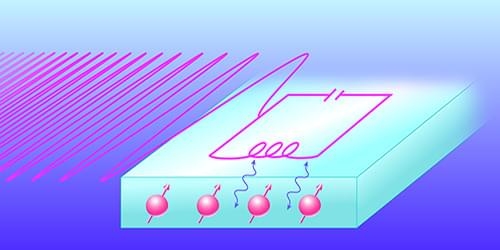
A new quantum random-access memory device reads and writes information using a chirped electromagnetic pulse and a superconducting resonator, making it significantly more hardware-efficient than previous devices.
Random-access memory (or RAM) is an integral part of a computer, acting as a short-term memory bank from which information can be quickly recalled. Applications on your phone or computer use RAM so that you can switch between tasks in the blink of an eye. Researchers working on building future quantum computers hope that such systems might one day operate with analogous quantum RAM elements, which they envision could speed up the execution of a quantum algorithm [1, 2] or increase the density of information storable in a quantum processor. Now James O’Sullivan of the London Centre for Nanotechnology and colleagues have taken an important step toward making quantum RAM a reality, demonstrating a hardware-efficient approach that uses chirped microwave pulses to store and retrieve quantum information in atomic spins [3].
Just like quantum computers, experimental demonstrations of quantum memory devices are in their early days. One leading chip-based platform for quantum computation uses circuits made from superconducting metals. In this system, the central processing is done with superconducting qubits, which send and receive information via microwave photons. At present, however, there exists no quantum memory device that can reliably store these photons for long times. Luckily, scientists have a few ideas.