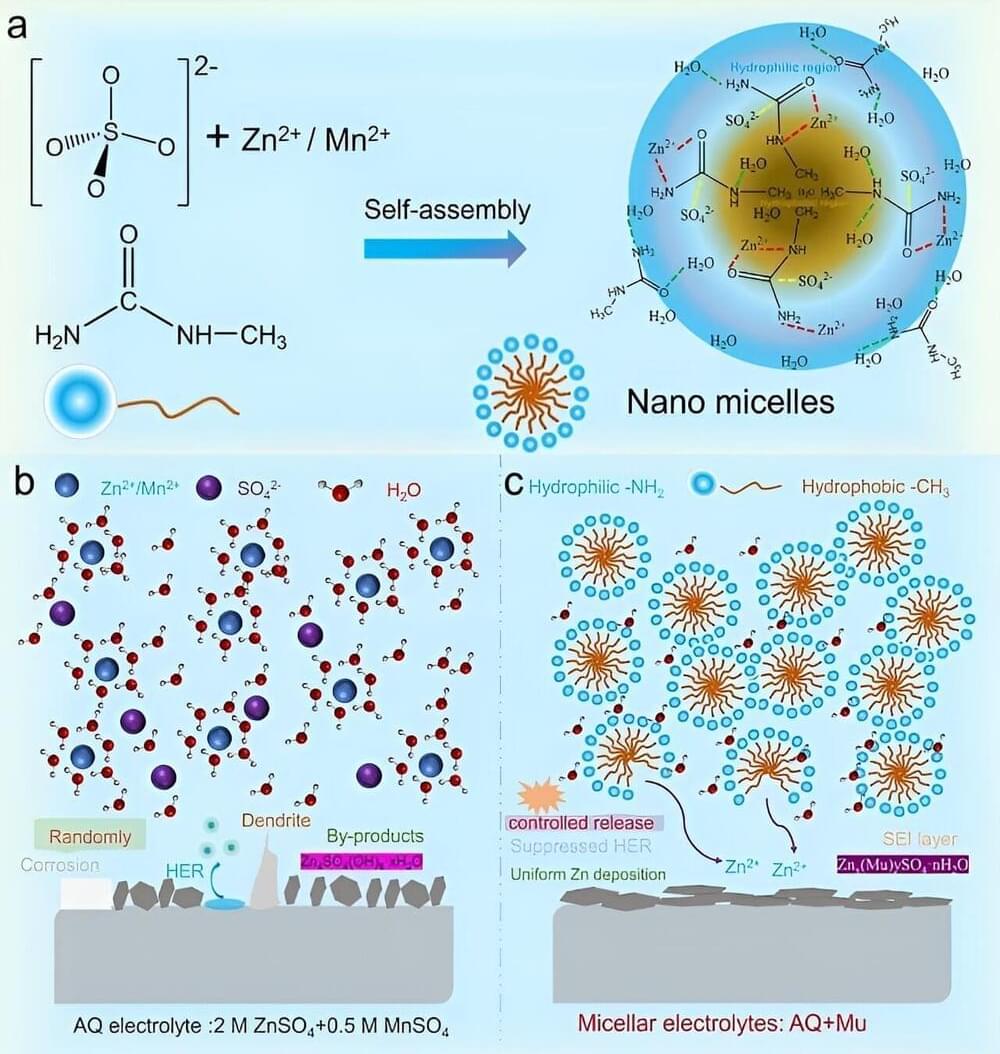
Engineering researchers at Lehigh University have discovered that sand can actually flow uphill.
The team’s findings were published today in the journal Nature Communications. A corresponding video shows what happens when torque and an attractive force is applied to each grain—the grains flow uphill, up walls, and up and down stairs.
“After using equations that describe the flow of granular materials,” says James Gilchrist, the Ruth H. and Sam Madrid Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering in Lehigh’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering and Applied Science and one of the authors of the paper, “we were able to conclusively show that these particles were indeed moving like a granular material, except they were flowing uphill.”