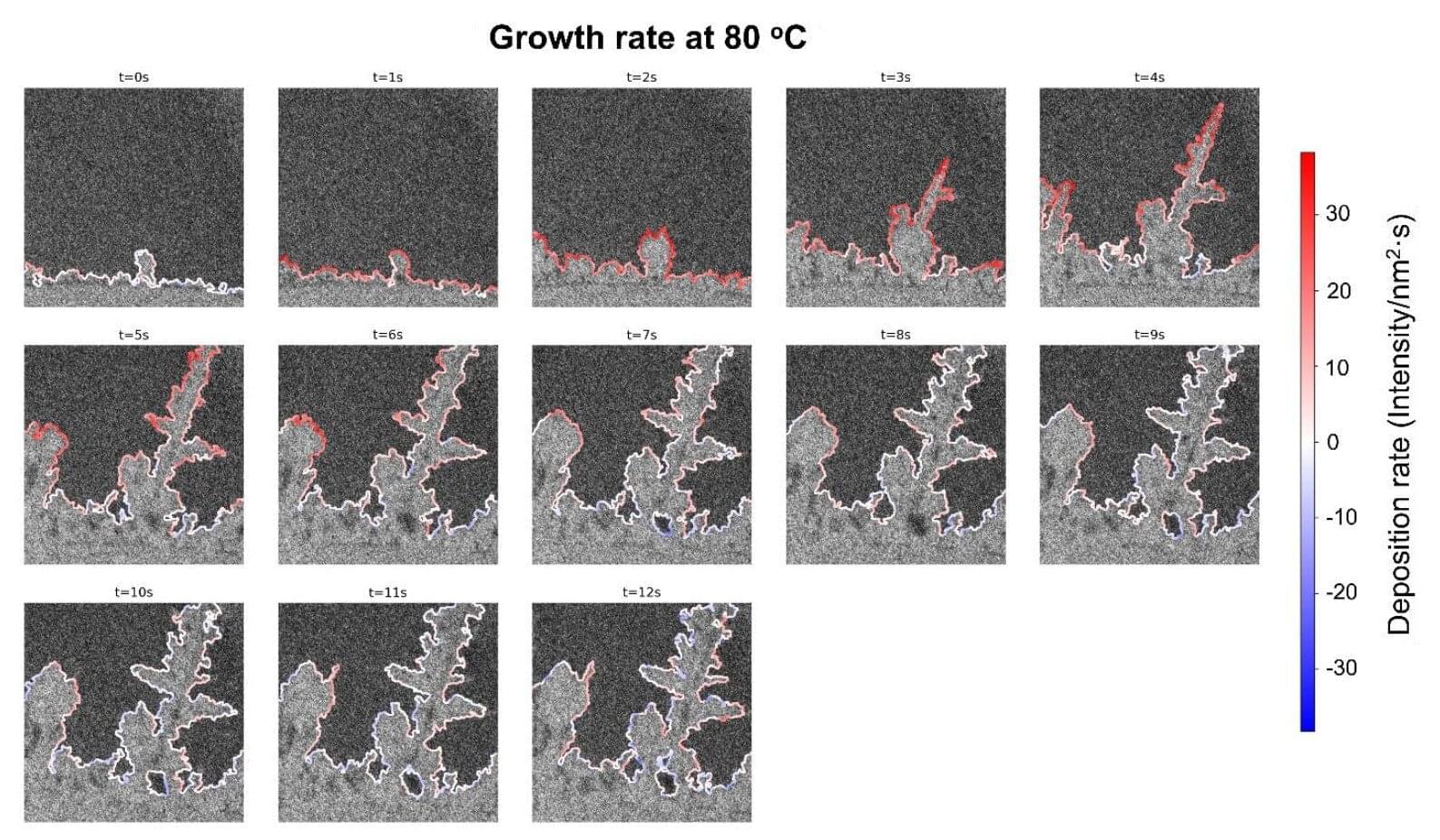
Much of the world’s lithium occurs in salty waters with fundamentally different chemistry than other naturally saline waters like the ocean, according to a study published on May 23 in Science Advances. The finding has implications for lithium mining technologies and wastewater assessment and management.
Lithium is a critical mineral in the renewable energy sector. About 40% of global lithium production comes from large salt pans, called salars, in the central Andes Mountains in South America and the Tibetan Plateau in Asia. In these arid, high-altitude regions, lithium exists below surface salt deposits, dissolved in extremely saline water called brine.
“We discovered that the pH of brines in these regions is almost entirely driven by boron, unlike seawater and other common saline waters. This is a totally different geochemical landscape, like studying an extraterrestrial planet,” said Avner Vengosh, distinguished professor of environmental quality and Chair of the Division of Earth and Climate Sciences at Duke University’s Nicholas School of the Environment, who oversaw the research.