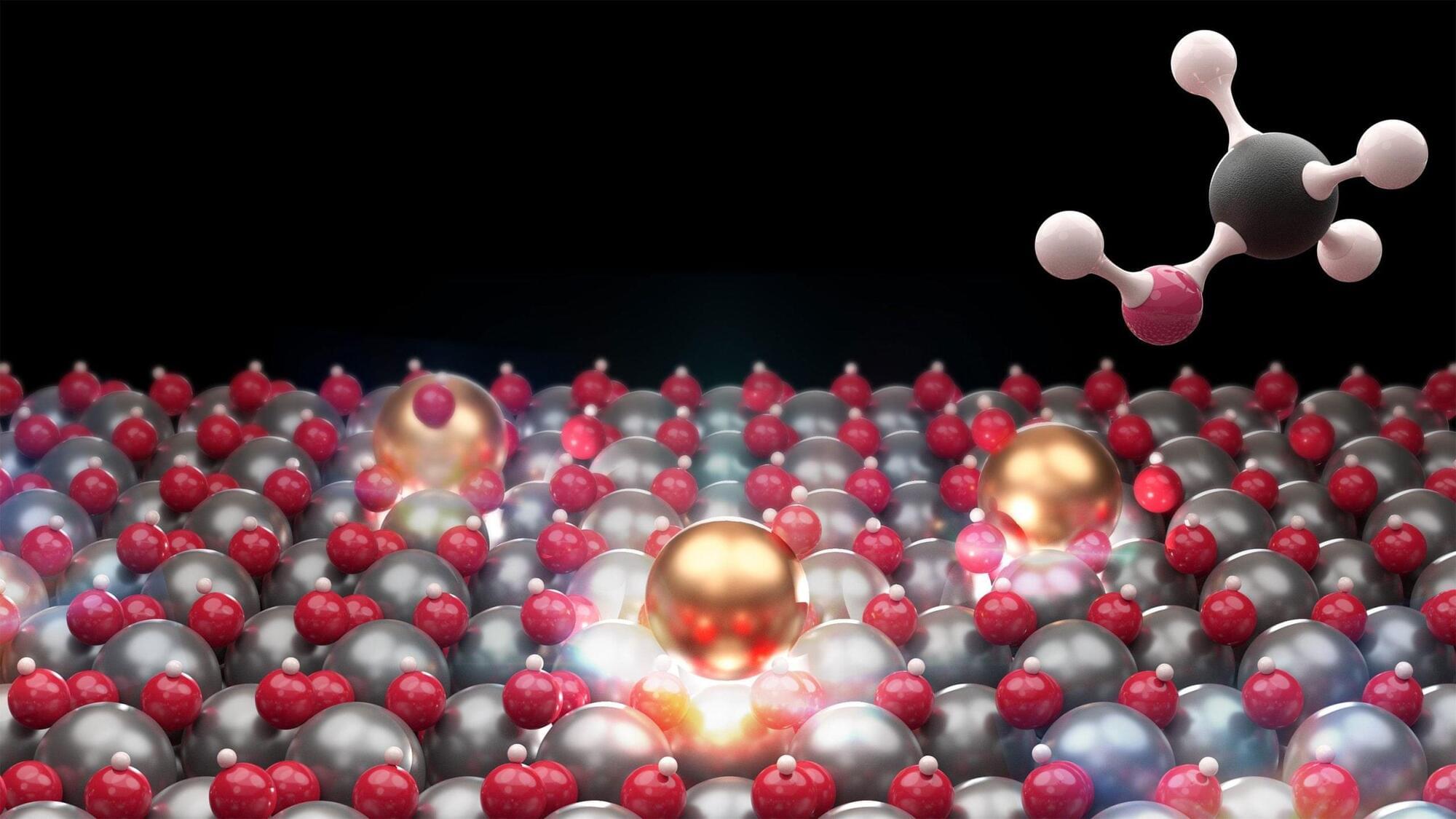
A new catalyst built from isolated indium atoms allows scientists to convert CO2 into methanol more efficiently while revealing the hidden chemistry that drives the reaction.


“It looks like a tiny solar system. But instead of planets, it’s a snapshot of my research journey in the lab,” says Sadiya Tanga, a chemistry graduate student at Ashoka University. Tanga’s work has focused on a type of drug molecule called proteolysis-targeting chimeras, or PROTACs for short. PROTACs have two active ends, one that grabs a target protein and another that grabs a molecular flag that tells the cell to break down the whole assembly as waste. “Each glowing flask and sphere holds a different compound I worked hard to design and synthesize,” Tanga says. “The colors you see are from parts of the molecules that shine under UV light.”
