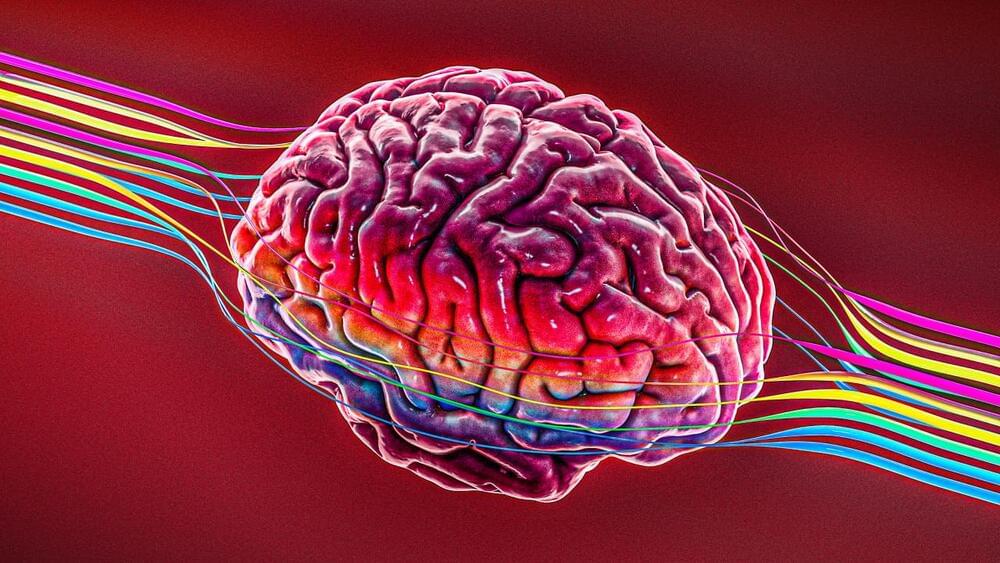
A paralyzed individual controls a neuroprosthetic without daily recalibration.



If “junk” DNA goes toxic, does that suggest it had an original normal function? See the conclusion of this new paper, “Native functions of short tandem repeats” (emphasis added):
Historically, repetitive elements within human genomes have been viewed as mostly unregulated ‘junk DNA’ that is not under selective evolutionary pressure. As such expansions of these repetitive elements are unfortunate accidents which become apparent and important only when they elicit highly penetrant and syndromic human diseases. Consistent with this line of reasoning, the field of REDs [Repetitive Element Diseases] has largely focused on emergent toxic mechanisms as drivers of disease only in the setting of large STR [Short Tandem Repeats] expansions rather than considering their pathology as alterations in the native functions played by these repeats in their normal genomic contexts. Here, we propose re-framing the discussion around repetitive elements in general — and STRs in particular — within human genomes.
For a while now, we’ve known there’s a complex interplay between our hormones, guts, and mental health, but untangling the most relevant connections within our bodies has proved challenging.
New research has found a single enzyme that links all three, and its presence may be responsible for depression in some women during their reproductive years.
Wuhan University medical researcher Di Li and colleagues compared the blood serum of 91 women aged between 18 and 45 years with depression and 98 without. Incredibly, those with depression had almost half the serum levels of estradiol – the primary form of estrogen our bodies use during our fertile years.
