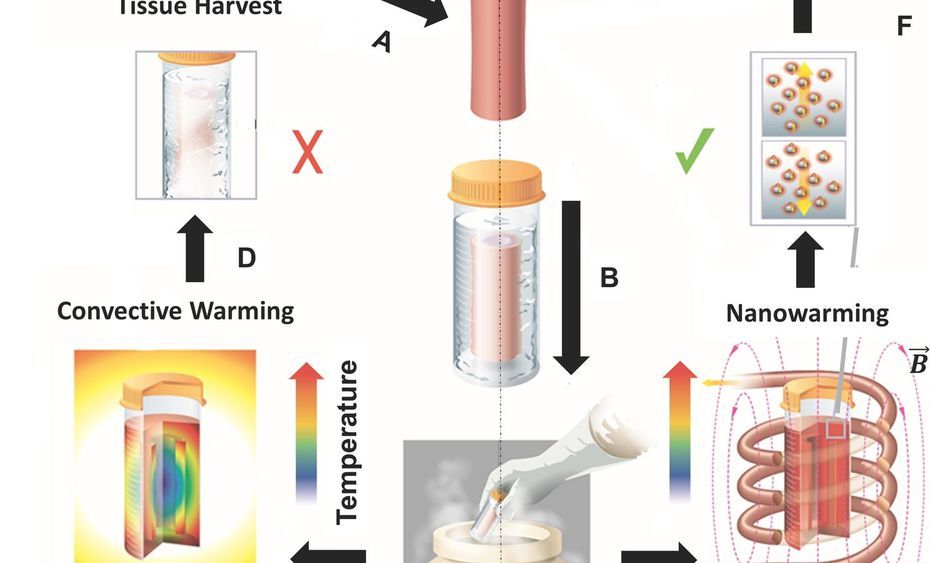
This technology may one day be used to revive patient suspended in cryonics.
A new way to warm up frozen tissue using tiny vibrating particles could one day help with the problem of organ shortages.
We know how to cool organs to cryogenic temperatures, which is usually below 320 degrees Fahrenheit. But the organs can’t be stored for long — sometimes only four hours for heart and lungs — because they get damaged when you try to warm them up. As a result, more than 60 percent of donor hearts and lungs aren’t transplanted. In a study published today in Science Translational Medicine, scientists used nanoparticles to warm up frozen tissue quickly and without damaging the organs. Within a decade, this could lead to being able to store entire organs in organ banks for a long period of time, the authors say.
For today’s study, the team rewarmed 50 milliliters of tissue and solution with magnetic nanoparticles. Magnetic particles create heat in electromagnetic fields, says study co-author Zhe Gao, an post-doc studying nanotechnology at the University of Minnesota. Basically, the scientists infused a tissue with a special kind of nanoparticle made of silica-coated iron oxide. Then, they expose it to a magnetic field. Think of the nanoparticles as antennae. Once they get pick up the “signal” from the magnetic fields, they start to vibrate, and this creates the heat that warms up the organ quickly.