By simulating the life cycle of a minimal bacterial cell—from DNA replication to protein translation to metabolism and cell division—scientists have opened a new frontier of computer vision into the essential processes of life. The researchers, led by chemistry professor Zan Luthey-Schulten at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, present their findings in the journal Cell.
The team simulated a living cell at nanoscale resolution and recapitulated how every molecule within that cell behaved over the course of a full cell cycle. The work took many years: vast computer resources, large experimental datasets, a suite of experimental and computational techniques and an understanding of the roles, behaviors and physical interactions of thousands of molecular players.
The researchers had to account for every gene, protein, RNA molecule and chemical reaction occurring within the cell to recreate the timing of cellular events. For example, their model had to accurately reflect the processes that allow the cell to double in size prior to cell division.

QUT researchers have developed a simple one-hour saliva test for a protein biomarker that has been linked with oral, colon and pancreatic cancers. The findings are published in the journal Talanta.
The paper is titled “Label free paper sensor and light driven material for the rapid screening of S100P cancer biomarker in saliva.” Corresponding author, Associate Professor Emad Kiriakous, from QUT’s School of Chemistry and Physics, said this technology could pave the way for simple, low-cost, point-of-care screening tools to help identify and treat cancer early.
Professor Kiriakous said the QUT team developed a rapid testing technique of saliva using paper coated in gold and silver nanoparticles to create a highly sensitive sensor that records the Raman spectrum (or SERS, the process by which a substance scatters laser light which is used to identify molecules) of saliva samples.

Imine-linked covalent organic frameworks (COFs) have been explored for various applications; however, chemical recycling of end-of-life COFs is an undeveloped area of research. Here, we report closed-loop recycling methods for imine-linked COFs, realizing their chemical depolymerization and reconstruction through d.

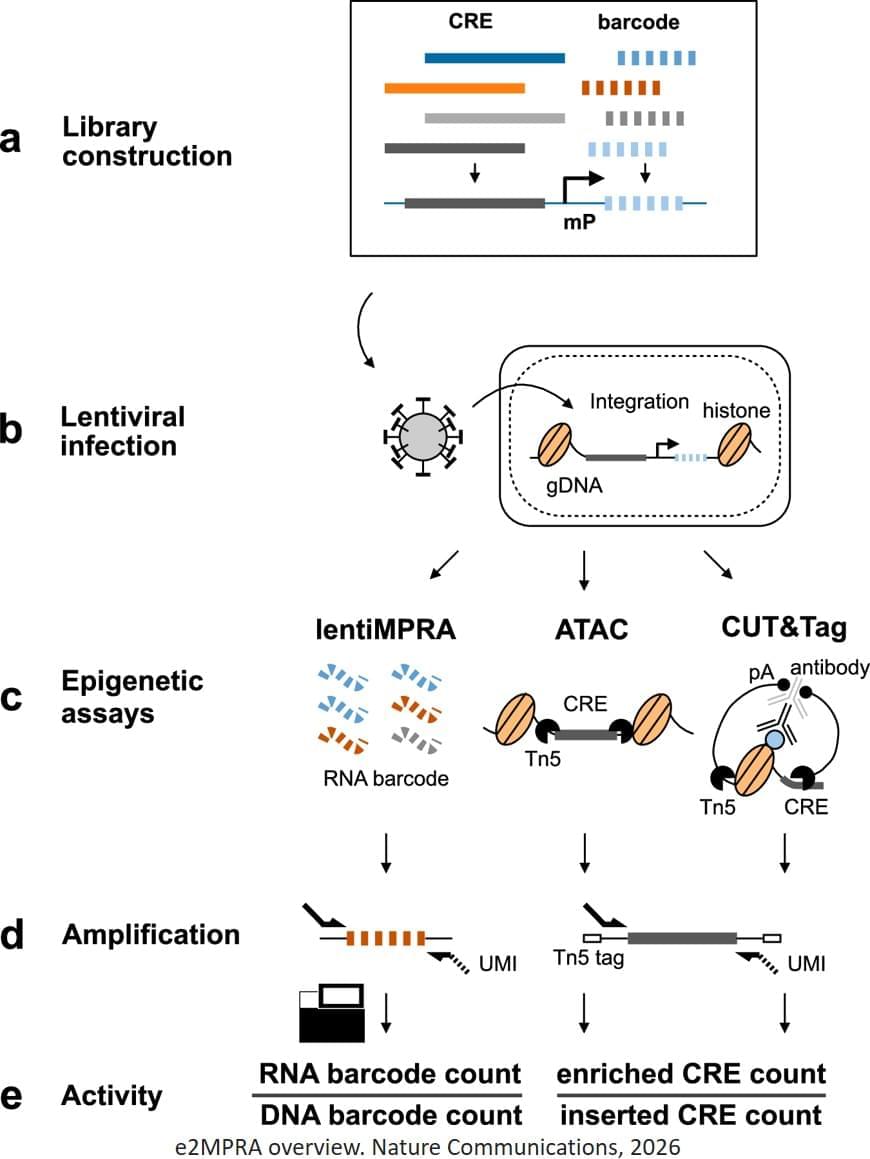
DNA is the blueprint of life. Genes encode proteins and serve as the body’s basic components. However, building a functioning organism also requires precise instructions about when, where, and how much those components should be produced. This layer of control is carried out by cis-regulatory elements (CREs), which are short stretches of DNA that serve as binding sites for transcription factors and help control the activity of nearby genes, hence are often described as the “switches” and “dials” of genes. Although CREs do not encode proteins themselves, they play a major role in shaping traits, guiding development, and influencing disease risk.
CREs control gene expression through epigenetic mechanisms, such as whether DNA is open and accessible and whether it carries markers associated with active gene regulation. Even small changes in CRE sequences can have substantial effect on gene expression. Until now, scientists have relied on separate experimental methods to study these processes. Some methods identify DNA regions that appear to function as regulatory elements, while others test whether a DNA sequence can activate gene expression. Because these approaches are usually performed independently in different experiments, it has been difficult to directly connect cause and effect or to systematically evaluate the impact of individual changes in the sequence.
