What Will A Future Climate Conference in 2051 Talk About, A Year After Net Zero?
COP27 just ended in Egypt. Will what was accomplished there impact the world and be reflected in conversations at conferences in 2051?
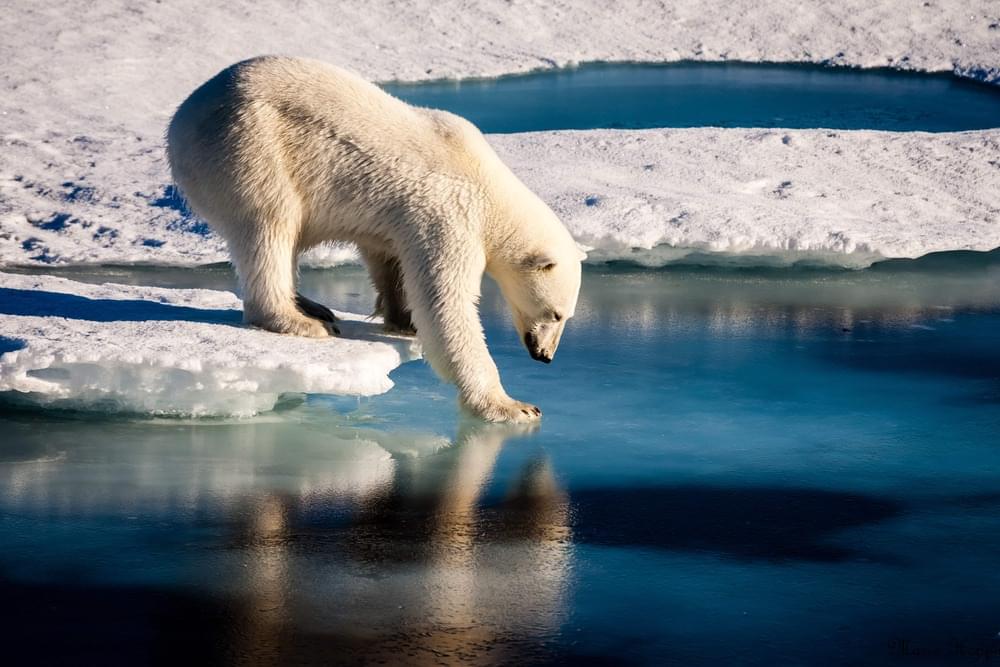


A new survey conducted by the Canadian government has found that polar bears in the country’s Western Hudson Bay, are dying at alarming rates. The researchers aerially surveyed the Bay and its nearby town of Churchill also referred to as the ‘Bear capital of the World’ in 2021 and found there were 618 bears only, compared to 842, five years ago when last counted.
The survey added that a significant decline has been noted in the population of adult female bears and cubs between 2011 and 2021.
“The observed declines are consistent with long-standing predictions regarding the demographic effects of climate change on polar bears,” said the researchers.

