Sascha Roth remembers the phone call came on a hectic Friday evening.
She was racing around her home in Washington, D.C., to pack for New York, where she was scheduled to undergo weeks of radiation therapy for rectal cancer. But the phone call from Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) medical oncologist Andrea Cercek changed everything, leaving Sascha “stunned and ecstatic — I was so happy.”
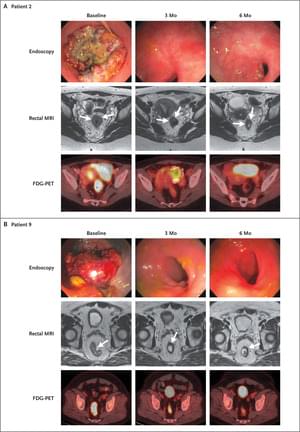
Dr. Cercek told Sascha, then 38, that her latest tests showed no evidence of cancer, after Sascha had undergone six months of treatment as the first patient in a clinical trial involving immunotherapy at MSK.
Rectal cancer patients saw their tumors disappear in a clinical trial involving immunotherapy at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center—without surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.