To overcome these limitations, the researchers developed an enrichment followed by epigenomic profiling massively parallel reporter assay (e2MPRA), a new technique that builds on their earlier lentiMPRA platform, which enables simultaneous analysis of thousands of CREs by tagging them with unique DNA barcodes that track their activity. e2MPRA takes this technique a step further by also capturing epigenetic states, allowing researchers to directly link what a CRE does with how it does it under identical experimental conditions.
E2MPRA was validated using two large libraries totaling approximately 10,000 sequences: one consisted of synthetic CREs with systematically arranged transcription factor binding sites, and the other contained known CREs in which small DNA changes were introduced to examine how each alteration affected function. For each CRE, the researchers measured three key features: how strongly it activates genes (regulatory activity), whether the surrounding DNA is open and accessible (chromatin accessibility), and whether it carries a chemical “active” mark (H3K27ac modification).
Using this approach, the team demonstrated that different CREs regulate genes in distinct ways. Some primarily boost gene activity without substantially altering DNA structure, while others mainly increase DNA accessibility. The researchers also found that the arrangement and order of the binding sites within a CRE can strongly influence its activity, much like word order can change the meaning of a sentence.
The team then used e2MPRA to examine how tiny DNA changes (as tiny as a single “letter” difference) can disrupt gene regulation. In regions containing the POU5F1::SOX2 binding site, which plays a key role in maintaining stem cell identity, mutations altered not only gene activity but also DNA accessibility and H3K27ac levels.
In contrast, changes in the YY1 binding site showed a more complex behavior: mutations reduced gene activity but increased DNA accessibility. These findings show that DNA variants can influence gene regulation through multiple, overlapping layers rather than through a simple on–off mechanism. ScienceMission sciencenewshighlights.

Researchers at Baylor College of Medicine have discovered a potential new strategy to fight back against Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, conditions that are linked to the toxic accumulation of Tau and alpha synuclein protein clumps in the brain. The team reports in Nature Communications that tubulin, the building block of microtubules, the cell’s internal ‘railway tracks, can stop Tau and alpha synuclein from forming toxic clumps and instead steer them into their normal, healthy roles.
“Tau and alpha synuclein are well known for their roles in neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. In these conditions, these proteins can misfold, stick together and form harmful aggregates that damage neurons and contribute to memory loss, movement problems and other symptoms,” said first author Dr. Lathan Lucas, postdoctoral associate of biochemistry and molecular pharmacology in Dr. Allan Ferreon’s lab.
