When the right gene is expressed in the right manner in the right population of stem cells, the developing mouse brain can exhibit primate-like features. In a paper publishing August 7th in the Open Access journal PLOS Biology, researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics (MPI-CBG) succeeded in mimicking the sustained expression of the transcription factor Pax6 as seen in the developing human brain, in mouse cortical progenitor cells. This altered the behavior of these cells to one that is akin to that of progenitors in the developing primate neocortex. Consequently, the mouse progenitors generated more neurons — a prerequisite for a bigger brain.
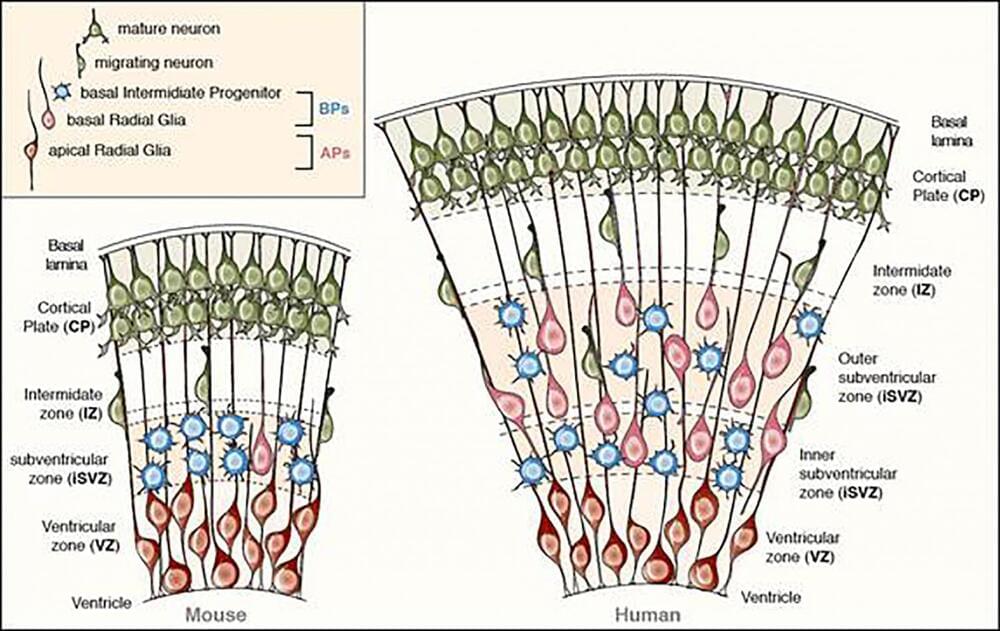
The neocortex consists of different types of progenitors, but one particular class, the basal progenitors, behave differently in small-brained animals such as mice than in large-brained animals such as humans. In humans, basal progenitors can undergo multiple rounds of cell division, thereby substantially increasing neuron number and ultimately the size of the neocortex. In mice, these progenitors typically undergo only one round of cell division, thus limiting the number of neurons produced. A potential cause underlying this difference in the proliferative capacity of basal progenitors could be the differential expression of Pax6 between species. Mouse basal progenitors, in contrast to human, do not express Pax6. “We were very curious to see what would happen if we were to change the expression pattern of Pax6 in developing mouse brain to mimic that observed in large-brained animals”, says Fong Kuan Wong, a PhD student in the lab of Wieland Huttner and first author of the study.
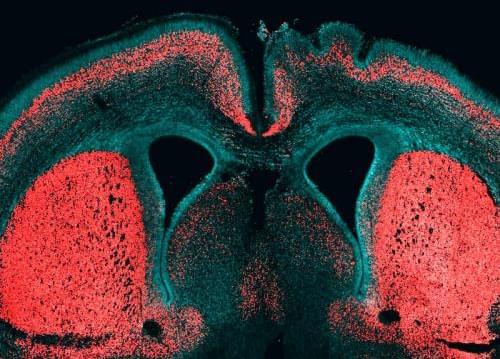
To this end, another PhD student in the lab, Ji-Feng Fei, generated a novel transgenic mouse line. This line provided the basis for altering the expression of Pax6 in the cortical stem cell lineage such that it would be sustained in basal progenitors. The researchers then introduced the Pax6 gene into the stem cells of these mice. Strikingly, sustaining Pax6 expression in mouse basal progenitors increased their capacity to undergo multiple rounds of cell division, as typically observed in primates. This not only expanded the size of the basal progenitor population in a way somewhat reminiscent to what is seen in large-brained animals. It also resulted in an increase in cortical neurons, notably those in the top layer, another characteristic feature of an expanded neocortex.