What causes the immune system, designed to protect us, to turn on the body and attack healthy cells? Common bacteria that reside in the human gut may be partly to blame, say Yale researchers, who studied the origins of a serious autoimmune disease that frequently affects young women.
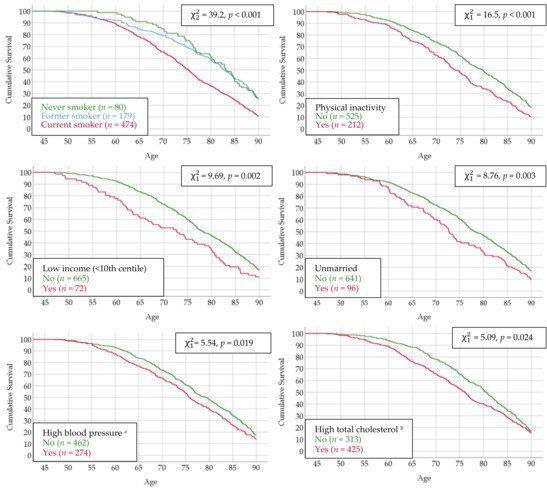
For their study, the research team focused on cells from patients with antiphospholipid syndrome, an immune system disorder that raises the risk of blood clots. This chronic condition can lead to lung clots, strokes, heart attacks, and in pregnant women, miscarriages or still births.
Using patient immune cells and antibodies, as well as animal models of the disease, the investigators did several experiments to explore the phenomenon. They found that a common gut bacterium, Roseburia intestinalis, can trigger the disease in individuals who have a genetic predisposition. In those patients, the immune system’s defender T and B cells react to a blood protein involved in clotting, and also to the bacteria, in certain amino acids found in the bacteria. Over time, this ongoing “cross-reactive” response leads to tissue damage and chronic disease.