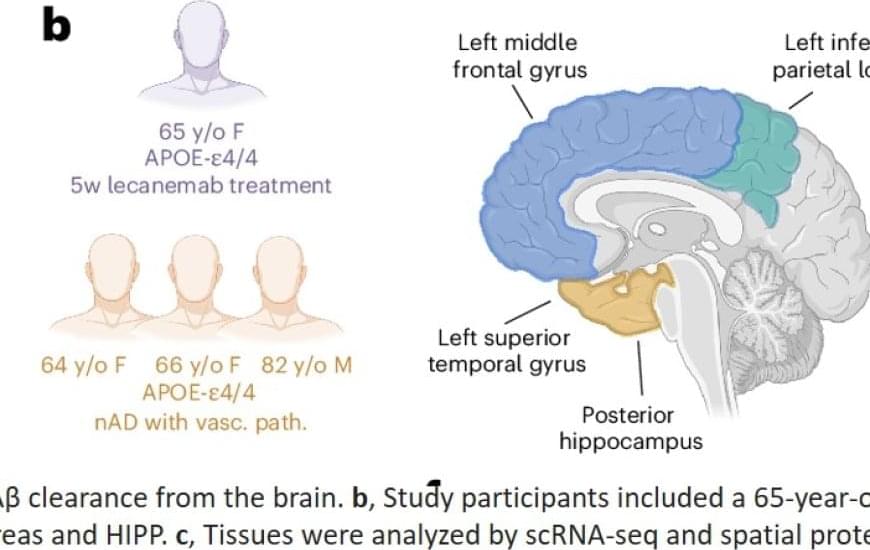
The study is the first to use a cutting-edge technique called spatial transcriptomics on human clinical-trial brains with Alzheimer’s disease. The technique allows scientists to pinpoint the specific spatial location of gene activity inside a tissue sample.
By analyzing donated brain tissue from deceased people with Alzheimer’s disease who received amyloid-beta immunization and comparing it to those who did not, the scientists found that when these treatments work, the brain’s immune cells (called microglia) don’t just clear plaques — they also help restore a healthier brain environment.
But not all microglia are created equal. Some are quite effective at removing plaques, while others struggle, the study found. Also, microglia in treated brains adopt distinct states depending on the brain region and type of immunization. Lastly, certain genes, like TREM2 and APOE, are more active in microglia in response to treatment, helping these cells remove amyloid beta plaques, according to the findings.
“The idea is that in people who already have Alzheimer’s disease, yes, you can maybe remove amyloid, but if the tau spread has been set in motion, you are fighting an uphill battle,” the author said. “But maybe, if you treat people so early that they don’t yet have tau pathology, you can stop the domino effect from happening. Our study is the first to identify the mechanisms in microglia, the brain’s immune cells, that help limit the spread of amyloid in certain brain regions following treatment with amyloid-targeting drugs.
For more than three decades, scientists have been racing to stop Alzheimer’s disease by removing amyloid beta plaques — sticky clumps of toxic protein that accumulate in the brain. Now, a new study suggests a promising alternative: enhancing the brain’s own immune cells to clear these plaques more effectively.
The findings could reshape the future of Alzheimer’s treatments, shifting the focus from simply removing plaques to harnessing the brain’s natural defenses.
Earlier attempts at an Alzheimer’s vaccine failed when the immune system’s response caused dangerous brain swelling. Even today’s FDA-approved antibody treatments remain controversial, offering only modest benefits with potential side effects and high-price points.