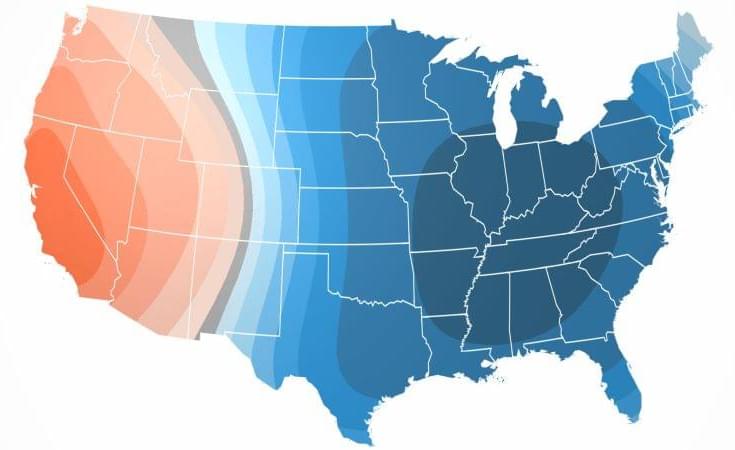
Millions of Americans are under critical weather alerts as a major winter storm is set to bring “life-threatening” cold temperatures and powerful winds to large swaths of the nation — with the mercury expected to drop as low as minus 20 degrees across the Midwest and Great Lakes.
More than 80 million Americans — spanning from coast to coast — are under various forms of wind chill alerts, according to FOX Weather meteorologist Christopher Tate.
“We could see wind gusts of 40 to 50 mph,” he told The Post on Wednesday. “I wouldn’t be surprised if we see an occasional gust of 60 along the coast.”
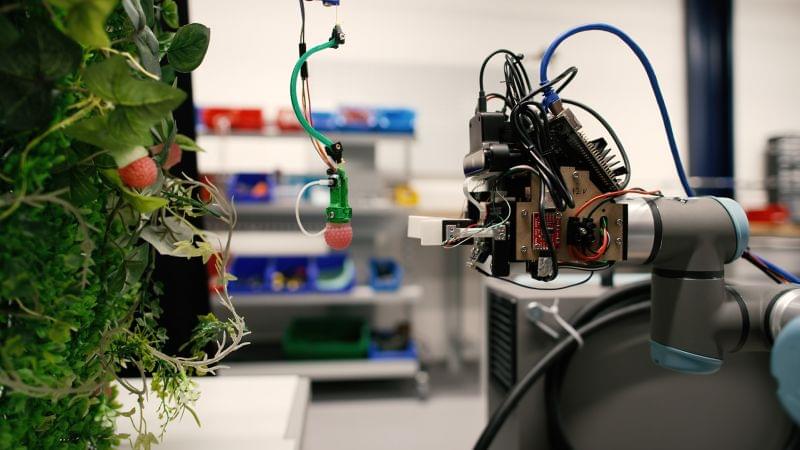

Around 38% of the world’s total landmass is used for agriculture – yet hunger is worsening, and food security is in crisis, threatened by pressures including climate change, conflict and global recessions.
While there’s no one-stop solution, technology can help to fill some of the gaps. Mechanical engineer Josie Hughes is on a mission to show how robotics can play a role in our everyday lives, particularly when it comes to food. Starting with LEGO robots as a child, the Cambridge graduate now leads the Computational Robot Design & Fabrication Lab (CREATE) at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL), where she’s one of the youngest researchers to join as a tenure-track assistant professor.
One of her innovations, a raspberry-picking robot powered by artificial intelligence, could help make farming more efficient and cost-effective, and solve labor shortages – which in the UK alone left £60 million ($74 million) worth of fruit and vegetables rotting in fields this summer. CNN spoke with Hughes about her research, and when robots might be harvesting your next meal.
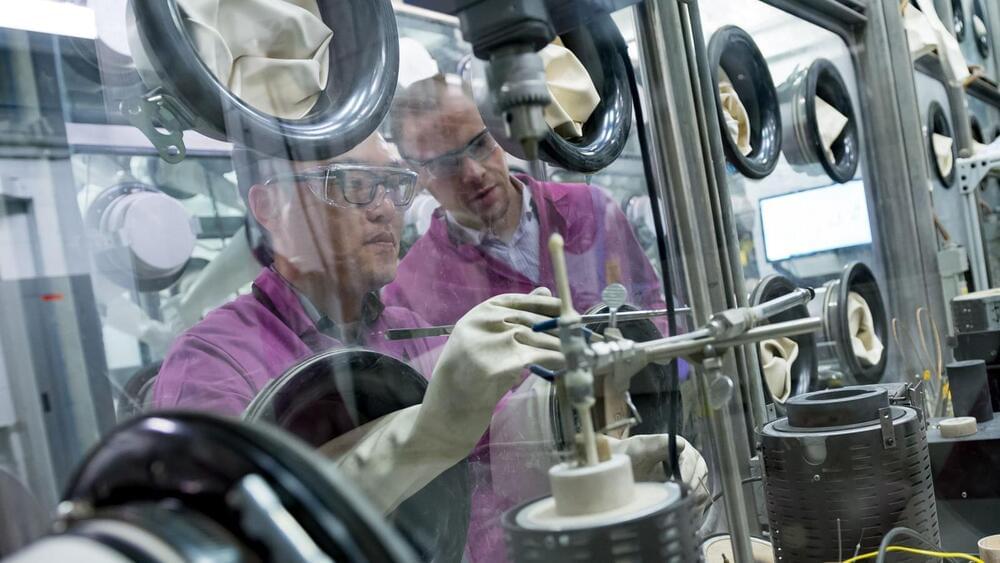