“But Tau and alpha synuclein also fulfill essential functions in healthy neurons—they help maintain cell structure and support communication by interacting with tubulin and contributing to microtubule assembly and stabilization.”

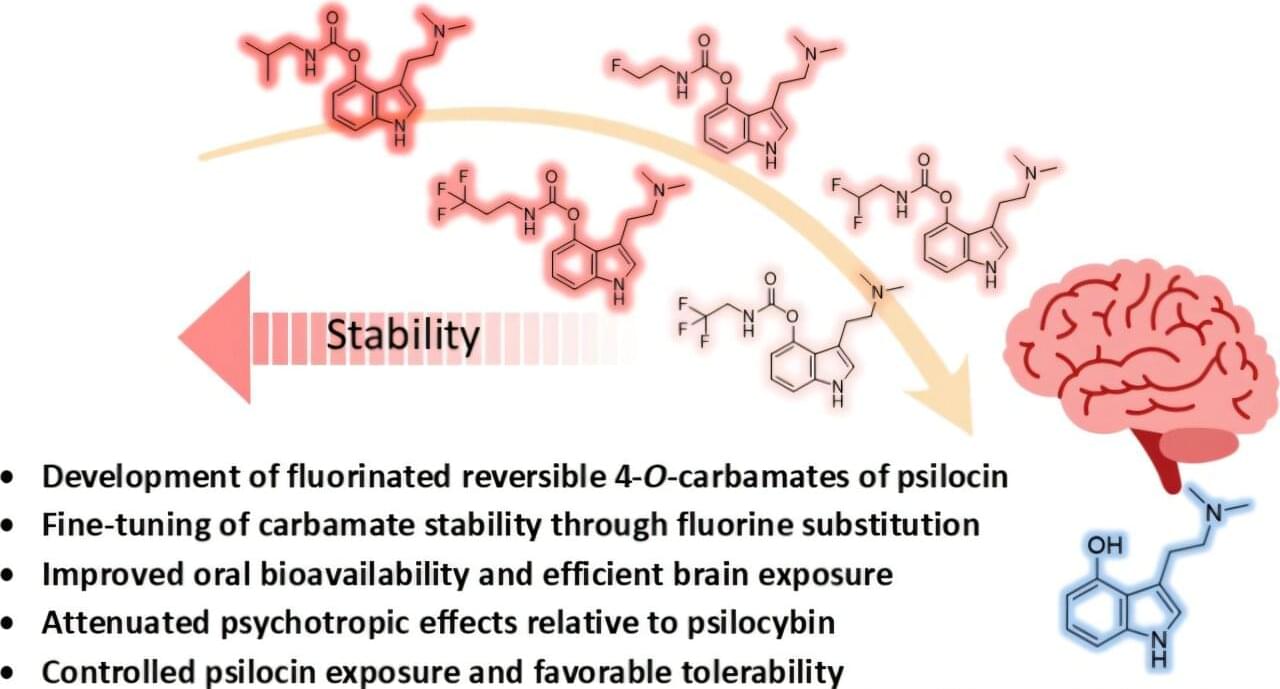
Psilocybin—the psychoactive compound in “magic mushrooms”—is gaining scientific attention for its potential in treating neuropsychiatric conditions including depression, anxiety, substance use disorders and certain neurodegenerative diseases. However, its hallucinogenic effects may limit broader therapeutic applications. Researchers publishing in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry synthesized modified versions of psilocin, the active form of psilocybin, that retained its activity while producing fewer hallucinogenic-like effects than pharmaceutical-grade psilocybin in a preliminary study in mice.
“Our findings are consistent with a growing scientific perspective suggesting that psychedelic effects and serotonergic activity may be dissociated,” says Andrea Mattarei, a corresponding author of the study. “This opens the possibility of designing new therapeutics that retain beneficial biological activity while reducing hallucinogenic responses, potentially enabling safer and more practical treatment strategies.”
Mood disorders and some neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease, involve imbalances of the neurotransmitter molecule serotonin, which helps regulate mood and other brain functions. For decades, scientists have been investigating the therapeutic use of psychedelics such as psilocybin on serotonin-signaling pathways. However, the hallucinations that can accompany these drugs may make people wary of taking them, even if there is a medical benefit.