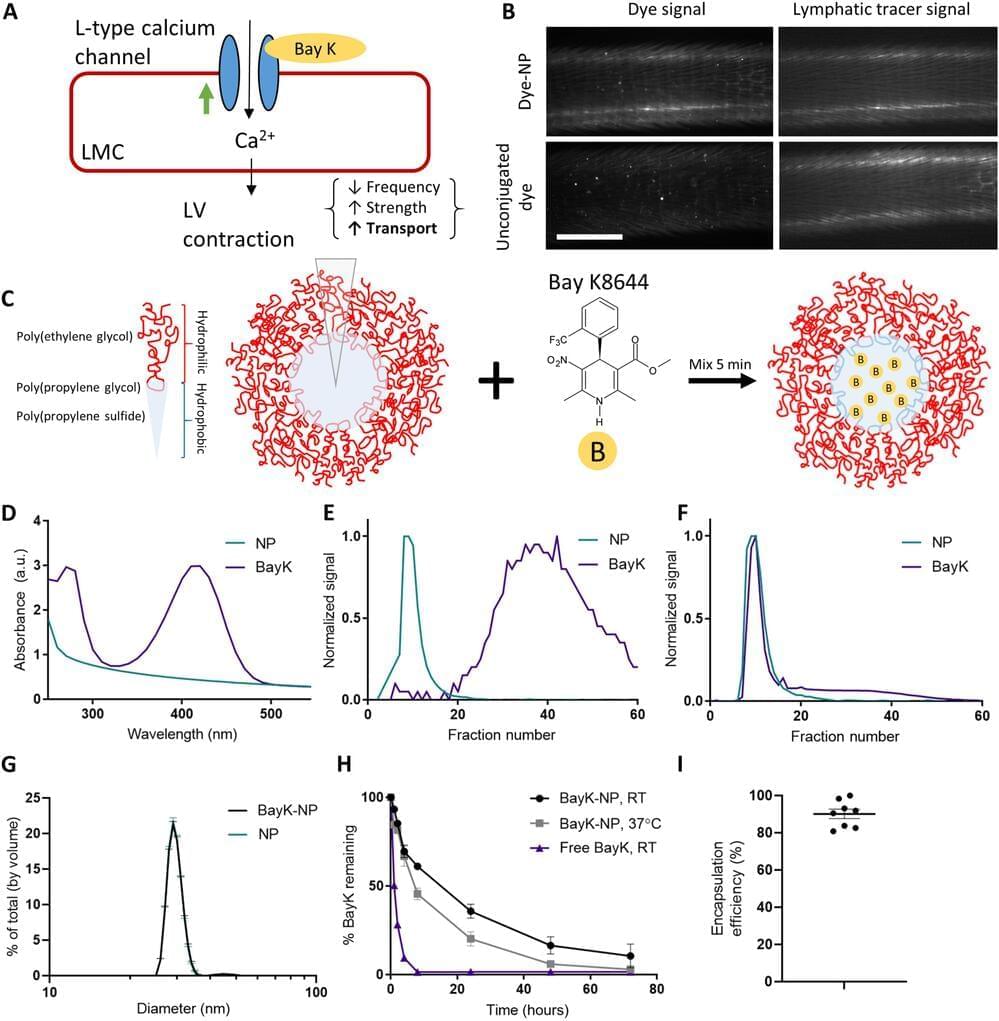
The human body is made up of thousands of tiny lymphatic vessels that ferry white blood cells and proteins around the body, like a superhighway of the immune system. It’s remarkably efficient, but if damaged from injury or cancer treatment, the whole system starts to fail. The resulting fluid retention and swelling, called lymphedema, isn’t just uncomfortable—it’s also irreversible.
When lymphatic vessels fail, typically their ability to pump out the fluid is compromised. Georgia Institute of Technology researchers have developed a new treatment using nanoparticles that can repair lymphatic vessel pumping. Traditionally, researchers in the field have tried to regrow lymphatic vessels, but repairing the pumping action is a unique approach.
“With many patients, the challenge is that the lymphatic vessels that still exist in the patient aren’t working. So it’s not that you need to grow new vessels that you can think of as tubes, it’s that you need to get the tubes to work, which for lymphatic vessels means to pump,” said Brandon Dixon, a professor in the George W. Woodruff School of Mechanical Engineering. “That’s where our approach is really different. It delivers a drug to help lymphatic vessels pump using a nanoparticle that can drain into the diseased vessels themselves.”
Growing brains can be a tricky process, but growing ones that can make muscles move? That’s an incredible feat. Here’s how scientists did it.
