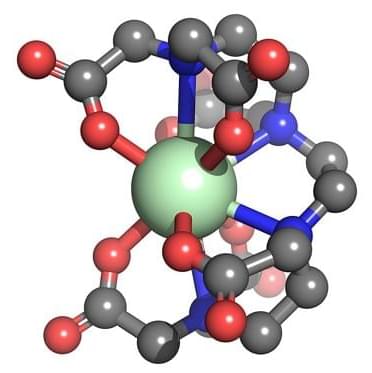
One of the greatest challenges facing the future of clean nuclear energy is scientists’ ability to recover heavy metals from nuclear waste, such as lanthanides and actinides. A new computational tool could help chemists design ligands to selectively bind valuable metals in organometallic complexes.
Nuclear waste contains a smorgasbord of elements from across the periodic table, including transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Ideally, scientists would like to reduce the amount of waste generated from nuclear reactors by separating out elements that could be repurposed elsewhere. To tackle these tricky chemical separation techniques, chemists often start with 3D structural models to design ligands that can selectively bind the desired metal to form an organometallic complex that can later be isolated.
Though researchers working with d-block organometallics have an arsenal of structural prediction tools at their disposal, there are no resources available to do the same for the full range of lanthanide and actinide complexes. That’s partly because these f-block elements can form higher coordinate complexes with ligands compared to d-block transition metals, according to Ping Yang and Michael G. Taylor, computational chemists at Los Alamos National Laboratory.