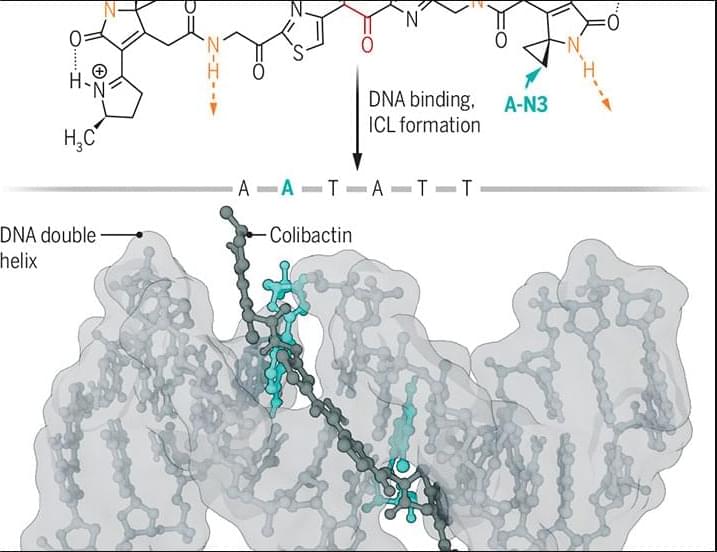
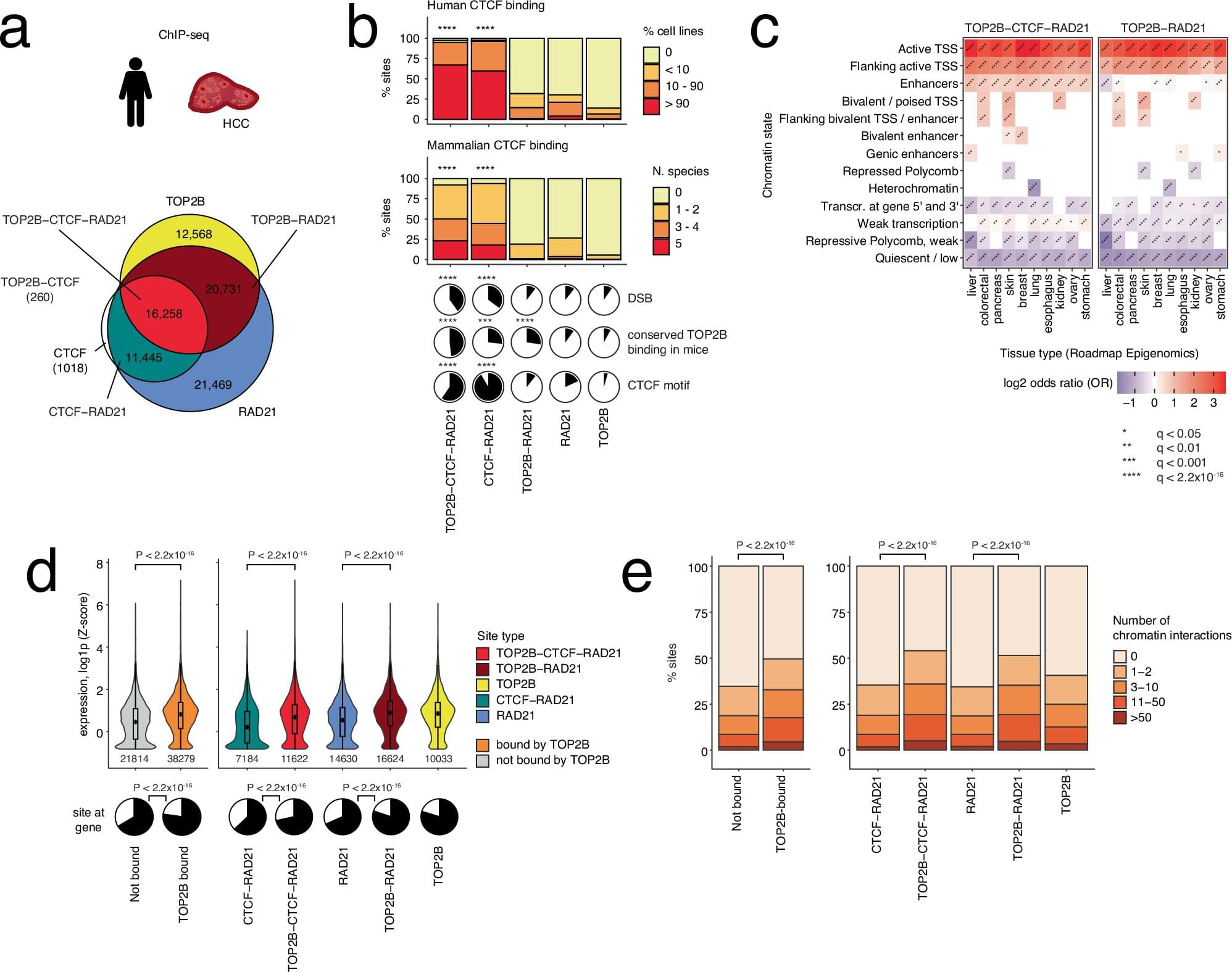
For example, certain strains of Escherichia coli produce the genotoxin colibactin, which causes DNA damage and is linked with colon cancer. However, the colibactin molecule is complex and unstable, which has made it challenging to elucidate its chemical structure and the mechanism by which it damages DNA. In the culmination of years of research from multiple laboratories, researchers in a new Science study reveal the structure of the active form of colibactin bound to DNA.
The findings go a long way toward explaining the mutation signatures associated with colibactin exposure and provide substantial insight into how colibactin contributes to colorectal carcinogenesis.
Learn more in a new Science Perspective.
The structure of the bacterial genotoxin colibactin bound to DNA shows how it might contribute to cancer risk.