How Close Are We to Farming Human Body Parts? — https://youtu.be/oRHxX9OW9ow.
Cerebral organoids at the air-liquid interface generate nerve tracts with functional output.
https://www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/cerebral-organoids-at-the-air…al-output/
“The capacity for this model to be used to investigate the way in which neurons connect up within the brain and with the spinal cord could have important implications for our understanding of a range of diseases. In particular defects in neuronal connectivity are thought to underlie various psychiatric illnesses, including schizophrenia, autism, and depression. ”
Cerebral organoids at the air–liquid interface generate diverse nerve tracts with functional output.
https://www.readcube.com/articles/10.1038/s41593-019-0350-2
“Finally, through electrophysiological and co-culture studies, we demonstrate functionality of these tracts, which are even capable of eliciting coordinated muscle contractions in co-cultured mouse spinal cord–muscle explants. This approach is likely to be a useful new tool, not only because of its ease, but also due to its util-ity in studying axon guidance, tract formation, and connectivity in a human system”
What’s Wrong With Growing Blobs of Brain Tissue?
https://www.theatlantic.com/science/archive/2018/04/what-hap…ns/558881/
“The stuff we really care about in the brain, like consciousness, are emergent phenomena—they arise from the collective workings of individual neurons, which create a whole that’s greater than the sum of its parts. The problem is that we don’t know at what level these phenomena emerge. A neuron is not conscious. A person is. What about all the steps in the middle? What about 2 million neurons? 20 million? 200 million?”
Elements is more than just a science show. It’s your science-loving best friend, tasked with keeping you updated and interested on all the compelling, innovative and groundbreaking science happening all around us. Join our passionate hosts as they help break down and present fascinating science, from quarks to quantum theory and beyond.

Researchers at Texas A&M University have developed the first molecular therapeutic for Angelman syndrome to advance into clinical development.
In a new article, published today in Science Translational Medicine, Dr. Scott Dindot, an associate professor and EDGES Fellow in the Texas A&M School of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences’ (VMBS) Department of Veterinary Pathobiology, and his team share the process through which they developed this novel therapeutic candidate, also known as 4.4.PS.L, or GTX-102. Dindot is also the executive director of molecular genetics at Ultragenyx, which is leading the development of GTX-102.
Angelman syndrome (AS) is a devastating, rare neurogenetic disorder that affects approximately 1 in 15,000 live births per year; the disorder is triggered by a loss of function of the maternal UBE3A gene in the brain, causing developmental delay, absent speech, movement or balance disorder, and seizures.
More than 150 million women worldwide use oral contraceptives to avoid unwanted pregnancies. However, a bombshell study released by researchers at the University of Oxford has now laid bare the risks involved. The study has reportedly established the link between the usage of progestogen and the increased risk of breast cancer.
Scientists from German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), together with colleagues from Germany, Israel, and the U.S., have found that the gut microbiome may modulate the efficacy of CAR-T cellular immunotherapy CAR-T cells in patients with B cell lymphomas. Individualized microbiome information retrieved from patients’ gut microbiomes prior to initiation of CAR T therapy could accurately predict their subsequent responsiveness to therapy, but only in the condition that these patients were not pre-treated with broad spectrum antibiotics.
Increasing evidence from human studies and preclinical experiments suggests that the gut microbiome may modulate the efficacy of T cell-driven cancer immunotherapies, such as immune checkpoint blockade. Immunotherapy with CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell has opened up new treatment options for patients with certain forms of refractory and relapsing B-cell leukemias or lymphomas. But the therapy is hampered by considerable heterogeneity in responses. Complete and long-term remission is only achieved in up to 40% of patients.
Researchers from multiple centers in Germany and the United States, led by Eran Elinav, director of the DKFZ-Weizmann Institute of Science Microbiome & Cancer Bridging division, have found that the gut microbiome may modulate the efficacy of CD19 CAR-T cell immunotherapy in patients with B cell leukemias and lymphomas.