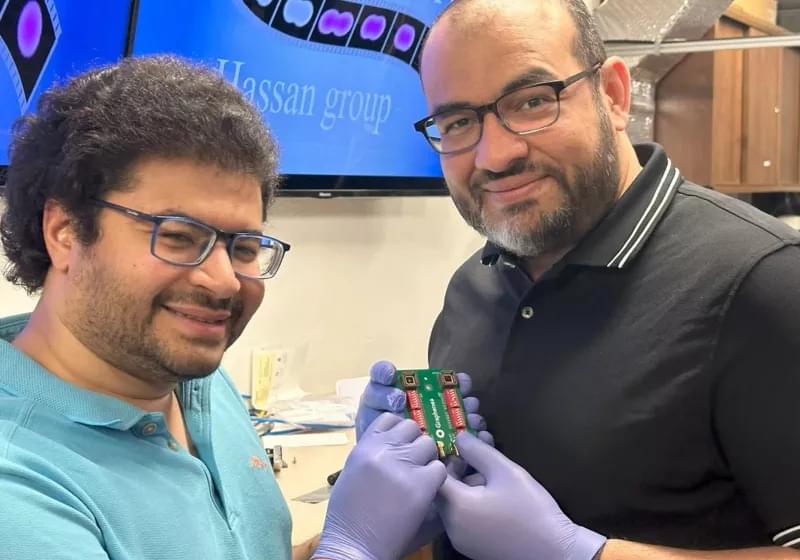
A pioneering method to simulate how nanoparticles move through the air could boost efforts to combat air pollution, suggests a study in the Journal of Computational Physics.
Tiny particles found in exhaust fumes, wildfire smoke and other forms of airborne pollution are linked with serious health conditions such as stroke, heart disease and cancer, but predicting how they move is notoriously difficult, researchers say.
Now, scientists have developed a new computer modeling approach that dramatically improves the accuracy and efficiency of simulating how nanoparticles behave in the air. In practice, this could mean simulations that can currently take weeks to run could be completed in a matter of hours, the team says.