Thulium fiber lasers, operating at a wavelength of 2 micrometers, are valued for applications in medicine, materials processing, and defense. Their longer wavelength makes stray light less damaging compared to the more common ytterbium lasers at 1 micrometer.
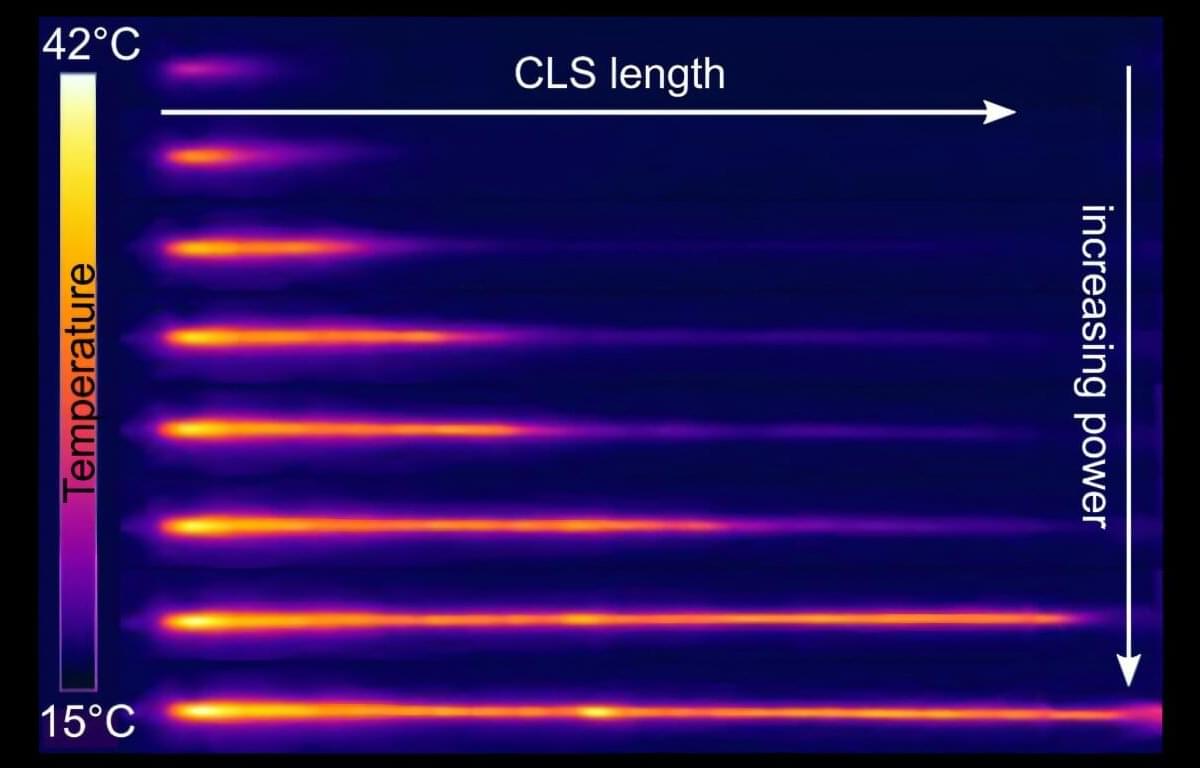
Yet, despite this advantage, thulium lasers have been stuck at around 1 kilowatt of output power for more than a decade, limited by nonlinear effects and heat buildup. One promising route to break this barrier is inband pumping—switching from diode pumping at 793 nm to laser pumping at 1.9 µm. This approach improves efficiency and reduces heat, but it introduces new challenges for fiber components, especially the cladding light stripper (CLS).