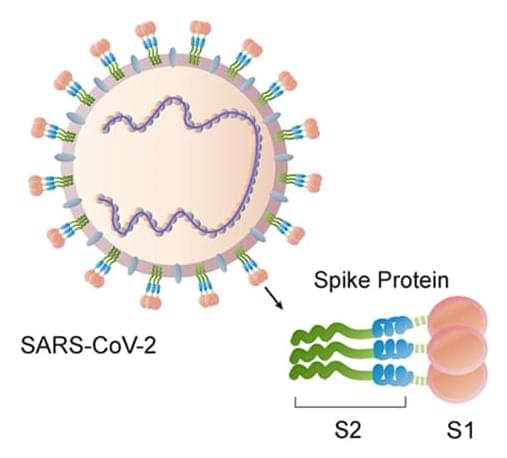
A universal coronavirus vaccine “could solve the problem of endless new waves of disease caused by variants with reduced vaccine sensitivity”.
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute in London have shown that a specific area of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is a promising target for a pan-coronavirus vaccine that could offer protection against new variants, as well as common colds, and help prepare for future pandemics.
Developing a vaccine against multiple coronaviruses is a challenge because this family of viruses have many key differences, frequently mutate, and generally induce incomplete protection against reinfection. This is why people can suffer repeatedly from common colds, and why it is possible to be infected multiple times with different variants of SARS-CoV-2.
A pan-coronavirus vaccine would need to trigger antibodies that recognise and neutralise a range of coronaviruses – stopping the virus from entering host cells and replicating.