Technology developed at Argonne can help narrow the field of candidates for molten salts, a new study demonstrates.
Scientists are searching for new materials to advance the next generation of nuclear power plants. In a recent study, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory showed how artificial intelligence could help pinpoint the right types of molten salts, a key component for advanced nuclear reactors.
The ability to absorb and store heat makes molten salt important to clean energy and national climate goals. Molten salts can serve as both coolant and fuel in nuclear power reactors that generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. They can also store large amounts of energy, which is increasingly needed on an electric grid with fluctuating sources such as wind and solar power.
Astronomical winter officially begins this Wednesday and Jack Frost will arrive in full force.
Temperatures will take a polar plunge this week, and even Florida won’t be spared, thanks to a strong high-pressure system sliding south from Canada.
“Very cold Arctic air masses will envelop much of the central and eastern half of the nation during the two week period, including the busy holiday travel season,” the Climate Prediction Center said.

Global payments giant Visa says it will invest $1 billion by 2027 to expand its investments in Africa amidst a digital payments boom on the continent.
Visa chief Al Kelly announced this pledge on Wednesday during the U.S.-Africa Business Forum, a sub-event in the broader U.S.-Africa Leaders Summit, a three-day event where U.S. President Joe Biden invited heads of state and senior government officials from Africa to discuss several issues ranging from food security to climate change.
“Visa has been investing in Africa for several decades to grow a truly local business, and today our commitment to the continent remains as firm and unwavering as ever,” said the Visa CEO in a statement.
A new study finds that Earth’s “stabilizing feedback” keeps global temperatures in check.
Researchers find Earth has a “stabilizing feedback” mechanism. The mechanism of “silicate weather” helps regulate the planet’s carbon cycle.
The planet balances out extreme climate shifts, according to the new study.
Our planet’s climate is a hot topic for discussion, and with good reason — Earth is the cradle of all our lives. What happens to it affects us and our children directly. But while we’re worried we may be changing its climate now, the history of the planet is rife with major climate cataclysms. It went through periods of boiling heat and ice ages, it was pummeled by radiation and asteroids… More.
Suffering the heat wave? Here are the top 10 hottest places on Earth right now
Structuring, Financing & Growing Novel Longevity Ventures — Dr. Tobias Reichmuth Ph.D., Founding Partner, Maximon
Dr. Tobias Reichmuth, Ph.D. is Founding Partner at Maximon (https://www.maximon.com/), The Longevity Company Builder, which empowers entrepreneurs to build impactful, science-based and scalable companies providing healthy aging and rejuvenation solutions.
Maximon recently announced the launch of their 100 million CHF Longevity Co-Investment Fund, which will be looking to invest up to CHF 10 million per company, which allows them to finance up to 10–12 start-ups in this fast growing industry over the next four years.
In 2020, Dr. Reichmuth launched the Longevity Investors Conference together with Marc P. Bernegger, another Maximon Founding Partner.
Dr. Reichmuth previously founded the climate-change infrastructure fund / asset management company SUSI Partners AG, where he spent over a decade specializing in infrastructure investments in the context of energy transition (renewable energy, energy efficiency, energy storage solutions) and invested more than one billion Swiss francs.

Scientists announced Tuesday that they have for the first time produced more energy in a fusion reaction than was used to ignite it—a major breakthrough in the decades-long quest to harness the process that powers the sun.
Researchers at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California achieved the result last week, the Energy Department said. Known as a net energy gain, the goal has been elusive because fusion happens at such high temperatures and pressures that it is incredibly difficult to control.
The breakthrough will pave the way for advancements in national defense and the future of clean power, Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm and other officials said.