Researchers at Bar-Ilan University have discovered how the longevity-associated protein Sirt6 orchestrates a delicate molecular balancing act that protects the body from age-related decline and disease. The new findings, just published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, reveal how Sirt6 preserves health during aging and may pave the way for therapies that promote a longer, healthier life.
Sirt6, often described as a master regulator of aging, is known for its powerful protective effects against age-related diseases such as cancer, diabetes, inflammation, and frailty. Its impact closely resembles that of calorie restriction, a dietary regimen proven in animals to extend lifespan and enhance the body’s natural repair and healing mechanisms.
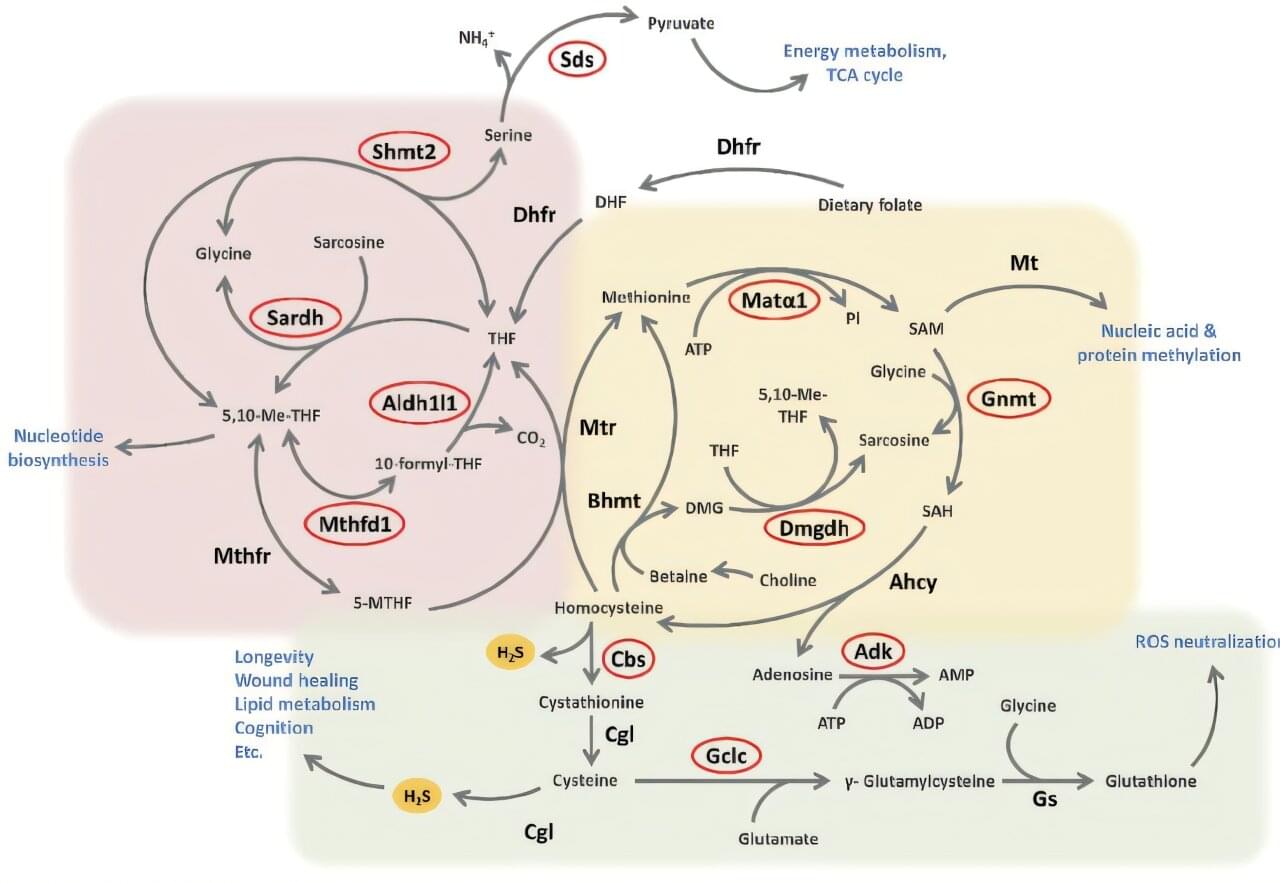
Calorie restriction—eating fewer calories without malnutrition—has long been known to improve health and extend lifespan. One of its key effects is to increase the body’s production of hydrogen sulfide (H2S), a tiny gas molecule that supports wound healing, heart health, and brain function. This new study found that as we age, H2S levels naturally decline, weakening these protective benefits.