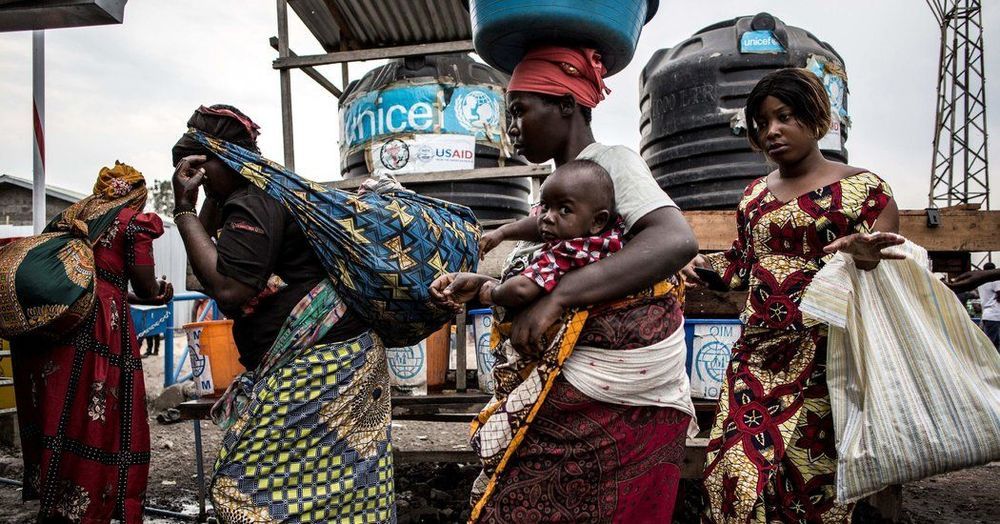
The year-old Ebola epidemic in the Democratic Republic of Congo is now considered a global health emergency, the World Health Organization said on Wednesday, in a formal declaration that many public health experts called long overdue.
“This is still a regional emergency and by no way a global threat,” said Robert Steffen of the University of Zurich, chairman of the W.H.O. emergency committee that recommended the declaration.
But the panel was persuaded by several factors that have made combating the epidemic more urgent in recent weeks: The disease reached Goma, a city of nearly two million people; the outbreak has raged for a year; the virus has flared again in spots where it had once been contained; and the epidemic hot zone has geographically expanded in northeastern Congo near Rwanda and into Uganda.