Research led by Sichuan University and Huazhong University of Science and Technology, China, has revealed genetic mechanisms that could prolong healthy aging. In the paper, titled “Partial inhibition of class III PI3K VPS-34 ameliorates motor aging and prolongs health span,” published in PLOS Biology, the team details the methods they used to narrow down the potential genomic pathways to a single gene that could be critical to extending healthy human longevity.
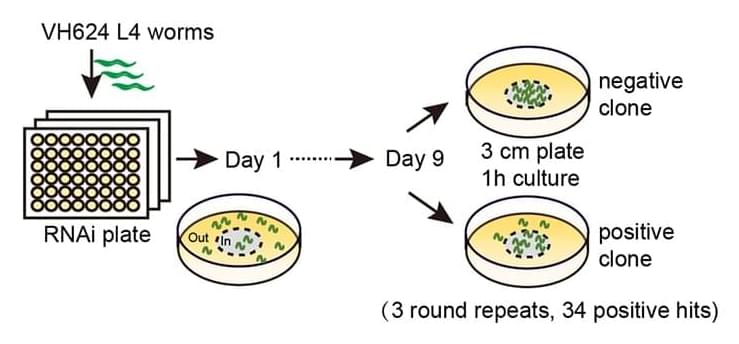
With a combination of genetic manipulation, behavioral assays, microscopy techniques, and electrophysiology, the researchers investigated the role of VPS-34 in motor aging. These methods allowed the researchers to gain insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying motor aging and the effects of VPS-34 inhibition on motor function, synaptic transmission, and muscle integrity.
According to the authors, increased life expectancy in recent decades has not been accompanied by a corresponding increase in health span. Aging is characterized by the decline of multiple organs and tissues and motor aging, in particular, leads to frailty, loss of motor independence, and other age-related issues. Identifying mechanisms for therapeutics to delay motor aging is crucial for promoting healthy aging.