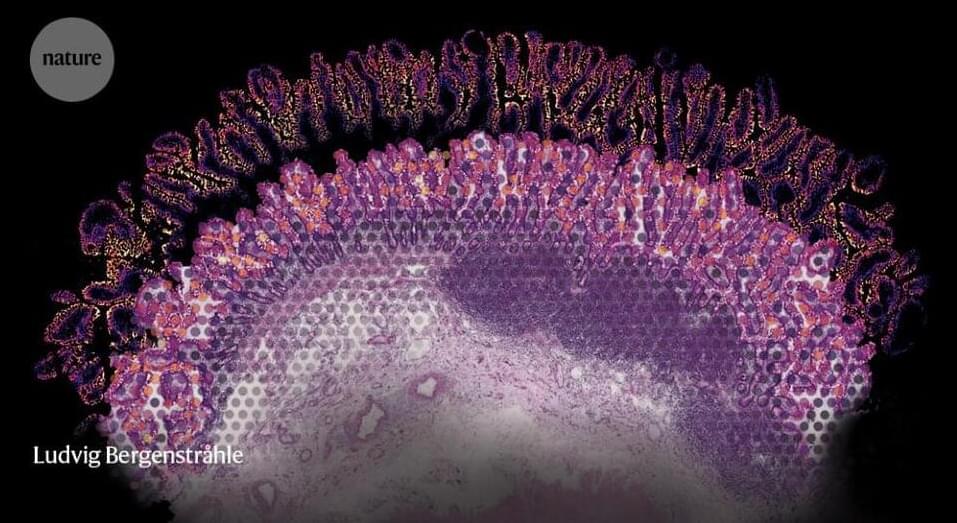
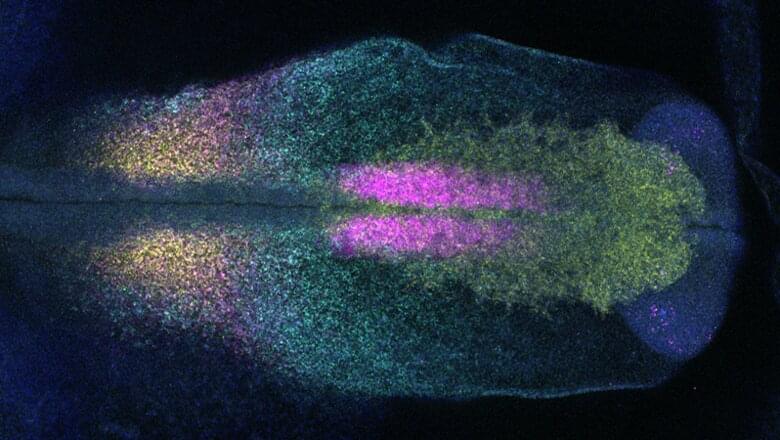
Under a microscope, mammalian tissues reveal their intricate and elegant architectures. But if you look at the same tissue after tumour formation, you will see bedlam. Itai Yanai, a computational biologist at New York University’s Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, is trying to find order in this chaos. “There is a particular logic to how things are arranged, and spatial transcriptomics is helping us see that,” he says.
‘Spatial transcriptomics’ is a blanket term covering more than a dozen techniques for charting genome-scale gene-expression patterns in tissue samples, developed to complement single-cell RNA-sequencing techniques. Yet these single-cell sequencing methods have a downside — they can rapidly profile the messenger RNA content (or transcriptome) of large numbers of individual cells, but generally require physical disruption of the original tissue, which sacrifices crucial information about how cells are organized and can alter them in ways that might muddy later analyses. Immunologist Ido Amit at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel, says that such experiments would sometimes leave his group questioning their results. “Is this really the in situ state, or are we just looking at something which is either not a major [factor] or even not real at all?”
By contrast, spatial transcriptomics allows researchers to study gene expression in intact samples, opening frontiers in cancer research and revealing previously inaccessible biology of otherwise well-characterized tissues. The resulting ‘atlases’ of spatial information can tell scientists which cells make up each tissue, how they are organized and how they communicate. But compiling those atlases isn’t easy, because methods for spatial transcriptomics generally represent a tension between two competing goals: broader transcriptome coverage and tighter spatial resolution. Developments in experimental and computational methods are now helping researchers to balance those aims — and improving cellular resolution in the process.