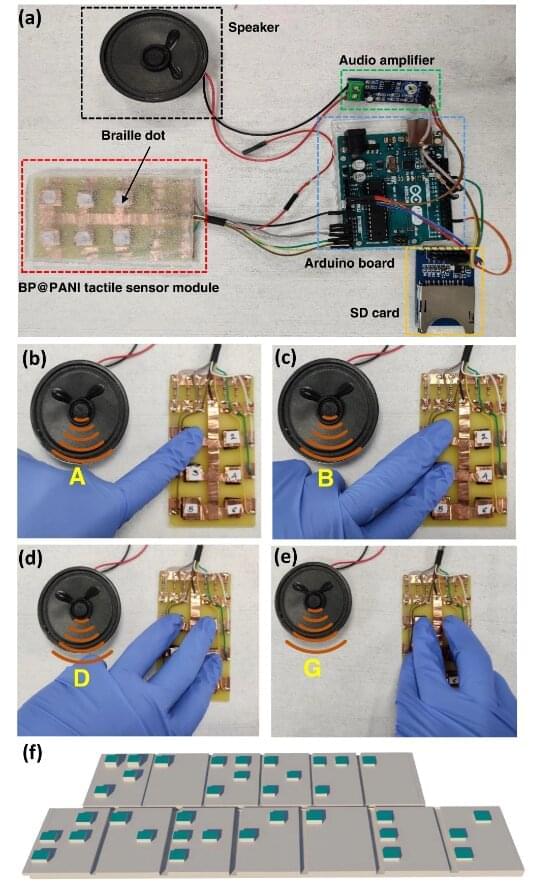
Researchers at the University of Chemistry and Technology in Prague have made progress in the field of assistive technology with the development of a novel auditory human–machine interface using black phosphorus–based tactile sensors. Research led by Prof. Martin Pumera and Dr. Jan Vyskočil has the potential to revolutionize communication for visually or speech-disabled individuals by providing an intuitive and efficient means of conveying information.
Assistive technology that utilizes auditory feedback has traditionally been employed by individuals with visual impairments or speech and language difficulties. In this study, the focus was on creating an auditory human-machine interface that utilizes audio as a platform for communication between disabled users and society. The researchers developed a piezoresistive tactile sensor using a composite of black phosphorus and polyaniline (BP@PANI) through a simple chemical oxidative polymerization process on cotton fabric.
The unique structure and superior electrical properties of black phosphorus, combined with the large surface area of the fabric, enabled the BP@PANI-based tactile sensor to exhibit exceptional sensitivity, low-pressure sensitivity, reasonable response time, and excellent cycle stability. To demonstrate the real-world application, a prototype device was created, incorporating six BP@PANI tactile sensors corresponding to braille characters. This device can convert pressed text into audio, aiding visually or speech-disabled individuals in reading and typing. It offers a promising solution for improving communication and accessibility for this demographic.